Cable Joints & Terminations HV
Partial Discharge On Outdoor Terminations | Case Study
December 8th, 2021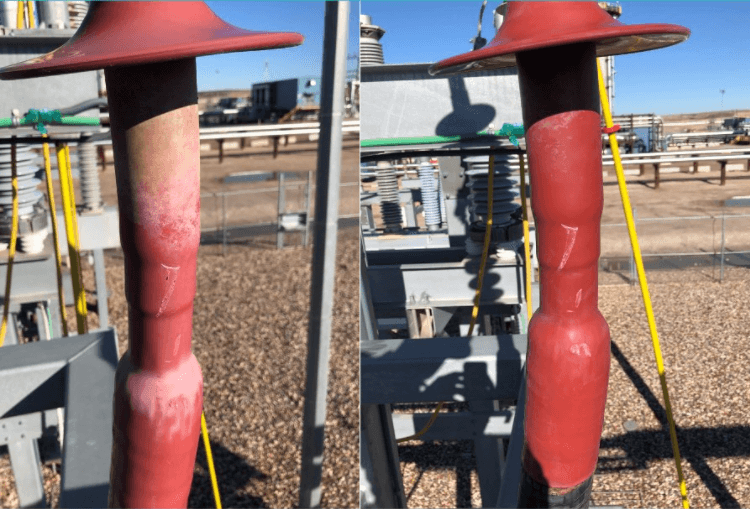
Cable termination H3 | Uneven contamination before and shown after cleaning
Partial Discharge
-
Special Thanks To William Higinbotham President at EA Technology for allowing T&D to republish
Below is a great example of using partial discharge instruments to prevent failures without doing unneeded maintenance.
Contamination of cable terminations
causes partial discharge
Cable terminations are often used outside on riser poles or substation structures to convert cables to overhead lines or busses. These terminations convert the very tightly controlled cable electric field into an uncontrolled air insulated application.
When applied properly, the field strengths are less than the insulation strength and therefore no partial discharge exists.
Under certain circumstances, even a well applied termination can have partial discharge as a result of contamination. Humid salt air leaves conductive deposits that often result in partial discharge. Because of this, terminations in coastal areas are highly prone to PD. Other types of contamination can result from pollution, or even dusty air. When an insulator gets unevenly coated in hydrophilic contamination, you can get what is called dry band discharge.
The uncontaminated sections of insulator tend to be hydrophobic, so the insulator has dry and wet areas that are insulating and conductive. This disturbs the field distribution and leads to discharge across the dry bands.
Given time this will erode the insulator and lead to flashover.
The challenge
A high voltage asset owner in central Canada has numerous terminations on substation structures. Clearly salt contamination is not the issue. However other contamination is building up unevenly on their cable terminations.
This operator is very proactive and does periodic PD surveys of both indoor and outdoor assets as part of their regular preventative maintenance. They use the EA Technology UltraTEV Plus2 with the UltraDish attachment for scanning terminations from the ground.

Cable termination H3 with uneven contamination
The test results
Two of the terminations (H1 and H3) scanned returned very high levels of ultrasonic energy. The phase resolved plots show typical PD results. The source is frequency locked to the power system and the impulses are occurring twice a cycle, half a cycle apart. The levels are approaching 40dBuV which is very high. The ANSI/NETA MTS 2019 standard calls for immediate action on levels greater than 6 dBuV.
Action taken
During the next scheduled outage, the insulators were cleaned and then rescanned. The ultrasonic energy was gone, proving that the discharge was a result of the contamination.

