Blog
An Assessment of Five Factors Affecting The Life Expectancy Of A Medium Voltage Electrical Splice
August 11th, 2020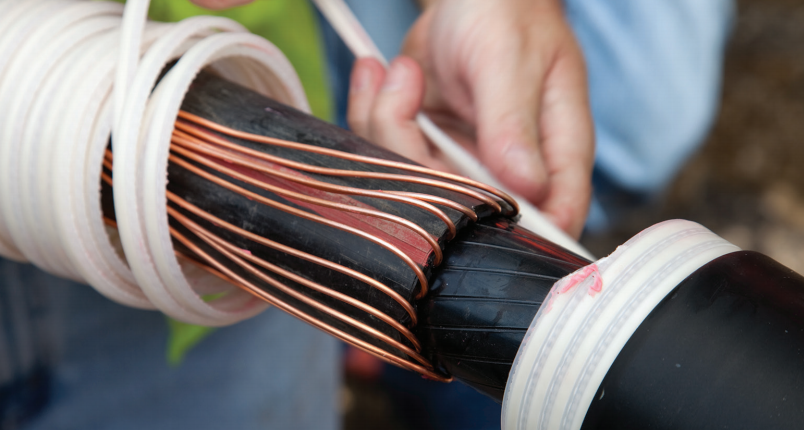
Cable Splice Lifetime Cycles
-
Written by George Fofeldea Power Engineer | 3M Canada August 2019
Abstract
How long can a medium voltage
Cable splice last?
There are many parameters that help to determine the overall life expectancy of a cold shrink or heat shrink cable splice. Of these parameters, there are five key reliability identifiers that give us great insight when estimating the overall life expectancy of an electrical cable splice. Those five identifiers are:
- Technology
- Materials
- Design
- Workmanship
- Testing procedures
Introduction
3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice was designed for easy cable splice installation and high reliability. It was introduced to the North American market in 1996.
The silicone rubber QS-III design revolutionized power cable splicing by addressing the installation pitfalls of traditional splices, which required pushing, pulling or heat.
By eliminating the need to apply heat and force, 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice offered the market a safer and more reliable solution to splicing medium voltage power cables.
Our over 23 years of field experience with 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice and over 40 years of field experience with 3M™ Cold Shrink QT-II and 3M™ Cold Shrink QT-III Terminations (Fofeldea G. 2018) helps us formulate a more robust understanding regarding the life expectancy of medium voltage cable accessories.
➡ Did you know? – 3M invented cold shrink technology over 50 years ago!
Materials & Methods

3M Shrink QS-III Splice
Medium voltage electrical splice life expectancy was determined using five critical reliability factors: technology, materials, design, workmanship and testing procedures.
The evaluation: an examination based on 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice’s 23 years in the field, failure investigation reports, and 50 years of cold shrink materials and design experience.
Discussion
By looking at the five reliability factors that affect the life expectancy of a medium voltage cable splice, this paper aims to identify the product with the highest reliability.
Technology
1.1. Disadvantages of heat shrink splice technology
In general, heat shrink splices require more installation steps compared to cold shrink splices (e.g., applying heat so the splice can conform to the cables) – leaving more room for installation error by the cable jointer.
Uneven heat application can result in burning different heat shrink layers and uneven wall thickness. If such mistakes are made during the installation process, the life expectancy of a heat shrink splice can be reduced.
1.2. Disadvantages of push-on splice technology
Aside from the more cumbersome installation steps (i.e., greasing cables, pushing splice body back and forth, asymmetrical cable preparation cutbacks, etc.), one significant disadvantage of push-on splices is the limited tolerance during installation. The push-on splice design only allows for a minimal semi-con overlap of ½ inch and a freshly installed splice can easily move, reducing this critical overlap.
For optimal life expectancy, a push-on splice must provide enough initial pressure so that it does not electrically fail. Additionally, the initial installation pressure must be low enough to allow for pushing the splice body onto the cable. However, research shows that for push-on splices, up to 90% of the initial pressure is lost during heat cycles (Amyot, N., et al. 2001), which reduces the overall life expectancy of the splice. Comparatively, the initial pressure in 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice is much higher and thermal cycles do not lower the pressure, which results in improved cable splice reliability.
1.3. Advantages of cold shrink splice technology
None of the disadvantages highlighted above apply to 3M Cold Shrink Technology. 3M designed this technology for long-term reliability – to last the life of the cable while helping to ensure excellent electrical performance. The dynamic “living” seal expands and contracts with variations in temperature and load on the cable.
The 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice firmly shrinks onto the cable insulation – providing an active seal, without loss of pressure due to cable heat cycling. Additionally, 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice has a wide application range, and the overall splice body design (i.e., length of semi-conductive inner electrode or outer shell) is designed to help minimize potential installation errors.

