Blog
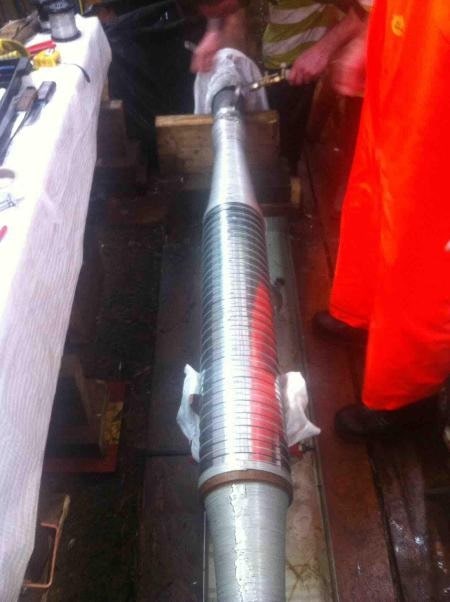
275kV Fluid Filled Straight Cable Joints
February 12th, 2020Image Courtesy of: David Young – HV / EHV Cable Jointer / Company Director at CRS (Cable Repair Services) Ltd
Pictured: 275kV Fluid Filled Straight Cable Joints


Jointers blog
Subscribe now to our POWER NEWSLETTER– a monthly email circulation packed with news, projects, videos, technical tips, training information, promotions, webinars, career opportunities and white papers.
Includes access to our popular JOINTERS BLOG with contributions from utility professionals, linesmen and cable jointers working on MV HV EHV cables and overhead lines typically at 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and up to 132kV.
Earthing Studies for Power Systems | Avoiding Step & Touch Potentials
February 12th, 2020
Earthing Studies for Power Systems | Avoiding Step & Touch Potentials
-
Guest Blog Courtesy of Covol - thanks to Paul Callaghan for allowing T&D to republish. -
Experts in Engineering Compliance for Industries in Electrical, Control and Instrumentation Services -
Visit Covol
EARTHING
What is earthing and why is it important?
Earthing of electrical systems has been around almost as long as the electrical system itself.
While there are still some specialised electrical systems out there that don’t need to be earthed as part of their design and operation, the vast majority of the ones we deal with do!
Quite simply, Earthing Systems exist to safeguard us against electrical shock. Electrical shock incidents can result in harm to a person with various degrees of consequence ranging from burns to death.
There are different codes of practice regarding earthing that depends on where you are in the world. Consequently, they all approach this subject in different ways through national regulations and standards. However, they all share the aim to achieve specific common objectives: the most important of which being safety to personnel.
When an electrical fault occurs, the short circuit energy must be dissipated as safely and as quickly as possible for the protection system to interrupt the current flow. Typically, the short-circuit current flows to earth rods and disappears into the Earth, causing a potential rise in hazardous conditions in and around the area of the earth rods.
What is Step and Touch Potential?
The difference in the surface potential experienced by a person bridging a distance with their feet apart without contacting any other grounded object is often referred to as Step Voltage Potential. You could be at risk of injury during a fault simply by standing near the grounding point.
The potential difference between the ground potential rise and the device surface potential at the point where a person is standing while in contact with the faulted structure is often referred to as Touch Voltage Potential.
How do we avoid Step and Touch potential?