Cable termination H3 after cleaning
The benefits
The immediate benefit is that these terminations are now less likely to fail. Long term the asset owner has learned how the PD survey process can be used to control cleaning cycles. Some terminations may need less frequent cleaning some may need more.
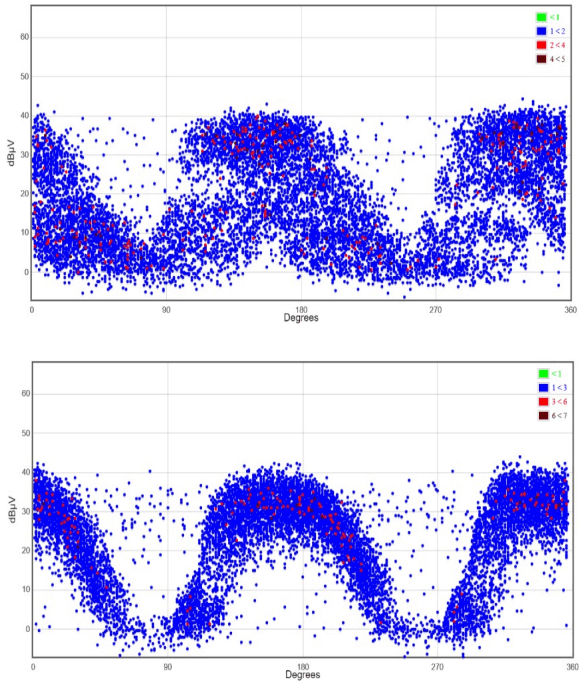
Ultrasonic PD results prior to cleaning
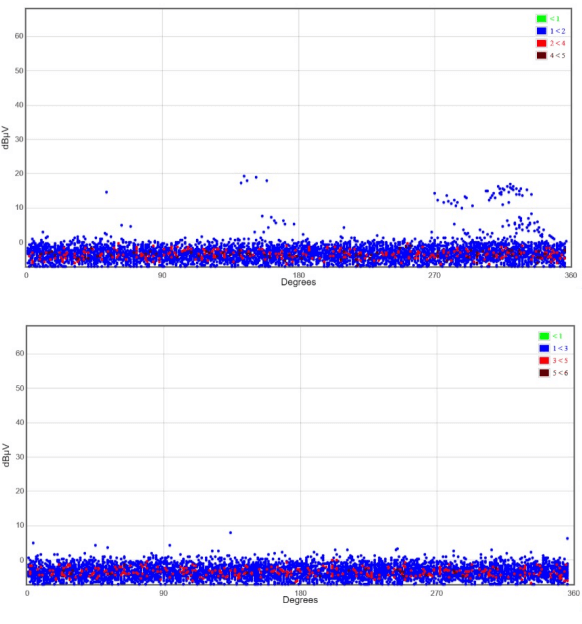
Ultrasonic PD results after cleaning
EA Technology
William G. Higinbotham has been President of EA Technology LLC since 2013. His responsibilities involve general management of the company, including EA Technology activities in North and South America. William is also responsible for sales, service, support, and training on partial discharge instruments and condition-based asset management. He is the author or co-author of several industry papers.

Thorne & Derrick
Thorne & Derrick International are specialist distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Duct Sealing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, cable jointing, substation, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV.
THORNE & DERRICK Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV
- Scope –single-source supply of extensive range of products
- Stock – a multi-million pound stock holding provides complete global supply solutions
- Staff – technical support from a trained, proactive and friendly team
- Delivery – UK stock turnaround with express logistics to all international destinations