3M Cold Shrink QS-III Splice provides constant inward pressure
Materials
When considering cable splice life expectancy, we also must evaluate the various materials used to manufacture cold shrink splices. There are two main types of materials used to manufacture cold shrink splices: ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber and silicone rubber.
The splices made from EPDM rubber have a lower elasticity coefficient, making them more difficult to install in cold weather. As a result, this material sometimes requires heat to shrink onto the cable.
130°C or 140°C
There are two types of silicone rubber materials used to manufacture cold shrink splices:
1. a clear, “unfilled” liquid silicone rubber
2. one that is “filled” with thermally conductive additives
The heat dissipating additives used in the 3M™Cold Shrink QS-III Splice enables us to meet the 130°C or 140°C cable emergency overload temperature requirements of IEEE 404, on both aluminum and copper conductors. (IEEE 404 requires that heat cycling testing be done at cable emergency overload temperature.)
3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III designs are tested to the worst-case scenarios on aluminum (AL) conductors with AL compression connectors, and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation. Because of the unique silicone material used for the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice the connector area in a 15 kV 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice typically runs 10°C – 15°C cooler than the conductor itself (see Figure 1 on page 10).
This is important because a good thermal heat dissipation by the splice body helps prolong life expectancy of an installed splice.
Cable Splice Design
Splice body design has an important influence over the long-term reliability of a medium voltage cable splice – directly impacting the life expectancy. Since we learned above that the material used for 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice helps to prolong life expectancy of an installed splice, we will now evaluate the design of 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice.
3.1. Electrical stress inside the cable splice
The electrode design of the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice is unique. It is designed to help provide precise control and management of the electrical stress along the cable-insulation interface and over the connector shield within the splice insulation. The precision geometry incorporates rounded inner electrode ends with an undercut inner electrode design and rounded outer semi-conductive shell to help reduce electrical stresses.
The 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice design requirements call for the maximum interfacial stress to be no greater than half of the stress over the connector shield and the maximum stress over the connector shield to be approximately equal to two-thirds of the maximum stress in the cable (see Figure 2).
Due to 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice’s precise geometry, the electrical stresses within the splice are less than those experienced by the cable insulation. E4 in Figure 2 is the highest electrical stress for a 15 kV cable and is approximately 72 V/mil. The maximum stress in the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice Body for a 15 kV cable is E2 and is approximately 36 V/mil – about half of E4. The installer cannot interfere in any way with E2 since it is inside the splice body (in other words, 3M manufacturing controlled). This low E2 stress enhances the safety and reliability of the splice body.
Furthermore, E3 in Figure 2 is situated at the cable insulation-splice body interface. E3 is an extremely important point since any cable preparation inconsistencies (e.g., potential knife cuts, dirt, humidity, etc., on the insulation) will increase the stress in this area.
With 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice’s unique undercut inner electrode design, E3 is only 12.7 V/mil and allows for enhanced safety and long-term performance.
To help demonstrate the positive impact of this intricate and precise geometric stress control design, we must look at the basic impulse levels (BIL) of the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice.
The 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice is rated one BIL higher than the corresponding splice classification; e.g., 25 kV splices meet the BIL requirements of 35 kV splices. This superior BIL classification is testimony to the low stresses inside the splice bodies, thus enhancing long-term reliability and improving the overall life expectancy. In a correctly installed 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice, the electrical stress in the splice is less than the stress in the cable.
E1, E2, E3 < E4
A well-designed splice combined with high-quality manufacturing, and a correct installation can remove the traditional splice weak link in a cable and increase life expectancy of the cable splice installation.
There are some cold applied splices, manufactured using EPDM rubber. In some designs, the manufacturing process of the EPDM-cold applied splices requires the grinding out of the inner conductive layer to provide the insulation interface. This provides a sharp point on the end of the electrode and a step between the insulation and the electrode, which is why a large amount of grease is required to lower electrical stress at these points.
In contrast, the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice electrode is molded and designed so that the electrode has a round shape, to help minimize the electrical stress. Minimizing electrical stress helps provide better long-term performance.

