Blog
Earthing Armoured Cables To Safely Protect LV AC Cables In The Solar Industry
February 28th, 2024Challenge | This week a Solar EPC client of Thorne & Derrick engaged our Technical Sales Department to assist with ongoing O&M issues relating to the termination connection of steel wire armour (SWA) on 450off 4 core x 240sqmm LV AC cables, 0.6/1kV – the outdoor location cables are connected to a string inverter and the MV station at the remote end on a UK based 50MW solar farm in Derbyshire. The cable armouring provides mechanical protection but is not intended to circulate electrical current.
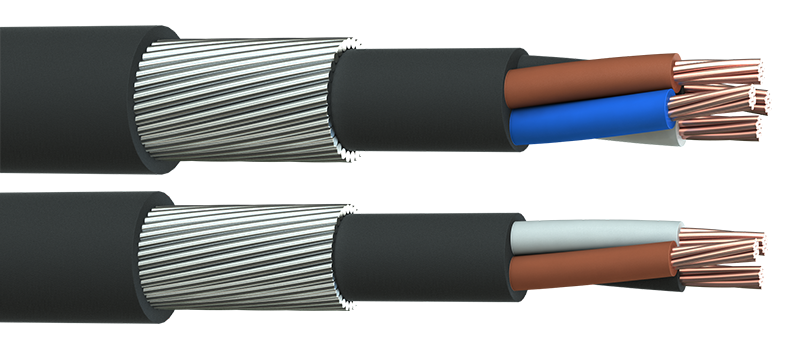
SWA Cable Steel Wire Armoured Cables | Image FS Cables
BS7671 Clause 522.8.10
“Except where installed in a conduit or duct which provides equivalent protection against mechanical damage, a cable buried in the ground shall incorporate an earthed armour or metal sheath or both, suitable for use as a protective conductor. The location of buried cables shall be marked by cable covers or a suitable marker tape. Buried conduits and ducts shall be suitably identified. Buried cables, conduits and ducts shall be at a sufficient depth to avoid being damaged by any reasonably foreseeable disturbance of the ground.”
Earthing Armoured Cables
Solution
Initially, from the viewpoint of the above British Standard the client considered connecting the wire armour at the MV station to ensure that during a fault (e.g.cable strike) an earth path exists to allow safe disconnection of the cable. Earthing the armours of buried SWA cables is important for safety – this prevents/reduces the severity of electric shocks and equipment damage should a person dig inadvertently into the cable. The cable wire armours provide a complete earth path around the cable. Utilizing a single phase within a 4 core cable as earth is not sufficient as it does not offer complete protection around the circumference of the cable. Also, in solar farm installations un-earthed wire armours can have induced voltage from excessive current generated. Therefore, the contractor should always consult the circuit designer.
Customer Service
From initial application, to concept, to design and to sample acceptance by the end client we subsequently completed the despatch and delivery of their order in 5 working days for 450off Armour Earthing Kits.
Important Note
Solderless earth kits that are intended for copper tape screens (MV cables) are a substandard method to earth SWA cables. Solderless earth kits utilize a constant force spring which do not offer a secure earth bond for SWA’s. Also, the cross sectional area of the braid within these kits is inadequate which is why you should always use an armour earth kit for this application. Contact us to discuss your application.

Innovative Connection & Grounding Solutions for LV Cables
Excerpt from Installation Instruction
Heat Shrink Outdoor Armour Earth Kit To Suit
XLPE SWA PVC
The Heat Shrink Outdoor Armour Earth Kit includes medium wall adhesive lined heat shrink tubes, mastic tapes, solder-blocked earth braids and clamps. Contact us for further information, technical support or for a quotation.

THORNE & DERRICK are Specialist Distributors of LV HV Solar Cable Accessories, Jointing, Termination, Earthing & Electrical Equipment 1500V DC to 33kV – we service UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, jointing, substation and electrical construction.
Since 1985, T&D have established reputation based on SERVICE | INTEGRITY | TRUST – we are highly customer responsive and absolutely committed to providing a world-class service.
We provide expert technical support and supply from a multi-million pound stock holding:
- Cable Joints, Terminations & Connectors
- Earthing & Lightning Protection
- Cable Accessories – Lugs & Glands
- Circuit Protection & Fuses
- Cable Cleats & Clamps
- Electrical Safety Equipment
- Cable Pulling & Laying Equipment
- Arc Flash Protection & Clothing
- Cable Duct Seals & Transit Systems
- Surge Arresters & Bushings
- MV HV Overhead Line & Substation Power Products
>> MORE INFO <<
Further Reading