Offshore Wind & Subsea Power Cables | Market Trends by ORE Catapult
December 1st, 2021
The following article, exploring offshore wind subsea power cables, has been republished with the kind permission from the authors: Othmane El Mountassir & Charlotte Strang-Moran from ORE Catapult | Published September 2018 | AP-0018
Installation, Operation & Trends
By the end of 2018, installed offshore wind power capacity will reach a total of 30.2GW, with 22.9GW of generation in Europe and 7.3GW across the rest of the world. The UK remains the global leader in offshore wind, with a total capacity of 6,385MW and an additional capacity of 3.2GW entering operation by 2020. As the industry’s generation capacity continues to grow, so does the need for developing reliable, high-capacity transmission cable technologies.
Subsea power cable failure is frequently reported as an issue for offshore wind farm operators. Such failures are reported to account for 75-80% of the total cost of offshore wind insurance claims – in comparison, cabling makes up only around 9% of the overall cost of an offshore wind farm. A lack of available data on cable failures led ORE Catapult to develop an interactive tool for internal use, which captures information about UK offshore wind projects and their power cables’ lifecycle from the installation to the operational phase.
This paper summarises some of the most pertinent insights on cable failures gleaned from the Catapult’s use of the tool and sets forth suggestions on how to improve knowledge-sharing in the offshore wind community to reduce the impact of future failures.
Headlines
- The UK’s operational offshore wind farms are using 62 export cables totalling a length of 1,499km and over 1,806km of inter-array cables to transport the 6,385MW of electrical generation.
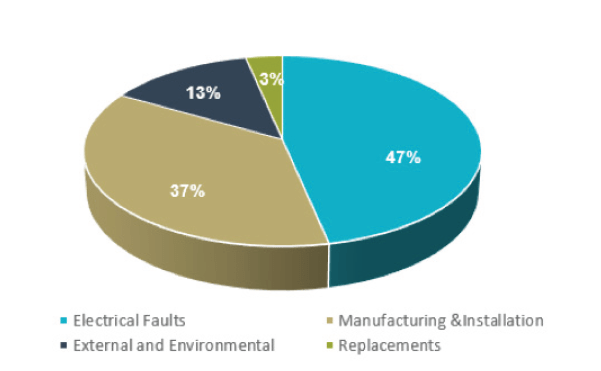
- A total of 43 array and export cable failures have been reported since 2007. Issues associated with manufacturing and/or installation are reported to be the most common cause of cable failure.
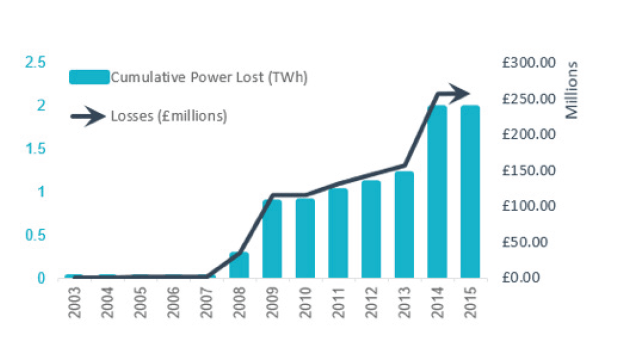
- From 2014 to the end of 2017, recorded cable failures at UK offshore wind projects have led to a cumulative loss of power generation of approximately 1.97TWh.
UK Offshore Wind Trends
The UK generates more electricity from offshore wind than any other country in the world. Operational offshore wind farms are currently generating 6,738MW using 1717 turbines.
In 2017, the UK installed 1681MW, representing more than half of the new offshore wind power capacity built in Europe. It is forecasted that by 2020, there will be a record-breaking year for new capacity – largely driven by delayed wind farms and the deployment of large-capacity turbines in the 7MW 8MW range. The following figures provide an insight into current UK offshore wind sector trends.
Wind Development: By the end of 2018, installed offshore wind power capacity will reach a total of 30.2GW worldwide, with 22.9GW of generation in Europe and 7.3 GW in rest of the world. The UK remains the European country with the largest installed capacity, reaching a total capacity of 7,851 MW by the end of 2018.
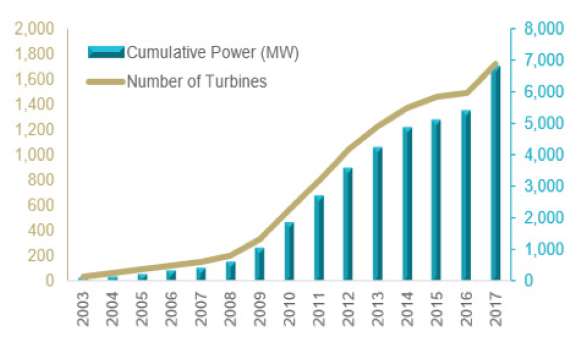
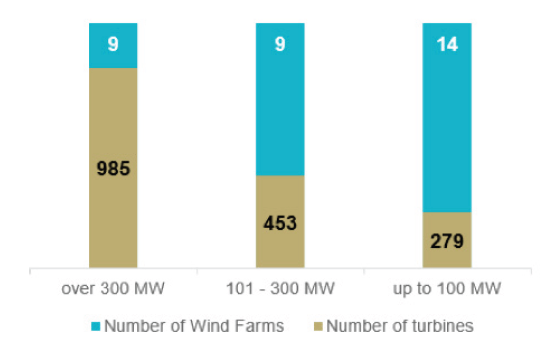
Farm Capacity: By categorising wind farms into three ranges of generation capacity, it can be seen that the larger the capacity range of the wind farms, the higher the number of wind turbines being used. It is expected that this trend will change with the deployment of higher-capacity turbines, reducing the number required.
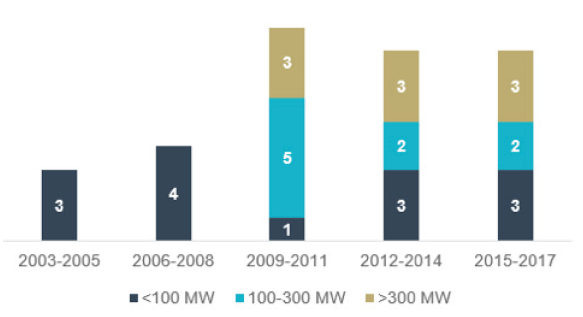
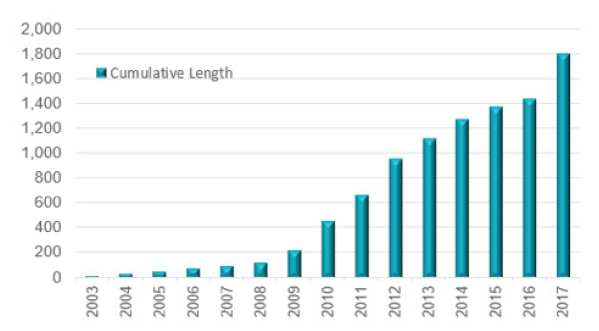