There are a variety of causes that lead to high Step and Touch potentials. An excellent earthing design and its continued upkeep is essential to avoid electric shock events. A well designed earthing system considers all possible causes to provide an effective means of dissipating the fault current into the earth without exceeding the safety boundaries or adversely affecting continuity of service. It provides a safe environment to protect personnel in the vicinity of those grounded facilities from dangers of electric shock under the fault condition.
What does this mean to me?
You should understand what earthing arrangements are in place, which should be documented, reviewed and tested and above all, you need to be clear that any mitigation you have in place is sufficient. If you don’t, then seeking the advice and support from a professional electrical engineering company would be a great place to start.
Above all, always remember that the earthing of electrical systems serves an invaluable purpose to keep both people and equipment safe.
3 key techniques to mitigate Step and Touch potential hazards:
- Carry out a detailed review of ground surface materials
- Conduct an analysis for soil resistivity
- Consider a review of additional ground conductors
What Earthing Studies services can Covol provide?
At Covol, we undertake studies to determine the overall effectiveness of the various earthing systems in order to satisfy the requirements of the HSE.
These cover the following areas:
Site Assessment
- Assess whether touch and step potential calculations are necessary and if so, ensure they are within tolerable limits as defined in BS EN 50522.
- Schematic drawings showing the earth connection arrangement for transformers. As each installation may be slightly different, a separate drawing is allowed for each transformer.
- Consideration of HV earthing for transformers.
Power Earthing
- Ensuring the reliable operation of protective relays and to ensure that no excessive touch and step potentials occur.
Static Earthing and Equipotential Bonding
- It is important to ensure that steel work is effectively bonded together to avoid the generation of a sparking hazard, which could ignite a flammable gas or vapour.
- Ensuring that all metalwork and noncurrent-carrying metalwork is securely bonded together so that in the event of a fault, it would prevent exposed items of metalwork that are not designed to carry an electric current from being made live.
Lightning Protection
- Ensuring that a lightning discharge will be diverted safely to earth without causing danger to personnel or any structural damage.
For the original blog article click here.
THORNE & DERRICK
Thorne & Derrick are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing businesses involved in cabling, jointing, substation, earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV. Supplying a complete range of power cable accessories to support the installation and maintenance of low/medium and high voltage power systems:
- Slip-on Cable Terminations
- Cold-shrink Cable Terminations
- Heat-shrink Cable Terminations
- Cable Joints – Heat & Cold-shrink
- Separable Connectors (Euromold)
- Surge Arresters & Switchgear/Transformer Bushings
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV

Latest Arc Flash Legislation & Regulation Explained By ProGarm
February 11th, 2020
ProGarm
Arc Flash Legislation & Regulation
-
by Mark Lant | Protecting Lives Through Innovative ARC Flash & Flame Resistant Clothing Solutions
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is acknowledged to be the last line of defence for workers, meaning that understanding the different standards governing PPE is of vital importance. Yet a study by ProGARM, arc flash protective clothing specialists, uncovered that 78% of industry workers were unfamiliar with the relevant legislation for protection of personnel against the hazards of arc flash incidents.
With so many different industries at risk of arc flash – a relatively misunderstood, but extremely common type of electrical explosion facing sectors from industrial electrical, to utilities, civil engineering and rail – Mark Lant, Technical Expert at ProGARM, explains the relevant legislation and guidelines to ensure managers and workers alike are up to date on the latest standard updates, and to ensure protection against the potentially fatal consequences of an arc flash.

Hazardex | this article was originally published in the February print edition of HazardEx magazine the UK’s leading publication for safety, health and hazardous area professionals. Register and sign-up here

Arc Flash Protection
IEC 61482-2
The first standard is IEC 61482. This is the overall standard covering protective clothing that protects against the thermal arc hazards of an electric arc, and covers many aspects of garment design and testing.
The thermal energy generated by an arc flash can reach temperatures of up to 19,000°C – up to four times hotter than the surface of the sun – and is the key element that distinguishes a ‘normal’ electrical blast from an arc flash blast.
To determine whether garments meet the requirements for this standard, all prospective PPE must pass one of two test methods: Open Arc or Box Arc.
These tests will measure the ATPV or the new ELIM ratings of a garment.
ATPV values are calculated from a prediction of the incident energy level of an arc flash, at which there’s a 50% probability that the heat transfer will cause the
PPE material to break open and expose the operative. However, the new ELIM ratings are measured to ensure a 0% probability.
It’s crucial to note that under the new ELIM testing, a product’s ELIM rating could be different from its ATPV rating, despite it being the same garment.
BS EN 1149-5
BS EN 1149-5 is the European Standard for garments that protect against electrostatic discharge in areas where there is a risk of explosion, and is most applicable to petrochemical and fuel distribution businesses. It states that workers must be provided with appropriate clothing consisting of materials which do not give rise to electrical discharges that can ignite explosive atmospheres. In other words – the outer fabric of the garments worn must be made from antistatic materials and cover all noncomplying materials.
The standard also states that non-dissipative materials (labels, reflective stripes etc.) must not exceed 50mm in length, unless they also pass the anti-static test.
RIS – 3279 – TOM
RIS-3279-TOM (formerly GO-RT 3279) is a high visibility standard that only applies to the rail industry in the UK, as opposed to the EU-Wide nature of other EN standards. The aim is to ensure that rail workers on or near the trackside are sufficiently visible to trains approaching at speed or any other traffic.
BS EN ISO 20471
Another standard concerning visibility is BS EN ISO 20471 specifying the requirements for clothing noticeability during the day and at night. It deals with things like illumination in car headlights and classifies garments based on the number of square meters of fluorescent fabric/reflective tape incorporated into the clothing. The BS EN ISO 20471 standard has replaced EN 471 which has now been withdrawn.
BS EN ISO 14116
BS EN ISO 14116 is the standard which has replaced the withdrawn EN533. It covers outerwear that would usually be worn over other protective garments. The objective is to ensure that, once in contact with the material, the amount the flame spreads and the time it burns are limited. This is tested using different codes; Index 1, 2 & 3, with each getting more rigorous as the numbers increase.
BS EN ISO 11612
The BS EN ISO 11612 standard replaces the now-withdrawn EN531 standard and applies to clothing intended for a wide range of application which offer limited flame spread and provide protection against various hazards including radiant heat, convective heat and splatters of molten metal. The standard requires that the material of a garment shall not ignite or melt and shall not shrink by more than 5% with mechanical strength and heat resistance at a temperature of 180°C.
There are several fabric tests within this EN standard, and the results of the tests are represented by the pre-fix letters A, B, C, D, E and F. The number after these letters indicate the performance of the fabric within this test. If a (0) is shown, then the fabric has not been tested or does not achieve the lowest value attainable with the test.
BS EN 13034
Protection against liquid chemicals falls under the bracket of BS EN 13034 which is in place to determine the garment’s resistance against small splatters or fumes of chemicals. This is achieved by chemical coating the garments in order to repel any contaminants and preserve the properties within the clothing. Testing for this standard consists of a ‘mannequin test’, in which the wearer must perform 7 basic movements and the permeability of the clothing to chemical is subsequently determined.
BS EN 14404
BS EN 14404 relates to trousers and coveralls which offer kneepad pockets to protect the wearer when kneeling. Knee pads are tested based on three properties – penetration resistance, force distribution and shock absorption. Two levels of protection can be provided according to BS EN 14404. Level 1 requires kneepads to provide protection against objects more than 1cm high. Level 2 requires pads to be able to withstand use under heavy conditions such as kneeling on stones in mines and quarries.
BS EN 343
Finally, BS EN 343 outlines the requirements garments must adhere to, with regards to protection against rain, snow, mist and ground moisture. BS EN 343’s icon shows an umbrella placed under two numbers that represent the X and Y values. The X value indicates the waterproofness and the Y value indicates the water vapour permeability. There are 3 classes for both X and Y values, with 3 being the highest and 1 the lowest.
This particular standard falls under the bracket of ‘self-certification’ meaning manufacturers are allowed to certify their own products. This is because the only risk to the wearer is getting slightly wet and is not life threatening.