Thorne & Derrick are Specialist Distributors of Innovation Tooling & Accessories for LV HV Power Systems to facilitate safe and reliable cutting, crimping, preparation, termination and installation of cables, 600V to 132kV.
T&D Supply PADS Network Rail Approved 3M Cable Terminations For TRU Project
February 23rd, 2024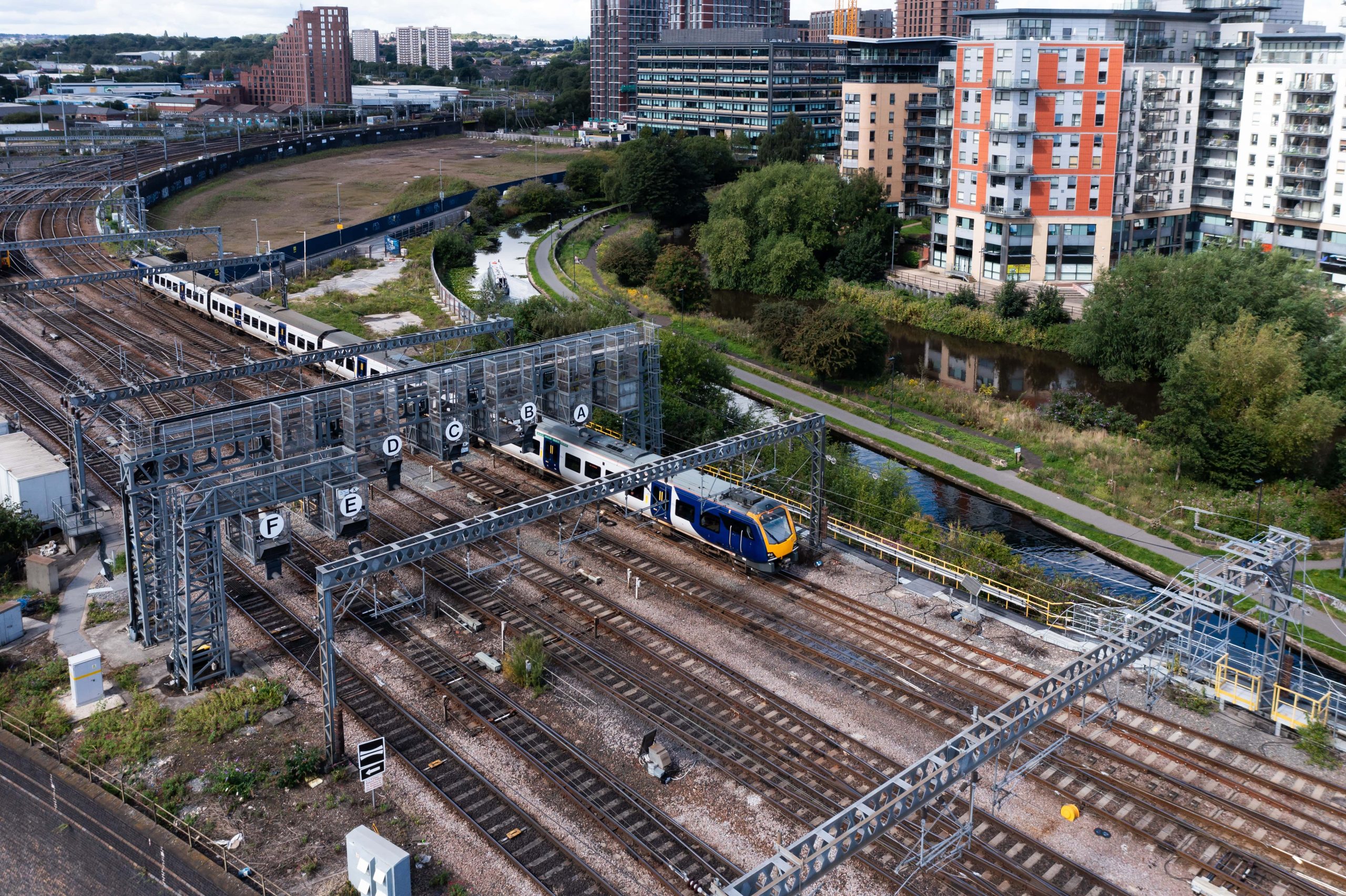
Thorne & Derrick | 3M Stockists & Key UK Distributor Since 1985
PR | Uploaded by Natalie Lundie | Supply Chain: Marketing Lead at Thorne & Derrick
3M Cable Terminations
PADS Network Rail Approved Medium Voltage Cable Accessories
Thorne & Derrick are proud to have supplied 3M Cable Joints & Terminations to the Transpennine Route Upgrade (TRU) project. Our partnership with 3M Electrical since 1985 has enabled us to deliver high-quality electrical solutions to various projects.
The TRU project involved the installation of an overhead gantry and the laying of 3km of high voltage cables through the deep Marsh Lane Cutting, which connects Leeds and Neville Hill. To ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations, the project required the use of PADS Network Rail Approved joints and terminations.
By supplying reliable and durable Cable Joints & Terminations, we were able to support the TRU team in accomplishing their goals. This project is crucial for the future electrification of the line east of Leeds, providing the necessary power infrastructure for efficient and sustainable transportation.
Transpennine Route Upgrade
The TRU project is a major programme of railway improvements aimed at bringing better journeys to passengers traveling across the Pennines between Manchester, Huddersfield, Leeds, and York.
Stretching across the North of England the 70-mile Transpennine main line serves 23 stations, crosses over and dips under dozens of bridges and viaducts, passes through six miles of tunnels, and crosses over 29 level crossings.
TRU will transform the Transpennine main line into a high-performing, reliable railway, bringing more frequent, more reliable, faster & greener trains. The Transpennine Route Upgrade East Alliance is a collaborative effort between several organisations including Network Rail, J. Murphy & Sons, Siemens, Systra, and VolkerRail. These companies have come together to deliver infrastructure improvements on the eastern part of the route between York and Leeds.
Thorne & Derrick are a Network Rail Approved Vendor, which means we have met the necessary criteria and have been approved to supply our products and services to Network Rail. PADS (Product Acceptance and Design Services) is the product approval process used by Network Rail.