Progressive Trends: Since the development of the first demonstrator projects in 2003, the UK’s offshore wind sector has witnessed strong growth, supported by government incentives and investor confidence in the sector. This can be demonstrated in the figure above, where we can see over the years an increase in the number of offshore wind farms and demonstrators with different generation capacities.
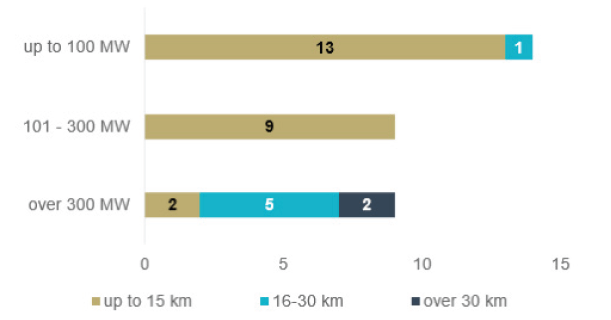
Distance from Shore: The UK’s geographic location makes it ideal for offshore wind generation. Early developments from the Round 1 and Round 2 leasing phases were relatively small and close to shore. In contrast, recent projects and future developments have seen and will see this distance increase to the 50-90km range from shore to take advantage of the wind strength in these areas.
Subsea Cable Trends
The rapid growth of the offshore wind sector has led to the development of a number of new subsea cable technologies. This was mainly supported by a robust cable-related supply chain with leading organisations in manufacturing, services and academia present across the UK. The demand for subsea power cables will continue to grow at a fast pace to support both future offshore wind development and the subsea power interconnector sector.
Export Cables are vital for transmission of the generated power to the grid. The UK’s operational offshore wind farms are using 62 export cables totalling a length of 1,499km. The voltage levels of these cables range from 33kV for nearshore wind farms without offshore substations, and up to 132kV, 150kV and 220kV for further-offshore sites with one or two substations.
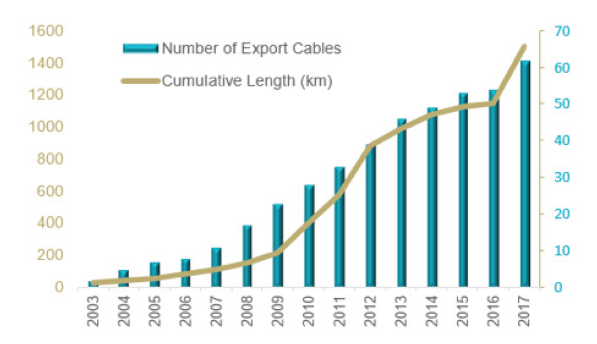
Export Cable Trends: Research and development activity has led to the development of new cable technologies. Since 2013, over 80% of projects in Europe have deployed export cables with a voltage greater than 150kV. Reflecting the rapid development of cable technologies, 80% of projects commissioned in 2018 will be using cables with a voltage level greater than 200kV.
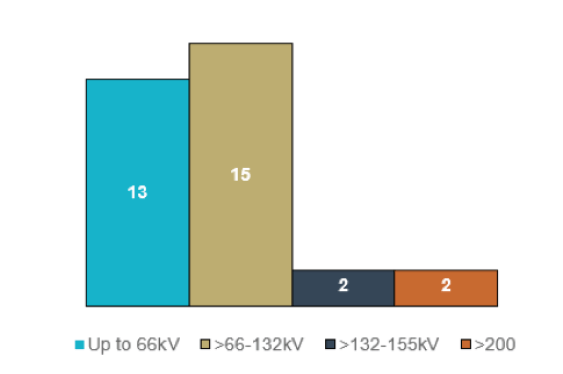
Array Cable Development: There are over 1,806km of inter-array cables in UK waters. To maximise generation revenue and achieve Levelised Cost of Energy reductions, offshore wind projects will continue to increase in size.
As such, the lengths of array cabling used is expected to increase due to the increased number of turbines and the distance between them.
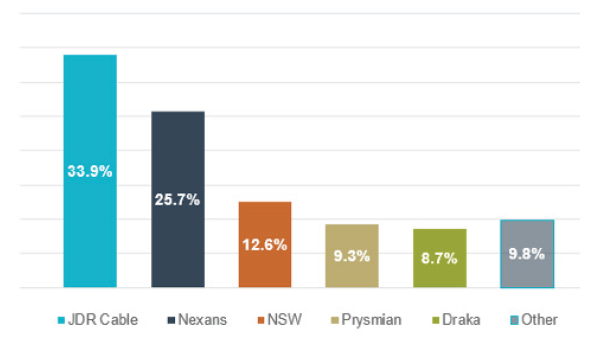
Array Cable Manufacturers: The cable market is generally global in nature and there are a number of suppliers available. A notable UK success has been achieved with JDR cables, which has supplied numerous UK offshore wind projects, as well as several overseas projects. The expansion of the market and growth of an indigenous UK supply chain is expected to help reduce costs.
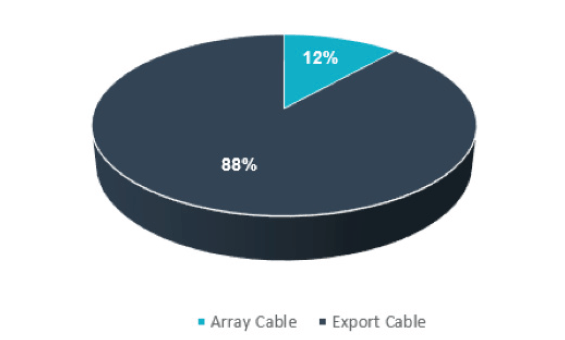
Cable Failure Trends
According to industry data obtained by the Catapult, cables account for the largest number of insurance claims in the offshore wind sector. Though subsea cable failures are reported often, publicly-available information remains scarce. The following figures, gleaned from the Catapult’s internal cable database, provide an insight into reported subsea power cable failures in the UK’s offshore wind sector.
Cable Failure: Incidents relating to the installation and operation of subsea power cables are found to be the most costly cause of financial losses in offshore wind industry. Since 2007, 43 known failures of wind farm array and export cables were reported. The issues associated with these failures vary in nature.
Causes of Failure: Issues associated with the manufacturing and/or installation phase are reported to be the most common cause of cable failure. The failure events reported include cases where unplanned faults have occurred, or when planned, pre-emptive repairs have been required to avoid the likelihood of fault.
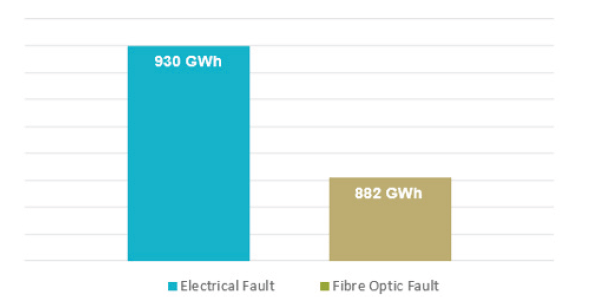