Mark Lant has been a Sales Manager at ProGARM for almost seven years and was previously involved in the sales team for ASKAS, a workwear safety brand based in Hull. Due to his large range of experience in the sales world of protection wear, Mark is perfectly placed to educate on how to protect lives through Arc Flash and flame-resistant clothing.
Thorne and Derrick are proud to be distributors of ProGARM arc flash clothing and protection.
We can help – should you require arc flash calculators or advice on the type of clothing and protection available please do not hesitate to contact us.
Further Reading
- Electrical Safety – Arc Flash Accidents & Electrocution In LV-HV Installations
- Arc Flash Calculation – Selecting Clothing & PPE To Protect Lives Against Arc Hazard
- Arc Flash PPE | 7 Top Considerations

Arc Flash Clothing | Polo Shirts | Jackets | Coveralls | Trousers | Sweatshirts | Helmets
Arc Flash Learning & Resources

Thorne and Derrick are proud to be distributors of ProGARM arc flash coveralls and protection.
We can help – should you require arc flash calculators or advice on the type of clothing and protection available please do not hesitate to contact us.
THORNE & DERRICK
Thorne & Derrick are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing businesses involved in cabling, jointing, substation, earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV. Supplying a complete range of power cable accessories to support the installation and maintenance of low/medium and high voltage power systems:
- Slip-on Cable Terminations
- Cold-shrink Cable Terminations
- Heat-shrink Cable Terminations
- Cable Joints – Heat & Cold-shrink
- Separable Connectors (Euromold)
- Surge Arresters & Switchgear/Transformer Bushings
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV

Nexans Euromold Connectors – Webisodes
February 6th, 2020
EUROMOLD CONNECTORS
uploaded by Chris Dodds | Sales & Marketing Manager at Thorne & Derrick
Thorne & Derrick International, based in the UK, are the Specialist Distributor for the Nexans Power Cable Accessory range of Screened Separable Connectors (Euromold), Cold-Applied (AIN AFN) & Heat Shrink Joints (JTS) & Cable Terminations (MONO) for Medium Voltage Power Systems up to 33kV; we hold extensive stocks and provide the most competitive commercial and technical levels of customer service in the UK.
Nexans have created a 4 Part Video series focusing on frequently asked questions regarding their Euromold range of separable connectors for the termination of polymeric cables into gas-insulated-switchgear.
Nexans Euromold products include MV-HV Connectors, Joints & Terminations to connect, splice, repair and maintain medium/high voltage cable and power distribution systems – commonly referred to as cable plugs, Tee’s or elbows the Euromold range of connectors suit all European DIN EN 50180 and American (ANSI) specification bushings.
Thorne & Derrick have created a 4 Part Blog Series to compliment the videos which can be found below.
Disclaimer : Product should be installed only by competent personnel trained in good safety practices involving high voltage electrical equipment. This video is not intended as a substitute for the installation instruction given with each kit and adequate training or experience in such safety practices.
Cable Innovation Tools & Accessories for Low & High Voltage Power Systems
Thorne & Derrick
Nexans Main UK Stockist & Distributor
Contact us for Competitive Prices & Fast Delivery from Stocks for Heat Shrink, Cold Shrink & EPDM Rubber Connectors, Joints & Terminations up to 66kV.
Thorne & Derrick International are specialist distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Accessories, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, jointing, substation, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV.
Stocking & Supplying | Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling Eqpt | Earthing & Lightning Protection | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV up to 66kV Ex Stock

Euromold MV HV | Cable Terminations, Connectors, Elbows & Joints

Installation & Clamping Of Nexans Euromold Compact Connectors Onto Mating Bushings – Part 4
February 3rd, 2020
Euromold Compact Connectors
Installation & Clamping Onto Their Mating Bushings MV HV
In this Webisode Nexans will show you how to correctly install the Euromold Compact Connectors onto their mating bushings of MV HV electrical equipment including switchgear and transformers providing power distribution at 11kV/33kV.
It is important to install the separable connector on its mating bushing in the correct way.
After cleaning and lightly lubricating both the connector and the bushing interface, you can push the connector onto the bushing.
You can now insert the clamping screw into the threaded hole of the bushing. It is important to do this hand first, to correctly engage the threads and avoid cross-threading.
Then a torque wrench should be used to tighten the clamping screw. The tightening torque that needs to be applied is specified in the installation instructions that come with the kit.
What About the Nexans Stud-nut Version?
With the stud-nut you first need to install the stud into the threaded hole of the bushing interface before doing anything else. The installation instructions indicate which tools can be used and which torque needs to be applied. What to do next?