PADS Approved Solution
The client contacted Thorne & Derrick requiring PADs Approved Joints & Terminations so the team could carry out planned major engineering works. As part of the TRU project they needed to install an overheard gantry and lay 3km of high voltage cables between East of Leeds Colton & Neville Hill.
The cable joints & terminations provided by Thorne & Derrick will be used to enhance the electrical connectivity and reliability of the railway infrastructure in this area. These components are crucial in ensuring efficient transmission of power and signals along the tracks.
3M cold shrink cable joints require no hot-work permit or special tools for installation – specified for rail cable sealing, insulation and protection and are approved by Network Rail for live rail terminations and inline cable joints for DC track feeder cable applications.
Why T&D?
One of the reasons Thorne & Derrick was chosen for this project was our ability to offer the best price and quickest delivery of the cable terminations. The delivery had to be completed within a specific timeframe in order to guarantee that the engineering works could proceed as planned. The terminations were available ex stock, meaning they could be shipped the next day.
The use of high-quality cable joints and terminations in the TRU project aims to minimise signal interruptions, electrical faults, and downtime on the line. Electrification of the line east of Leeds is an important step towards achieving efficient and sustainable transportation in the future. This demonstrates a commitment to delivering a modern, efficient, and reliable railway network. Ultimately, this will lead to improved train performance, reduced delays, and a better overall experience for passengers.
⚡️ November: The TRU team installed an overheard gantry and laid 3km of high voltage cables through the deep Marsh Lane Cutting between Leeds and Neville Hill.
These will provide the power for future electrification of the line east of Leeds. pic.twitter.com/Y7q19tdrh6
— The Transpennine Route Upgrade (@theTRUpgrade) December 31, 2023
The project’s investment in the latest technologies and partnerships with trusted suppliers like Thorne & Derrick aim to provide a safe and seamless travel experience for passengers in the East Leeds Colton and Neville Hill area.
As a Network Rail Approved Vendor, Thorne & Derrick is proud to serve the rail industry as a reliable and trusted supplier, helping to contribute to the efficient and reliable functioning of the national railway infrastructure in the UK and meeting the demanding requirements of the rail industry.
With our extensive range of PADS Approved Medium Voltage Joints & Terminations available from stock, T&D is well-equipped to support the Transpennine Route Upgrade and other railway projects in the future.
Thorne & Derrick’s experience and expertise in the electrical distribution industry, combined with our strong relationship with 3M Electrical, have allowed us to contribute to significant infrastructure projects like the TRU. We remain committed to delivering reliable and innovative solutions to our customers in the UK.
Installation of Medium Voltage Termination
3M Cold Shrink technology ensures quick, easy and safe installation of the QTIII Termination Body by pulling and unwinding the plastic support core in counter clockwise direction. Specialist cable jointing tools are not required. Included with each kit are installation instructions for the 3M QTIII Series Terminations.
3M 95-EP631-2 uses innovative Cold Shrink Technology combined with Network Rail (NR) and PADS Approval to meet the requirements for the installation on medium voltage electrical infrastructure – forming part of rail cable joints & terminations range by 3M Electrical.
3MCold Shrink High Voltage Termination Kit QTEN is suitable for application up to 72.5 kV (U_max) single-core copper wire-screened cables. The silicone cold shrink insulation body provides an easy and secure solution for cable termination.
The 3M 95-EP620-1R cold shrink cable termination, with PADS Approval for used on high voltage power networks at Network Rail, is suitable for the connection of 52kV single core polymeric insulated cables with copper wire screens
PADS Approved Rail Equipment
Thorne & Derrick stock and distribute a wide range of cable accessories and electrical equipment for rail applications. These accessories are used by contractors who work on various aspects of the rail system, including low voltage power distribution, high voltage electrification, substations, DC traction and networks, OLE (overhead line equipment), and track feeder cable renewals.
Our product range includes cable terminations, joints, cable repair products, and connection products that are approved by Network Rail PADS. These products are suitable for medium voltage cables and can handle voltages up to 66kV.
The cable accessories provided by Thorne & Derrick include options like heat shrink, cold shrink, push-on, and slip-over varieties. These accessories are used to joint, terminate, and connect medium and high voltage power cables to various equipment such as oil, air, or gas insulated switchgear, transformers, motors, and overhead lines including 3M Cold Shrink, Pfisterer CONNEX and Nexans Euromold products.