Fibre Optic and Electrical Faults: In the UK’s offshore wind sector, recorded faults of electrical origin were found to be higher than fibre optics failures. To date, power losses due to fibre optics failure reached an estimated value of 600GWh, while losses due to electrical faults were estimated at 1,160GWh. It should be noted that electrical failures may sometimes lead to the failure of fibre optics.
Costs of Failure: The cost of a cable failure can be considerable, taking into account repair costs and generation revenue loss. From 2014 until the end of 2017, recorded cable failures at UK projects have led to a cumulative generation loss of approx. 1.97TWh, equating to approx. £227M*. This figure demonstrates beyond doubt that the sector is still in need of innovative cable installation and repair technologies. *Based on a strike price of £115/MWh.
Discussion and Next Steps
The UK has a robust subsea cable-related supply chain, encompassing manufacturing, service providers and academia. However, there is still a lack of communication between stakeholder groups. For example, the standardisation of cable installation practices may lead to fewer installation issues, while the dissemination of learned experiences can be used to predict or avoid certain failures and also bridge innovation gaps in manufacturing. However, this is only possible if the parties involved are willing to share the required records. There is a consensus from market stakeholders that subsea cable project activities are currently dispersed, and a more structured and co-ordinated process is required to pull promising technology and ideas through development and demonstration. However, proposed concepts aimed at developing a subsea cable database, which informs and enables stakeholders to identify and bridge gaps in innovation – has been met with scepticism from a number of systems owners and operators; questions remain over whether a live, regularly-updated database would be providing ongoing value and longevity.
To ensure the successful development and implementation of appropriate technologies and processes aimed at reducing cable failures within the offshore wind industry, ORE Catapult is acting as a driver for a number of initiatives such as the Offshore Wind Innovation Hub, subsea cable innovation challenges, and technology demonstration opportunities for SMEs at its Levenmouth Demonstration Turbine. The Catapult also anticipates launching a publicly-available web-based platform dedicated to subsea power cables. To help solve some of the challenges around offshore wind subsea cable applications, ORE Catapult has developed a dedicated internal database and an Offshore Wind Innovation Hub strategic programme dedicated to subsea power cables and future systems. The aim of the internal cable database platform is to provide quantitative information and evidence to support building a consensus to solve common cable issues, while the Offshore Wind Innovation Hub was established to co-ordinate the sector’s innovation needs and provide a comprehensive view of the research funding opportunities available.
It is beyond question that the offshore wind sector will continue to expand further over the coming decades. Future wind farms will make use of higher-capacity turbines and will be located further offshore: with that comes the requirement for robust cable technologies and safe installation and operational practices. The sector must learn from the wider industry and share information and lessons learned so that costs can continue to fall, helping the wider offshore wind supply chain continue its trajectory of growth.
Further Reading
Lead-Free Cables | The Future for Offshore Wind Farms
Providing Electrical Safety & PPE to Offshore Wind Farm Workers
Pipe & Cable Seals for Offshore Windfarm Substations, Enclosures & Foundation

