Nexans ITK Cold Shrink Termination | XLPE Indoor Single Core 12kV 24kV MV Cables
Published 04 Dec 2018

Heat Shrink | Cold Shrink | Slip-on | Cable Terminations
Stocked by Thorne & Derrick UK & Export Sales | Nexans ITK224
Cable Terminations
Nexans ITK are single core cold shrink cable terminations for use indoor and specified to terminate and connect medium/high voltage cables in the following voltage classes:
- 6/10 (12) kV
- 6.35/11 (12) kV
- 8.7/15 (17.5) kV
- 12/20 (24) kV
- 12.7/22 (24) kV
Cold Shrinkable terminations require no “hot-working” for safe use in potentially explosive atmospheres and hazardous area locations – the cable terminations are designed for use with polymeric insulated cables (XLPE & EPR). To enable the fault repair, extension, splicing and jointing of existing LV MV HV power cables up to 33kV we also stock a complete range of cold shrink joints.

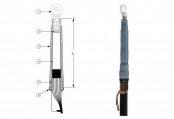
Cold Shrink Indoor Cable Terminations 11kV 24kV Nexans ITK – Design
Indoor cold shrink cable termination kit list comprising:
- Cable lug (not included in the standard kit) – both crimp cable lugs and shearbolt lugs are suitable
- Water sealing mastic
- Silicone cold shrink tube
- Stress control mastic
- Conductive EPDM ring
Nexans ITK COLD SHRINK TERMINATION SPECIFICATION
The following tables enable the selection of cable terminations using Cold Shrinkable technology manufactured by Nexans:
| Cable Termination Cold Shrink |
Voltage Um (kV) |
Strike Distance L (mm) |
Diameter Over Core Insulation (mm) |
Conductor Sizes (sqmm) | ||
| min | max | min | max | |||
| Nexans ITK 212 | 11kV / 12kV | 260mm | 14 | 33 | 50sqmm | 400sqmm |
| Nexans ITK 312 | 11kV / 12kV | 300mm | 30 | 50 | 400sqmm | 1000sqmm |
| Nexans ITK 224 | 20kV / 24kV | 260mm | 14 | 33 | 25sqmm | 240sqmm |
| Nexans ITK 324 | 20kV / 24kV | 300mm | 30 | 50 | 300sqmm | 800sqmm |
Nexans ITK selection table
For Indoor MV HV Cable Terminations
Select the Nexans part number corresponding to both the system voltage and the cable insulation diameter in mm.

Kit Contents For Nexans ITK Terminations
| Nexans ITK Cold Shrink Cable Termination | Voltage Um (kV) |
Diameter Over Core Insulation (mm) |
Conductor Sizes (sqmm) | ||
| min | max | min | max | ||
| 3 x Nexans ITK 212 | 11kV 12kV | 14 | 33 | 50sqmm | 400sqmm |
| 3 x Nexans ITK 312 | 11kV 12kV | 30 | 50 | 400sqmm | 1000sqmm |
| 3 x Nexans ITK 224 | 11kV 24kV | 14 | 33 | 25sqmm | 240sqmm |
| 3 x Nexans ITK 324 | 11kV 24kV | 30 | 50 | 300sqmm | 800sqmm |

All commercialised European standard cable lugs can be used. Cable lugs should be within the dimensions specified (not applicable for Nexans ITK 312 and ITK 324).
Euromold ITK cold shrink terminations covers voltages from 12kV to 24kV with a maximum conductor size of 1000sqmm. MV indoor termination suited for 11kV polymeric single core cables and will provide the necessary seal against moisture penetration and perfect electrical field control.
Nexans Euromold High Voltage Heat Shrink & Cold Shrink Cable Terminations up to 33kV.
Nexans
Thorne & Derrick distribute the complete range of medium/high voltage electrical equipment manufactured by Nexans – this includes Euromold bushings for use with oil fluid or gas insulated switchgear or transformers and associated screened separable connectors according to both IEC (Euromold) and IEEE (Elastimold) for the termination, connect+disconnect of MV-HV cables onto power distribution systems. To protect power systems against high voltage surges resulting from lightning or switching a complete range of surge arresters are available to be used with Euromold connectors in 11kV/12kV, 24kV and 33kV/36kV voltage classes.

Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV
➡ Read: Thorne & Derrick Announce Distribution Agreement & Contract With Nexans

Further Reading
-
 Cold Shrink Indoor Cable Terminations 11kV 24kV Euromold ITK
Size: 147.24 KB
Cold Shrink Indoor Cable Terminations 11kV 24kV Euromold ITK
Size: 147.24 KB