Furthermore, some EPDM-cold applied splices have a separate cold applied insulation shield as part of the manufacturing process. As a result the complete splice body cannot be tested to the two production test requirements as requested by the IEEE 404 – the standard allows for different material and subcomponent tests in exchange.
3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice is one molded splice body and each body is tested according to the production
test requirements of the IEEE 404, which help enhance safety and reliability.
3.2. Complete continuation of all cable layers
3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice continues all the layers of the cable. The outer shell of the splice consists of a thick 3-4 mm layer of semi-conductive material, with short-term short circuit current initiating capacity. This layer overlaps the cable semi-conductive layer with a firm grip, and forms a solid shield of semi-conductive material, from one side to the other of the splice.
This helps provide long-term reliability insurance, as it does not rely on a copper mesh for semi-conductive layer continuity, as seen with other cold applied designs.
The 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice bodies comply with the requirements of the IEEE 592 (also known as the “nail test”). This is because of the thick, molded outer semi-conductive shell. Other cold applied designs use a thinner painted outer semi-conductive layer and cannot comply with the IEEE 592 requirements.
While compliance to IEEE 592 is not mandatory as per IEEE 404, 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice does comply with the IEEE 592 test, offering a superior and more reliable product.
3.3. Margin of error in installation
The length of the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice allows the outside semi-conductive layer to extend over the cable semi-conductive layer, past the minimum ½ inch requirement. This makes the splice more forgiving when it comes to mispositioning errors.
Similarly, the inner semi-conductive electrode is quite long, allowing for use of any long or short connectors and minimizes mistakes in insulation length removal. Therefore, the design of 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice helps decrease the margin of error during installation.
3.4. BIL voltage
As described in Section 3.1, 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice is tested for a normal AC voltage level (e.g., 15 kV, 25 kV, 28 kV, etc.) and exceeds the BIL requirements of the next AC voltage level. This is due to the low electrical stress design criteria that 3M employs and the many design features that are incorporated in the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice body.
Basic Insulations Levels (BIL) reveal the safety and reliability of a given design, which is why successive BIL test rounds are done in the IEEE 404. It should also be noted that 3M conducts other internal tests, exceeding IEEE 404 requirements. For example, a 25 kV AC splice is required to pass a 150 kV BIL.
3.5 Quality and reliability in manufacturing
Each individual 3M splice body is factory tested – two production tests (PD and AC withstand) are performed. A manufacturing date stamp on a 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice indicates that the splice body has passed both production tests and are defect-free. As a result, it is unlikely for a customer to receive a defective product.
COld Shrink Workmanship
Workmanship is a key component in every power cable accessory installation. Although 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice is designed to help mitigate many installation errors through design, proper cable preparation techniques must be employed.
The same cable preparation techniques are to be used regardless if the cable will be spliced or terminated on a pole or terminated through an elbow or deadbreak connectors. 3M application engineers conduct failure investigations and provide end users with analysis reports that identify root causes for failures and make suggestions for improving installations.
The majority of these laboratory investigations pinpoint poor workmanship in cable preparation techniques as the leading root cause for the failures, in conjunction with/or separate from other types of mistakes (e.g., mispositioning of the splice body, wrong cutbacks, connector related installation mistakes, incorrect use of certain tapes, etc.).
➡ Did you know? – 3M offers online training modules to help our customers improve their cable preparation skills and medium voltage splice installation techniques.
Cable Splice Testing procedures
Many different cable testing procedures are available and used in the field. The IEEE 400 describes the test methods and procedures. Not all test methods are equal in the sense that the cables are stressed differently. The IEEE 400 also lists the advantages and disadvantages of the given test methods.
For example, over the years many utilities have moved away from Direct Current High Potential (DC Hi-Pot) testing due to the many drawbacks that this type of testing presents and since it ages and speeds time to failure of an existing cable with incipient defects before testing. Type testing done in 3M laboratories both on new and aged splices removed from the field help us understand long-term performance and help better predict life expectancy.
Field cable testing depending on the exact test method employed can negatively impact the remaining cable life and the estimated life of the splices in that loop. The testing conditions, the test method, the number of tests done over the life of the cable with splices included in the circuits, are all factors that must be considered when estimating life expectancy of cables and splices. Many of these factors are within the unique control of the utility.
Conclusion
The life expectancy of the 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice helps meet or exceed the life expectancy of the cable because 3M employs the best materials, design and manufacturing techniques available, to make the most reliable cable splice possible.
Over 23 years of excellent 3M™ Cold Shrink QS-III Splice track record in conjunction with over 50 years of cold shrink technology innovation have led to the development of cold shrink splice and termination products for applications up to 69/72.5 kV (3M Company. 2012) that have helped enhance the safety, reliability and life expectancy of cable accessories.