LV, MV & HV JOINTING, EARTHING, SUBSTATION & ELECTRICAL EQPT
Thorne & Derrick are Specialist Distributors to the UK and international Offshore Wind & Renewable industry to provide safe and reliable LV HV Electrical Cable & Power Distribution Systems up to 66kV – we are highly customer responsive and absolutely committed to providing a world-class service.
Contact our UK Power Team for competitive quotations, fast delivery from stock and technical support or training on all LV-HV products.
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV

See how T&D support, supply and service the Renewable Energy industry.

MV HV Cables 11kV 33kV 66kV | Cable Joints, Terminations & Connections
Cleaning Wipes & Solutions for Low & High Voltage Switchgear
November 3rd, 2021HYSO QD
HYSO QD from Socomore is the former PF-QD manufactured by PT Technologies Europe – HYSO QD is a quick drying residue free manual cleaning solvent for surface cleaning and degreasing in manufacture, maintenance and fabrication activities. HYSO QD removes general soils, oils, greases and combustion residues.
Features & Benefits of HYSO QD
- Low odour, fast evaporating cleaning solvent
- Suitable for use in poorly ventilated or confined spaces
- Leaves no residue after complete evaporation
- Non corrosive to metal such as copper, aluminium, magnesium and stainless steel
- Compatible with resins, plastics and elastomeric rubbers
- Available in liquid and pre-saturated on low lint wipes such as SOCOSAT 15233 – a cloth compliant to AMS 3819C qualification requirements
- Pre-saturated wipe system eliminates the hazardous storage, transport and logistical issues of loose flammable liquids
HYSO QD is a fast evaporating and odourless solvent for zero residue cleaning and degreasing of low and high voltage switchgear. A non corrosive electrical cleaning solvent on metal such as copper, aluminium, magnesium and stainless steel – suitable for use on metal and painted switchgear surfaces. Compatible with resins, plastics and elastomeric rubbers, the low surface tension provides excellent wetting action, even with difficult plastics.
HYSO QD is suitable for a variety of LV-HV switchgear cleaning applications, in general and specific niche industries such as aerospace and power.
* Switchgear cleaning and maintenance
* Surface cleaning and preparation
* Removing petroleum based oils
* General cleaning and degreasing in manufacture, fabrication and maintenance applications
HYSO QD has additional worker benefits along with its impressive compatibility and cleaning abilities : quick drying, non toxic, has a low skin irritation potential and as it is odourless, eliminates strong smells in the workplace – especially important for those working in confined spaces on low and high voltage switchgear and cabinets.
Switchgear Cleaning Guidance
1. Apply a thin film of cleaning solvent using the liquid or impregnated wipe.
2. Allow 1-2 minutes for surface action to dislodge switchgear contaminants.
3. Wipe off with the same wipe or with a clean, dry lint free cloth (recommended). Repeated use of the impregnated cleaning wipe without further solvent addition is possible until the cleaning wipe becomes saturated with contaminant.
See Also | PF Wipes Cable Cleaning Solvents & Products
Techlube | Market-leading Cable Pulling Lubricant