To view the full range of PADS approved rail equipment that Thorne & Derrick can offer click here – Rail Cable Accessories LV HV

Electrical Safety in Wind Turbines
February 20th, 2024
Authored by Pieter Pijnenburg | Arc Flash Engineer from Leaf Electrical Safety

Electrical Safety
Any industrial or commercial workplace requires arc flash and electrical safety training, and it is essential in order to make sure your staff members know what they need to do to remain safe.
Leaf Electrical Safety is an electrical safety company that can provide expert advice on electrical safety to help teams build processes and improve safety culture. Working primarily across Canada and the USA, they help solve your industrial electrical safety problems.
Electrical safety compliance training should keep you on the edge of your seat, wanting more, because it will highlight the dangers that your team faces on a daily basis. Special thanks to Jon Travis for the kind permission to republish.
→ See original article here!
- What are the electrical safety hazards in wind turbines?
- How do I ensure my team works safely around them?
- What PPE should my electrical workers be wearing?
- How do you perform grounding with wind turbines?
Let’s jump right in!
The Definitive Guide to Arc Flash By Thorne & Derrick
WIND POWER FACILITY ELECTRICAL SAFETY
In our ever-changing renewable world, the safety of personnel is still and should remain a paramount concern. Wind Energy Conversion Systems (WECS) are some of the more prominent types of renewable generation whose safety concerns are exacerbated by two main factors:
- Remoteness: due to the nature of wind turbines being remote and/or offshore, any hospitalisation can turn into a race against time.
- Confined spaces: the electrical components and work areas within a wind turbine are typically in confined spaces, which becomes more problematic when you add multiple workers into the mix.
WHAT ARE THE ELECTRICAL SAFETY HAZARDS
IN WIND TURBINES?
In order to mitigate hazards and allow for adequate protection, WECS equipment and operators should be adequately equipped to deal with the following main hazards issues that commonly occur in WECS:
- Arc Flash
- Shock
- Overloaded Circuits
- Defective Insulation
- Wet Environment
- Damaged or Worn Equipment
ARC FLASH RISK IN WIND TURBINE
Potential arc flashes in WECS are potentially life-threatening issues which require detailed analysis and physical protection to be accounted for. Arc flash hazard analysis (incident energy calculations) is typically used and utilises standards such as IEEE 1584-2018 to perform the calculation. Once the calculation is made and the proper arc flash boundaries are determined, personal protective equipment (PPE) can be assigned based on the calculations (see CSA Z462 for more details).
SHOCK RISK IN A WIND TURBINE
Shock risk, like an arc flash, is a potentially life-threatening hazard if not properly accounted for. Usually, a shock risk assessment is performed to look at key system parameters such as voltage level, shock boundary, environment, equipment type, and condition.
OVERLOADED CIRCUITS
Overloaded circuits can cause various problems and increase the risks of shock and arc flash considerably if not protected and isolated properly. Preventative measures can be taken through routine inspection of protection devices and physical circuitry (with proper PPE) to check for any abnormalities in the equipment.
DEFECTIVE INSULATION
Defective insulation can cause system malfunction and exponentially increase the potential arc flash and shock risks. Regular insulation resistance (IR) tests, whose procedure for electric machinery is highlighted in IEEE 43-2013, should be performed to test the dielectric strength of the insulation.
WET ENVIRONMENT
Wet surfaces can prove hazardous to people as well as electrical equipment. In order to reduce these potential hazards, regular equipment checks should be carried out on the exterior and interior of the WECS for potential water seepage/damage.
DAMAGED OR WORN EQUIPMENT
Equipment can be compromised from its normal working state for a variety of reasons, but compromised equipment can cause major problems if it is not repaired or replaced quickly enough. To mitigate this, scheduled maintenance procedures should be made and followed (see CSA Z463).
ELECTRICAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR WIND TURBINE WORKERS
PROPER PERSONAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT
Each hazard risk category requires a different level of protection. Categories range from 1 to 5 as defined within CSA Z462 and laid out below as follows:
| PPE category | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Incident Energy | Up to 4 cal/cm² | Up to 8 cal/cm² | Up to 25 cal/cm² | Up to 40 cal/cm² | Up to 75 cal/cm² |
Figure 1:PPE category as defined by CSA Z462
ARC FLASH BOUNDARY
An arc flash boundary is the shortest distance at which a person working at the time of an arc-flash incident may receive an onset of a second-degree burn or worse (1.2 cal/cm2) if not adequately protected by flame-resistant (FR) clothing.
LABELING
Labelling is defined in CSA 22.1-18 for both small (64-300) and large (64-400) wind turbines as “a permanent marking” that must be created near an easily accessible location near the disconnecting for the wind turbine output circuit (64-300) or base of the tower (64-400) and display the following critical information:
- Overcurrent protection values provided by the wind turbine for the stator and rotor, if applicable;
- Short-circuit current rating (SCCR);
- A brief system description, including the type of generator (synchronous or induction);
- Rated output current; and
- Rated output voltage at the grid connection to the turbine.
- Warning notice (large turbines only)
Furthermore, arc flash and shock hazard labels should be provided for large wind systems. These labels are covered in CSA Z462 Annex Q, which highlights procedures for labelling arc flash hazards and shock protection. The minimum arc flash label requirement per CSA 22.1-18 (Canadian Electrical Code Part 1) is:

Figure 2:CSA Arc Flash label template for CSA 22.1 Requirements
Whereas the CSA Z462 recommends that the label look something more like:

Figure 3:CSA Z462 Annex Q Recommended ARC Flash label structures
WIND TURBINE GROUNDING
Like any generator, the WECS should be properly grounded and follow CSA standards and IEEE 142. Proper grounding of turbines follows the general ruleset of AC connections as defined by CSA 22.1 Section 64-312 as:
- 1) Exposed non-current-carrying metal parts of towers, turbine nacelles, other metallic equipment, and insulated conductor enclosures shall be bonded to ground in accordance regardless of voltage.
- 2) Metallic towers or supporting structures shall be bonded to the ground with a minimum No. 6 AWG.
- 3) Guy wires used to support turbine towers need not be grounded.
- 4) Towers or structures shall be grounded by means of grounding electrodes to limit voltages imposed by lightning.
- 5) Notwithstanding Subrule 4), metal towers located on steel-supported buildings shall be bonded to non-current-carrying metal parts of the building.
FAULT FINDING & TESTING
To effectively find faults in a WECS, proper fault monitoring relay devices should be installed particularly:
- 50 – Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
- 51 – AC Time Overcurrent Relay
- 59 – Overvoltage Relay
These devices will be able to monitor and indicate the levels of key parameters such as voltage and current.
ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDS AND TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE WIND ENERGY INDUSTRY
CSA 22.1-2018 lists several safety requirements for both small and large wind turbines (64-300 tot 64-414), including marking, maximum voltage, insulated conductors, wiring methods, overcurrent protection, disconnecting means, grounding and bonding, maintenance receptacles, lightning protection, surge protection and system demarcation (large turbine).
Training requirements are highlighted in Annex U of CSA Z462, which highlights procedures for human performance in electrical safety. It highlights risk control methodologies and procedures for human performance, such as
- Job planning and pre-job briefing tool
- Job site review tool
- Post job review tool
- Procedure use AND adherence tool
- Self check with verbalization
- Three-way communication tool
- Stop when unsure tool
- Flagging and blocking tools

ELECTRICAL SAFETY PROVIDERS
Thorne & Derrick protect substation engineers, asset managers, SAPS, cable jointers, overhead linesmen and utility workers with PPE and safety equipment: this includes insulating gloves, arc flash clothing, voltage detectors, insulating matting and portable earthing to ensure worker safety when carrying out repair and maintenance on LV-HV switchgear, transformers, substations and turbines.
All of our Cable Connection & Energisation Accessories including Medium & High Voltage joints, terminations, connectors and cleats are tested to the latest international standards and supporting ranges of professional installation tools are stocked to reduce incident, accident and downtime to plant and people.

Use of Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL Live Line Testers & Indicators
February 16th, 2024
Use of Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL Live Line Testers & Indicators
Voltage Detectors Distributed from Stock | Approved Supplier | UK & Export Sales
Pfisterer Voltage Detectors
Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL is a capacitive voltage detector—the universal Medium & High Voltage Detection & Live Line Tester (LLT) product range for nominal voltages from 110kV to 220kV. The voltage detector presents the operating voltage when brought into contact with the MV HV overhead lines and conductors.
The Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL voltage detector provides a high level of user-friendliness and user safety – KP-Test 5HL is designed and type-tested to Standard IEC 61243-1.
Other versions of the HV high voltage detector with deviating voltages, ranges of nominal voltages, frequencies, and languages are available on request.
KP-Test 5 range of instruments from Pfisterer can detect voltage level 1 to 420 kV AC.
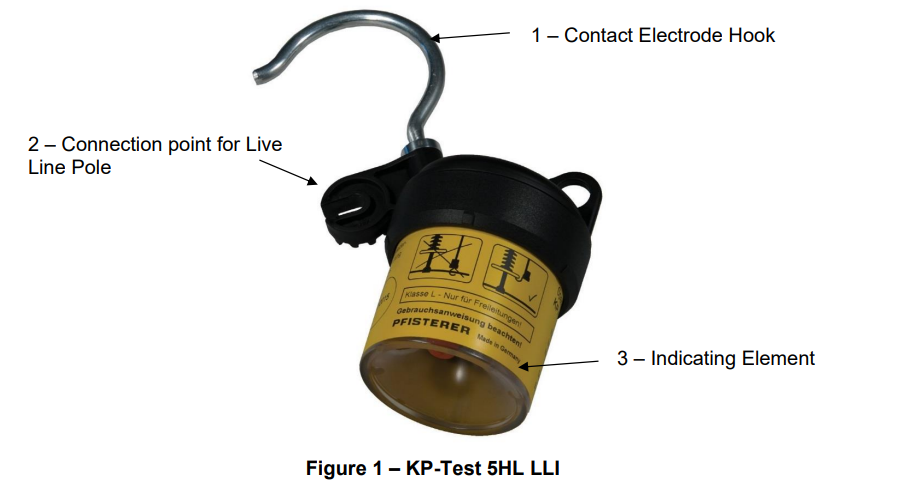

Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL
KP-Test 5HL Live Line Indicators
The KP-Test 5HL is one of several certified live line indicators (LLI’s) that have been used to test 25kV conductors to ensure that they have been disconnected from the power source prior to connecting to earth or testing before touching. LLIs are safety devices on which human lives may depend. These should be handled with extreme caution and protected against damage.
To discharge any induced voltages, field equipment earthing, also known as portable earthing, may be necessary when employing voltage detectors to determine whether operating voltages are present on MV-HV power cables or overhead lines. This is because the equipment may be operating close to live conductors.
KP-Test 5HL is limited to use on the lowest conductor of the objects being tested, such as the bottom autotransformer feeder (ATF) or contact wire. Only those with a valid competency (authorised person or nominated person) and who have attended a familiarisation briefing should use it.
| Voltage Detector Part Number | Nominal Voltage (kV) | Nominal Frequency (Hz) | Diameter of hook (mm) |
| KP-Test 5HL | 110-220 | 50 | 70 |
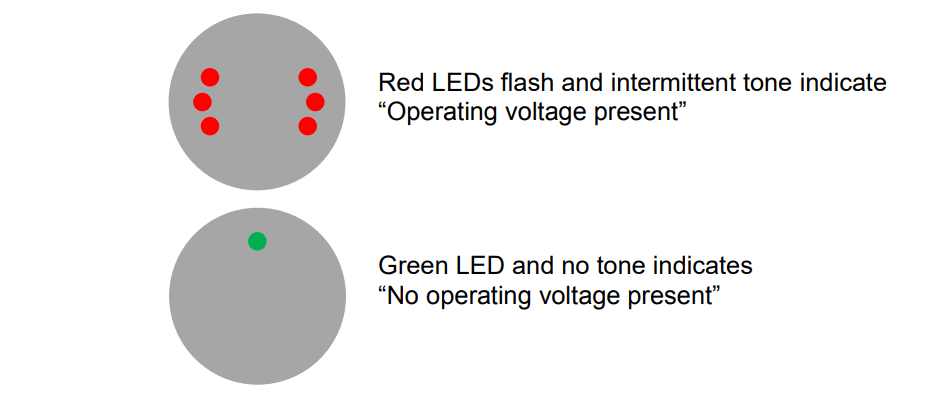
Benefits of using Voltage Detectors
Furthermore, voltage detectors are crucial instruments made to improve electrical safety in a range of settings. These tools are essential for averting mishaps, lowering the risk of casualties, and safeguarding infrastructure. An extended explanation of the features stated is provided below:
- Weather Resistance: They are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including rain. This allows operators to use them in diverse weather conditions without compromising their functionality. This feature ensures that the detectors remain operational even when exposed to rain, providing continuous safety in outdoor settings.
- Personnel Safety: Voltage detectors significantly reduce the risk of serious injury to personnel working with electrical systems. Their ability to detect live voltage without physical contact ensures that operators can assess the presence of electrical energy safely. This minimizes the chances of electrical accidents, protecting personnel from electric shocks and other potential hazards associated with working in proximity to live electrical components.
- Infrastructure Protection: Voltage detectors play a vital role in safeguarding electrical infrastructure. By providing a means to detect live electrical components, they help prevent accidental damage to critical equipment and wiring. This protection extends the lifespan of electrical systems, reduces the frequency of repairs, and contributes to the overall reliability of the infrastructure.
- Quick Drying: After being exposed to rain or wet conditions, voltage detectors are designed to dry quickly once not in use. This feature is essential for maintaining the reliability of the device. The rapid drying capability ensures that the detector can be stored or reused promptly after exposure to moisture, minimizing downtime and allowing for efficient use in dynamic work environments.

THORNE & DERRICK
Thorne & Derrick stock and distribute PFISTERER CONNEX Connectors for medium / high voltage cable connection and termination to electrical systems up to 33kV – we provide competitive prices for PFISTERER CONNEX connectors used to terminate and connect polymeric insulated MV-HV cables into gas insulated switchgear and electrical equipment from extensive UK stocks.
Thorne & Derrick are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing businesses involved in cabling, jointing, substation, earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV. Supplying a complete range of power cable accessories to support the installation and maintenance of low/medium and high voltage cable systems:
- Slip-on Cable Terminations
- Cold-shrink Cable Terminations
- Heat-shrink Cable Terminations
- Cable Joints – Heat & Cold-shrink
- Separable Connectors (Euromold)
- Surge Arresters & Switchgear/Transformer Bushings