Figure 1: Temperature profile for a 15kV cable splice configuration
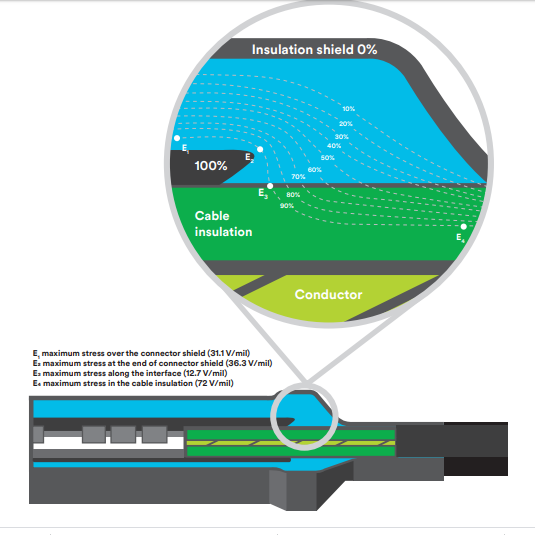
Figure 2 15kV Stress Plot
References
- 3M Company. 2012. 3M™ Cold Shrink Joints and Terminations for high voltage applications
- Amyot, N., et al. 2001. The Effect of Thermal Cycling on the Cable Joint Interfacial Pressure
- Fofeldea, G. 2018. Geometric vs. Capacitive Stress Control: choosing cable termination accessories to help reduce
electrical stress - Fofeldea, G. 2015. How do you take your splice? Integrated or not

THORNE & DERRICK are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Duct Sealing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – we service UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, cable jointing, substation earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV.
Since 1985, T&D have established an international reputation based on SERVICE | INTEGRITY | TRUST.
Contact us for 3M Electrical, ABB, Alroc, AN Wallis, CATU Electrical, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, CSD, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Euromold, Filoform , Furse, Lucy Electric & Zodion, Nexans, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec, Sicame, WT Henley.
Intellix BMT 330 | HV Bushing Monitoring & Partial Discharge Detection for Substation
August 11th, 2020
HV Bushing Monitoring & Partial Discharge Detection for Substation | Intellix BMT 330
Intellix BMT 330
HV Bushing Monitoring & Partial Discharge Detection for Substation
Bushings account for a large proportion of High Voltage (HV) substation failures, often causing severe and costly damages. The Intellix BMT 330 is a HV bushing monitoring and partial discharge detection equipment to be used on substations detecting failures and issues efficiently and effectively.
Preventive maintenance, early replacement and regular offline testing has been employed to address this issue in the past. Now, technology exists that enables asset owners to detect impending failures and reduce their maintenance costs.
.
The Intellix BMT 330 is an online system that continuously monitors the condition of the bushings in real-time and can also detect developing Partial Discharge (PD) activity in the transformer main tank. It will alert personnel of fault conditions at an early stage and provide vital health information on the bushings and the transformer.
Furthermore, it provides end users with the information they are used to receiving from offline tests, namely changes in capacitance and power factor, to assess the bushing dielectric efficiency and insulation integrity.