Cable Pulling & Cleaning Products
Thorne & Derrick International are the UK’s leading stockist and supplier of Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment for the installation of underground land and subsea power cables and overhead lines up to 400kV – the products support cable pulling teams to install LV MV HV cables into trench, cable duct, risers and all forms of cable containment.
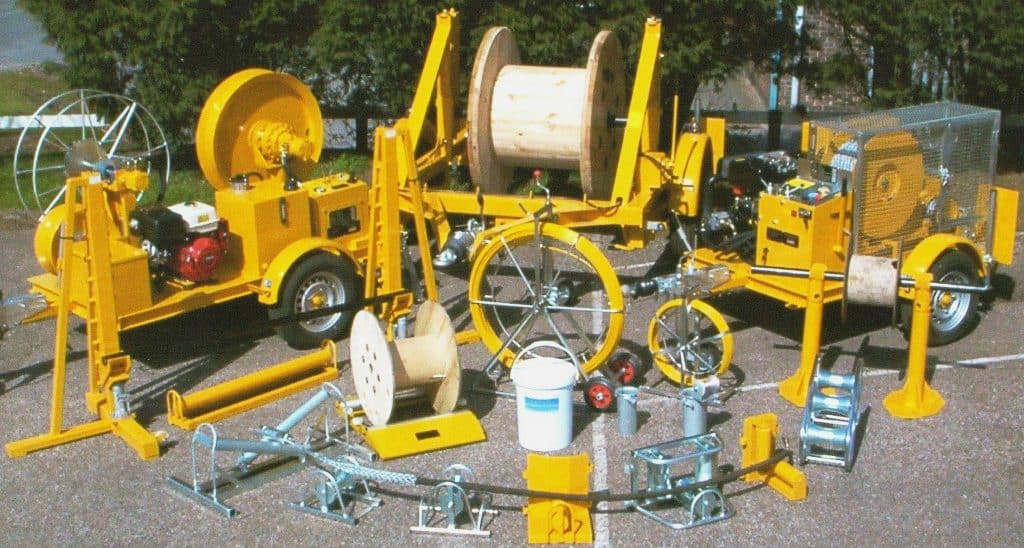

T&D distribute the complete range of LV-HV Cable Pulling and Laying Equipment including cable rollers, cable socks, cable jacks, cable drum trailers, cable lubricant, underground cable protection and conduit duct rod.