How do Nexans continue with the installation?
- Clean & lightly lubricate both the connector and the bushing interface, before pushing the connector onto the bushing
- DO NOT lubricate the threaded stud or any other threaded parts. The next step is to install the nut onto the threaded stud
- Screw it onto the screw by hand just like the installation of the clamping screw. Use a torque wrench to tighten the nut
- The tightening torque that needs to be applied is specified in the installation instructions that come with the kit
- Complete the instructions of the connector by installing the basic insulating plug and cap by following the steps in the installation instructions
Please Note: Only the components included in the kit should be used.

Nexans Euromold Separable Connectors | 33kV MV HV Elbows Tees Plugs
Further Reading
- Water Sealing, IP Rating & Temperature Range Of Nexans Euromold Connectors
- Different Insulating Epoxy Plugs & How To Install The Cap On Nexans Euromold Interface C Compact Connectors
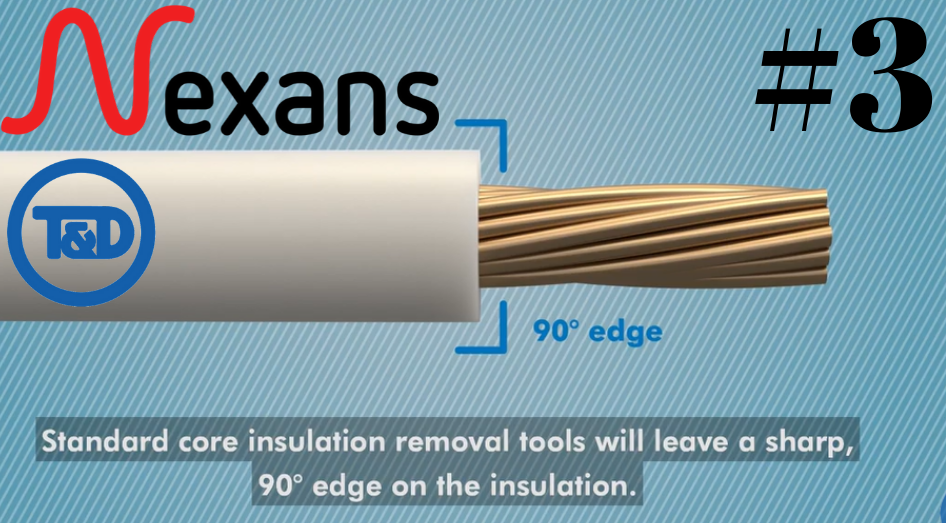
- Bevelling The Edge Of The Core Insulation During Installation Of Nexans Euromold Connectors
Thorne & Derrick
Nexans Main UK Stockist & Distributor
Contact us for Competitive Prices & Fast Delivery from Stocks for Heat Shrink, Cold Shrink & EPDM Rubber Connectors, Joints & Terminations up to 66kV.
Thorne & Derrick International are specialist distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Accessories, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, jointing, substation, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV.
Stocking & Supplying | Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling Eqpt | Earthing & Lightning Protection | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV

Euromold MV HV | Cable Terminations, Connectors, Elbows & Joints

Thorne & Derrick distribute the most extensive range of MV HV Medium & High Voltage Cable Joints, Terminations & Connectors from manufacturers including 3M, Prysmian, Nexans Euromold, Elastimold, Pfisterer CONNEX & SEANEX.
Heat shrink, cold shrink, push-on and slip-over cable accessories enable the jointing, terminating and connection of 11kV-33kV and 66kV-132kV cables to oil, air or gas insulated switchgear, transformers, motors and overhead lines distributing electricity at medium/high voltages.
Thorne & Derrick hold large stocks of 11kV 33kV 66kV Joints & Terminations suitable for XLPE, PILC and EPR cables, in both heat shrink and Cold Shrink technologies, to service the medium/high voltage power cable accessory requirements of UK and international customers.