Intellix BMT 330
Intellix BMT 330
Features & Benefits
- Comprehensive monitoring of transformer bushings and PD activity on a 3-phase transformer or a bank of 3 single phase transformers
- One product combining online continuous bushing monitoring and partial discharge activity in the transformer main tank using the same bushing adaptor
- One diagnostic software, GE’s Perception, used for bushing information, PD activity and DGA data analysis, resulting in familiar easy-to-use information
- One supplier installing, servicing, ensuring proper communication and minimizing administrative burden in order to lower the total cost of ownership of your transformer
INTELLIX BMT 330
Applications
Power Utilities
- Enables condition-based maintenance of transformer bushings
- Designed for various three phase configurations
Metals
- Monitors bushing conditions to avoid unplanned production stoppage
- Monitors PD in over-stressed assets in aluminium or steel mills
Petrochemical
- Detects arcing faults with transformers
- Monitors bushing health to avoid catastrophic failures of transformers
NEWS | GE announces a new addition to its comprehensive portfolio of transformer monitoring & diagnostics solutions. The Intellix BMT 330 Bushing Monitoring & Partial Discharge detection system is an on-line system that continuously monitors the condition of transformer bushings and detects developing partial discharge (PD) activity in the transformer main tank on single phase or three phase substation transformers in utility and industrial applications. Bushings account for a large portion of transformer failures, often causing severe and costly damage. With this comprehensive active monitoring system, asset owners and operators are alerted to potential issues before they become critical failures – reducing equipment losses and costs associated with maintenance, asset replacement and system downtime.
The Intellix BMT 330 can be utilized as a standalone system or as an integrated solution with GE’s Kelman™ TRANSFIX Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) mutigas analyzer, Multilin 845 Transformer Protection System and Perception™ Fleet Management software to provide comprehensive situational awareness and visualization of the transformer’s condition and root cause of transformer failures.

THORNE & DERRICK are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Duct Sealing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – we service UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, cable jointing, substation earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV.
Since 1985, T&D have established an international reputation based on SERVICE | INTEGRITY | TRUST.
Contact us for 3M Electrical, ABB, Alroc, AN Wallis, CATU Electrical, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, CSD, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Euromold, Filoform , Furse, Lucy Electric & Zodion, Nexans, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec, Sicame, WT Henley.
Rewriting The R&D Rulebook With Ellis Patents
August 10th, 2020
Ellis Patent Vulcan+ Cleat
-
Article Written By Stephen Walton Technical Director At Ellis Patents
Ellis Patent Vulcan+ Cleat
Thorne & Derrick Internatonal, based in the UK, are an Ellis Patents distributor for their market-leading and innovative range of cable cleats manufactured in the UK.
At first glance, the cable cleat may not seem like a product ripe for design and manufacturing innovation.
Its role in securing electrical cables in the event of a short circuit is seemingly straightforward enough to preclude it from such activity but look more closely and you’ll quickly realise you are wrong.
Stephen Walton, Technical Director of Ellis Patents, outlines how the company has evolved from being a manufacturer of traditional, standard cable cleats to solving installation and safety issues for the likes of Siemens, while also embracing new technology to rewrite the R&D rulebook.
For a long time, Ellis banged the drum about the importance of correctly specified cable cleats. The key selling point is the fact that, without correct specification, all a cable cleat would do is add to the potentially life-threatening shrapnel during a short circuit situation.
Ellis’s drumming these days is significantly quieter. The market is now well aware of the need for cleats. As a result, it has become increasingly congested, with more manufacturers than ever making them and, in some cases, producing virtual replicas of the most popular.
Ellis has responded to these changing market conditions by subtly shifting its focus. The company’s latest change has been focused on what and how it sells – a shift of approach that was born out a growing demand for project-specific solutions.
Initially, this was confined to bespoke cable cleats being designed and manufactured to exact client specifications and short-circuit tested to exact project conditions. This now has developed to a stage where Ellis is called in, presented with a problem and asked to solve it.
For example, the company helped Siemens with the installation and subsequent restraint of seven large diameter high voltage (HV) cables on HelWin 2 – a 690MW offshore HVDC platform.
Ellis’s cable guide clamp provided low-loss transmission between the North Sea offshore wind farm, Amrumbank West and Germany’s onshore grid.
Today, Ellis has an in-house R&D facility that enables it to deliver new, production-ready products in a matter of days. It recently developed a twist foot fixing mechanism that reduces installation cost and time for its Emperor and Vulcan+ cable cleats in less than a fortnight.
Utilising its own 3D CAD rapid prototyping facilities, and Stratasys Objet 24 and 30 printers, the development process began with a brainstorm during which possible solutions were suggested and sketched.
The most popular of these were then drawn up in 3D and printed overnight. Samples were cleaned, assembled and function tested the following morning. The promising designs were then refined and reprinted over the following days until a final version was agreed on and a functional prototype printed and passed on to sales and production for feedback.
To take a product from an idea to a fully functional, production ready prototype in less than a fortnight really does rewrite the R&D rulebook.
Traditionally, creating a production-ready prototype would have required the development of injection moulding tools, which involved significant investment in time and resources, and typically took six to eight weeks to manufacture.
Once received, only small changes to the tools were feasible, meaning any major alterations added another 6-8 weeks to the entire process.
However, by harnessing 3D printing technology and bringing as many elements of the design and testing process in-house, Ellis can now work within the tight timeframes of a live project and ensure it doesn’t lose any momentum by delivering bespoke solutions to installation issues in days.
The new product Ellis’s new twist foot cleats, which are supplied pre-fitted on its Emperor and Vulcan+ cleats, are suitable for all installations using cable channel and ladder with inverted rungs. There are singlefooted versions for cables in trefoil up to 58mm and double-footed versions for cables with diameters ranging from 59-128mm.
The single version locks in place with nothing more complex than a 90º turn and the tightening of the integral securing bolt, while the double-footed version is secured with tabs that are simply rotated 90º to engage the channel nut before the securing bolt is tightened.
Stephen Walton is Technical Director of Ellis Patents. A Chartered Mechanical Engineer with over two decades of  industry experience, Stephen joined Ellis in 2015 and has since played a key role in the development of a large number of new and improved products, as well as in the positioning of the North Yorkshire company as the first port of call for contractors seeking bespoke solutions to installation headaches, and project-specific cable cleat solutions. He has also been one of the driving forces behind Ellis’s early adoption of new technology, which is helping the company rewrite the R&D rulebook.
industry experience, Stephen joined Ellis in 2015 and has since played a key role in the development of a large number of new and improved products, as well as in the positioning of the North Yorkshire company as the first port of call for contractors seeking bespoke solutions to installation headaches, and project-specific cable cleat solutions. He has also been one of the driving forces behind Ellis’s early adoption of new technology, which is helping the company rewrite the R&D rulebook.