Voltage Detectors | Phase Comparators | Insulating Poles | Portable Earthing | LV MV HV
Basics of Cable Design and Engineering for Power Systems
January 29th, 2024
Guest Article : Authored by Ryan Smith MSc MIET | Owner of EasyCableSizing.com
As an Electrical Engineer, I’ve always been fascinated by the “hows and whys” in the design and engineering of power cables. In this Article, I delve into the essential aspects from the core components of a power cable to the considerations in choosing the right materials.
components of a power cable to the considerations in choosing the right materials.
Key highlights include:
- the critical roles of conductors, insulation, and sheathing
- a comparative look at copper and aluminium in cable applications
- insights into the evolving world of eco-friendly materials in cable design
- importance of understanding electrical properties like conductance, resistance, capacitance, and inductance
I also discuss the significance of standards like IEC 60287 and IEC 60502 in cable sizing, essential for anyone working with MV and HV power cables. Whether you’re a fellow engineer, a student, or just curious about the field, I believe there’s something valuable for everyone in this piece.
→ See original article here!
Table Of Contents
1.Introduction to Cable Engineering
1.1 Definition and Scope
2. Cable Construction Basics
2.1 Core Components of a Power Cable
2.1.1 Conductors
2.1.2 Insulation
2.1.3 Sheathing and Jacketing
2.2 Types of Power Cables
2.2.1 Low Voltage Cables
2.2.2 Medium and High Voltage Cables
3 Material Selection in Cable Design
3.1 Conductive Materials: Copper vs. Aluminium
3.2 Insulation Materials: XLPE, PVC, and Others
3.3 Advances in Eco-friendly Materials
4 Electrical Properties of Cables
4.1 Conductance and Resistance
4.2 Capacitance and Inductance
4.3 Impedance Considerations
5 Cable Sizing and Capacity Considerations
5.1 Calculating Current Carrying Capacity
5.2 Factors Influencing Cable Sizing
5.3 Utilizing Standards for Sizing
5.3.1 IEC 60287 Standard
5.3.2 IEC 60502 Standard
6 Key Takeaways
Introduction to Cable Engineering
Definition and Scope
Cable engineering is a specialised domain focusing on the design, implementation, and optimisation of electrical power cables. This field encompasses a range of activities from material selection to performance testing, ensuring that cables meet the demands of modern electrical networks.
Cable construction Basics
Core components of A POWER CABLE
Underground power cables consist of a minimum of two components, a conductor and insulation, however these are usually accompanied by other elements, each playing a critical role in overall functionality:
cONDUCTORS
Conductors are the principal element of a power cables, responsible for transmitting electricity. They are typically made of materials like copper or aluminium, chosen for their excellent conductivity and durability. In other applications where conductors are required, other materials are often used, like gold, but these aren’t feasible for power applications due to their high cost.
iNSULATION
Insulation in power cables primarily provides segregation from a conductor and other conductive materials, whether they’re intended to be conductors or not, but also protects it from environmental factors.
Sheathing and Jacketing
Sheathing and jacketing provide an additional layer of protection to cables, safeguarding against physical damage and environmental factors. This layer is crucial for cable longevity and reliability.
Types of Power Cables
Power cables are categorised based on their voltage capacity:
Low voltage Cables
Low voltage cables are designed for applications with voltage requirements commonly up to 1000V. They are commonly used in residential and commercial settings for everyday electrical needs, and in industrial settings for smaller loads. Learn more about low voltage, heavy-duty industrial cables like the H07RN‑F rubber cable in our detailed selection guide.
Medium and High Voltage Cables
Medium and high voltage cables cater to more demanding applications, such as industrial plants, generation, and power transmission lines. They are able to handle higher voltages and are key in large-scale power distribution.
Material Selection in cable design
Conductive materials: Copper vs. aluminium
The two main materials used for conductors are copper and aluminium, due to their wide availability and relatively low cost.
- Copper, known for its superior conductivity and durability, is often preferred for certain applications, despite its higher cost.
- Aluminium, being lighter and more cost-effective, is a viable alternative, especially for large-scale power transmission.
Insulation Materials: XLPE, PVC, and Others
Different insulation materials like XLPE, PVC, and EPR play a crucial role in cable performance:
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Known for high temperature resistance and excellent electrical properties, ideal for high voltage applications.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Offers flexibility and durability, used in a wide range of cable types.
- EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber): Notable for dielectric strength, flexibility, thermal stability, suitable for high stress environments.
- Others: Includes materials like Teflon and Rubber, chosen for specific applications based on properties like fire resistance, low toxicity, or extreme environmental conditions.
Advances in Eco-friendly Materials
The cable industry is evolving towards eco-friendly materials like polypropylene (PP) to minimize environmental impact. PP stands out for its excellent insulating properties and recyclability, making it a promising material for next-generation power cables. However, its application in cable insulation still faces challenges, such as optimising its mechanical and electrical properties. This drive towards sustainable materials is redefining cable technology, balancing environmental considerations with performance requirements. For an in-depth understanding, read more about the potential of PP in power cable insulation in this research article.
Electrical properties of cables
Conductance and resistance
Understanding the conductance (G) and resistance ® of power cables is essential for evaluating their performance. These properties are inversely related, where G=1⁄R. Conductance represents a cable’s ability to allow electric current flow, while resistance quantifies the opposition to current flow. This affects cable efficiency, with lower resistance implying less energy loss as heat. Factors such as material type, cross-sectional area, and temperature influence these properties.
To learn more about the impact of resistance in power systems, consider reading this comprehensive guide on resistance and its effects.
Capacitance and Inductance
Capacitance © and inductance (L) are key factors in cable design, affecting how cables react to different electrical loads and frequencies. Capacitance in cables arises from the electric field between conductors, typically calculated using where is the permittivity of the insulating material, the area of the conductor, and the distance between conductors. Inductance, on the other hand, is influenced by the magnetic field around the conductor and is given by , where is the permeability of the material, the number of turns in the coil, the area, and the length of the coil.
Impedance Considerations
Impedance (Z) in cables, a combination of resistance, inductance, and capacitance, is crucial in AC power systems. It can be represented as , where is the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance. Impedance affects signal quality and power loss in cables, and its proper management is vital for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of electrical systems.
For an in-depth understanding of impedance and its impact on power systems, you might find this resource on impedance in AC circuits useful.
Cable sizing and capacity considerations
Calculating current carrying capacity
There are various methods used to calculate the current carrying capacity of cables (or ampacity), although the two methods predominantly referenced and used are IEC 60287 and Neher-McGrath. Both IEC 60287 and Neher-McGrath methods consider the heating of a conductor, and the cable’s and surrounding mediums’ ability to dissipate the heat until thermal equilibrium is met. An increase in current results in an increase in temperature, and the less thermal resistivity the cable and surrounding medium have, the more current can be carried.
Factors Influencing Cable Sizing
A principal consideration in cable sizing is the insulation selected for the conductor, as this determines the maximum temperature that can be reached before causing overheating and unnecessary stress or damage to the cable. Beyond that, it is primarily the surrounding medium and installation conditions that influence the thermal resistivity.
For cables installed underground, the soil itself has a thermal resistivity value to be considered. If sand, bentonite, or concrete are used, their own thermal resistivity values and geometry are incorporated into the formulas to determine the cable’s ampacity. If a cable is installed in a duct, the geometry, thermal resistivity of the duct itself, and the filling medium (such as air or bentonite) must also be considered.
Another major factor affecting the ampacity of cables is their proximity to other heat sources, such as other circuits (which are assumed to reach 90°C if insulated with XLPE), hot water pipes, steam pipes, etc. This mutual heating significantly impacts the ampacity calculations, especially in shared trenches or when cables are installed in ladders or trays.
Utilizing Standards for Sizing
When determining the appropriate size for power cables, adhering to established standards is crucial. These standards provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating various factors, ensuring that the chosen cable meets both current and future demands of electrical networks while adhering to safety and efficiency guidelines.
IEC 60287 Standard
The IEC 60287 standard is renowned for its systematic approach to cable sizing. It accounts for numerous factors, including conductor temperature, load pattern, cable laying conditions, and the thermal resistivity of the surrounding environment. This standard is particularly valued for its detailed thermal model, essential in accurately predicting cable behaviour under varying operational conditions.
EasyCableSizing.com plans to integrate this model into its platform, enhancing its cable sizing capabilities.
IEC 60502 Standard
IEC 60502 covers the requirements for the manufacture and testing of cables ranging from 1kV to 30kV. It includes tables of multipliers used against standard cable ampacity tables to determine adjusted ampacities based on specific conditions. These tables are derived from methodologies in IEC 60287, offering a practical guide for cable system development.
EasyCableSizing.com utilizes the IEC 60502 methodology in a user-friendly manner, helping users quickly and efficiently determine cable ampacities. This approach simplifies the complex process of cable sizing, making it accessible to a wider range of professionals and ensuring compliance with international standards. In Understanding the IEC 60502 Sizing System: A Double-Edged Sword this standard in particular is discussed in more detail.
Key Takeaways
- Cable Engineering’s Core Focus: Emphasizes the design, implementation, and optimization of electrical power cables, highlighting its crucial role in modern electrical networks.
- Components of Power Cables: Details the significance of conductors, insulation, and sheathing in cable construction, and their impact on cable functionality and durability.
- Conductive Material Choices: Discusses the use of copper and aluminium in power cables, outlining their advantages based on conductivity, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Insulation Material Varieties: Explores different insulation materials like XLPE, PVC, EPR, and their roles in high voltage applications, flexibility, and thermal stability.
- Eco-friendly Material Trends: Addresses the shift towards sustainable materials like polypropylene in the cable industry, balancing environmental considerations with performance requirements.
- Electrical Properties in Cables: Analyses essential properties such as conductance, resistance, capacitance, and inductance, crucial for cable efficiency and performance.
- Impedance in AC Power Systems: Highlights the importance of impedance, combining resistance, inductance, and capacitance, and its effect on signal quality and power loss.
- Current Carrying Capacity Methods: Compares IEC 60287 and Neher-McGrath methods for calculating ampacity, focusing on thermal equilibrium and thermal resistivity.
- Influences on Cable Sizing: Discusses how insulation, installation conditions, and surrounding medium impact cable sizing and thermal resistivity.
- Standards for Cable Sizing: Underlines the importance of adhering to standards like IEC 60287 and IEC 60502 for accurate and safe cable sizing, integrating these standards into EasyCableSizing.com for user-friendly access.
ib vogt – company