Ellis Patents Vulcan, Atlas & Emperor Cable Cleats
Ellis Patents are global leaders in the innovation and manufacture of nylon cable cleats, aluminium cable cleats and stainless steel cable cleats – Ellis satisfy the operational requirements of the construction, oil, gas, rail, utilities, wind energy and power generation industries.

Further Reading
- IEC 61914 – Cable Cleats & Short Circuit Protection Calculations
- Fire Resistance & Cable Cleats – Surviving Fire, Flame & Extreme Heat
- Triplex Cleats – Selection Guide for Cleating 11kV BS7870 Part 4.10 Cables
- Stainless Steel Cable Cleats – Preventing Galvanic Corrosion Of Cable Fixings
- Ellis Patents Cable Cleats & Cable Basket Tray for Securing High Fault Level Cables
- Stainless Steel Cable Cleats v Ties – The Myths Debunked By Ellis Patents
Thorne & Derrick
T&D are Specialist Distributors to UK Distribution Network Operators (DNO’s), NERS Registered Service Providers, ICP’s and HV Jointing Contractors of an extensive range of LV, MV & HV Jointing, Earthing, Substation & Electrical Eqpt – this includes 11kV/33kV/66kV joints, terminations and connectors for both DNO and private network applications.
Contact our UK Power Team for competitive quotations, fast delivery from stock and technical support or training on all LV-HV products.
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV

BAND-IT Bolt Clamp & Band – Pole Mounting 5G Communications Equipment
August 10th, 2020
BAND-IT Bolt Clamp and Band
BAND-IT Bolt Clamp & Band
Supporting the Rollout of 5G Wireless Networks
Roll-out of the next generation of cellular communications hardware, known as 5G, requires equipment to be upgraded and additional towers added to provide the wireless service.
The BAND-IT Bolt Clamp and Band are extensively specified for securing the new communications equipment boxes to poles and towers. The advantage to installers is that the bolt clamp can be installed with just a wrench or ratchet and is adjustable to various mounting hardware and pole diameters.
With an estimated 400 times as many 5G towers needed the time savings at installation translates to major cost savings for installers.
The BAND-IT Banding Edge
- Easy to install, BAND-IT banding systems require no special tooling
- Cut to length to attach hardware to poles of various sizes
- Quicker installation than Band & Buckle system
- Galvanized carbon steel and aluminum for corrosion resistance extending life of product
Stainless Steel Product Features
- Available in two sizes: 3/4” for lighter duty and 1-1/4” for heavy duty
- Pairs with BAND-IT Band or Giant Band, sold in rolls and cut to length on-site

Stainless Steel Band Strapping & Clamping Systems | BAND-IT

THORNE & DERRICK are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Duct Sealing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – we service UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, cable jointing, substation earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV.
Since 1985, T&D have established an international reputation based on SERVICE | INTEGRITY | TRUST.
Contact us for 3M Electrical, ABB, Alroc, AN Wallis, CATU Electrical, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, CSD, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Euromold, Filoform , Furse, Lucy Electric & Zodion, Nexans, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec, Sicame, WT Henley.
Use Of SF6 Gas In The Electrical Transmission Industry
August 10th, 2020
Use Of SF6 Gas In The Electrical Transmission Industry
SF6 Gas
In The Electrical Transmission Industry
Bluefield
Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) gas circuit-breakers have been a critical technology under review by the European Union (EU) for some time. Bluefield applied our collective knowledge and learnings to inform and recommend an alternative the use if SF6 gas-type switchgear.
Problem
A site required upgrades to its existing High Voltage (HV) electrical switchboards. The site’s aim was to reduce all arc flash hazard categories to ‘everyday work clothing’ or less.
Bluefield identified that the existing switchboard equipment utilised the SF6 gas-type circuit-breakers
SF6 gas circuit-breakers have been a critical technology under review for some time.
Bluefield further investigated the risks of use, possible alternatives, and opportunities for the site to reduce its arc flash hazards.
Investigation
- The European Union EU regulation 517/2014, due to be reviewed in 2020, will potentially declare the complete phasing out of the use of SF6 gas type equipment.
- SF6 is the greenhouse gas with the most significant global warming potential (GWP) – 22,800 times more than CO2.
- SF6 decomposes under electrical stress, forming toxic by-products; this by-product, disulphur decafluoride (S2F10), has a toxicity on a par with phosgene gas, and is extremely hazardous to employees.
- Only licensed or authorised hazardous waste managers are permitted to handle, transport, and recycle SF6 (OPSGG 1989)
- A significant number of assets in the site’s HV electrical infrastructure utilised SF6 gas type circuit breakers.
Results
Bluefield recommended the use and future change out to Vacuum-type circuit-breakers.
Service experience shows them to be reliable, almost maintenance-free, and safe under operating conditions. They have negligible global warming potential (GWP), with no reporting required under the Synthetic Greenhouse Gas Management Act, no suffocation or poisoning risk due to toxic by-products or leakage, and no fire hazards or explosion risk due to over-pressurisation or overheating of the gas.
Bluefield also recommended the installation of remote or wireless switching of circuit breakers to remove the arc flash hazards associated with this task.
The site subsequently changed its business philosophy on the use of SF6 gas-type circuit-breakers. They implemented the use of Vacuum circuit-breakers, and utilised remote switching to achieve their target for arc flash reduction and risk mitigation.
About Bluefield

Bluefield believes that: –
- Equipment reliability starts with the quality execution of the lifecycle maintenance plan
- Software solutions should make it easier and less labour intensive to operate equipment within design limits and execute quality maintenance to a defined lifecycle plan
- Maintenance management is about managing maintenance and reliability, whereas asset management is about making sure the physical assets deliver the best bottom line outcomes for the business
We have proven our ability to assist our clients in mining, rail and gas industries to sustainably get more from their assets; more throughput, more reliability, more uptime, more productivity and more cost reductions. Our methods ensure that the site teams own the improvements and therefore they actually get implemented. We use the latest technology to get results faster.

Specialist Suppliers of High Voltage Electrical Equipment & Cable Accessories
LV, MV & HV Jointing, Earthing, Substation & Electrical Eqpt
Thorne & Derrick International are specialist distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Duct Sealing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, cable jointing, substation, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV.
THORNE & DERRICK Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV

Thorne & Derrick | Stockists & Suppliers | Joints Terminations Connectors up to 66kV