ib vogt is firmly committed to supporting the decarbonisation of the global electricity sector. The company focuses on the global development of turnkey PV plants and battery storage projects as well as the expansion of its IPP portfolio. In these areas, the company performs all integral services of the value chain from development, financing, and EPC, to O&M and asset management.
Headquartered in Berlin, Germany, ib vogt has established various offices across Europe, Asia Pacific, the Americas, and Africa as part of its presence in over 30 countries. The company works together with numerous partners globally, augmenting its in-house team of over 700 staff. ib vogt has built or has in construction more than 3.1 GW of PV power plants globally with a project pipeline of more than 45 GWp.

Thorne & Derrick distribute the most extensive range of MV HV Medium & High Voltage Cable Joints, Terminations & Connectors from manufacturers including 3M, Prysmian, Nexans Euromold, Elastimold, Pfisterer CONNEX & SEANEX.
Heat shrink, cold shrink, push-on and slip-over cable accessories enable the jointing, terminating and connection of 11kV-33kV and 66kV-132kV cables to oil, air or gas insulated switchgear, transformers, motors and overhead lines distributing electricity at MV HV.
T&D hold large stocks of 11kV 33kV 66kV Joints & Terminations suitable for XLPE, PILC and EPR cables, in both heat shrink and Cold Shrink technologies, to service the medium/high voltage power cable accessory requirements of UK and international customers.