Heat Shrink Terminations | Tracking on Medium Voltage Cable Terminations
November 1st, 2021By Stephen Harrison | Training & Technical Manager Current Training Service Pty Ltd
Terminations for MV Power Cables
The image shows a shed (rain shed) – this is a heat shrink moulded part and component of standard medium voltage cable terminations. The installed rain shed is in operation on a 33kV indoor installation – tracking and discharging can be seen on the outside of the shed (rain shed) element of the cable termination and if left unchecked this will eventually cause the MV cable to fail in the field. At 33kV (Um 36kV) this cable termination was suffering a tough time whilst in service and it was eventually pulled out of operation after the discharge was identified. The discharge and tracking can be seen between the surface of the anti-tracking tube and the shed (rain shed) collar which is due to poor installation by the cable jointer. Sheds (rain sheds) must be shrunk down with collar connecting to the anti-tracking tubes evenly. If in doubt how and where the shed (rain shed) is to be installed, refer to manufacturer’s instructions.

Thorne & Derrick | Distributors of Medium Voltage Joints, Terminations & Connectors

3M Electrical | Nexans Euromold | Pfisterer CONNEX | Main UK Stockists
Flooding & Underground Cables: Myth or Reality?
September 6th, 2021
Protecting Underground Cables
This Article was originally published by T&D World.
From Superstorm Sandy to Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, Maria, Florence and Michael – the volume of rain and storm surge has and can cause unprecedented flooding.
Flooding negatively impacts power systems – but not for the reasons you might think. Power Delivery Intelligence Initiative (PDi²) is taking on the myth that flooding compromises underground cables.
Medium and high voltage cables are designed to be direct buried, often in areas where they will be below the water table and permanently in a wet environment. Under normal weather conditions, manholes and vaults are often full of water and need to be pumped out for even routine inspections.
Outer jackets for these cables, made of polymeric materials, resist moisture permeation to prevent water incursion into the cable over the life of the system.

Roxtec Cable Transits provide effective protection to LV HV substation cables against flood damage and water penetration be it in dry or wet conditions.
In the rare instances that water permeates a cable jacket, certain insulations, including tree-retardant crosslinked polyethylene, are designed to resist growth of water trees that could cause premature cable failure. In addition, cable also can be manufactured using moisture-blocked conductor, water-swellable tapes and powders and corrugated sheath to make them more moisture impervious.
Underground cables are expected to meet rigorous standards specifically addressing operation under adverse weather conditions like flooding. These standards take into consideration both moisture and chemical resistance as there can be significant differences between rain and flood water. ICEA, ANSI and AEIC require adherence to a variety of test procedures that address moisture barriers, water-blocking components, water-resistance tests and other sealing components and technologies.

CSD RISE Duct Seals – combining ease of installation with cable duct sealing and protection against water, gas and fire.
Cables are rarely at fault for failures related to flooding.
The biggest concern for flooded underground systems are the open-air terminations at ground level where external or internal contamination has occurred due to poor sealing. However, technology is improving here as well.
Certain elbow and T-bodies are typically submersible and have not shown any significant negative impact after flooding. Joints and other accessories like link boxes are used in manholes and vaults and can be designed and installed in such a way that they can operate submerged in water without compromising cable insulation integrity.
Areas known for periodic flooding can take additional measures for outer protection of cable joints like metal housings moulded with epoxy coatings or fibreglass boxes filled with water sealants.
These designs are typically electrically screened with electrical fields that are fully contained within the solid insulation of the cable.
Myth – flooding and underground cables
busted.
Cables are made to resist water under both normal and extreme operating conditions. As long as water does not extend to the exposed terminations, there is little risk of failure due to flooding.
Where terminations are at ground level, technology and products exist to mitigate the chance of failure. These solutions should be part of storm hardening efforts and decisions regarding choices for new and rehabilitated power infrastructure.

Joint | Terminate | Connect Medium & High Voltage Cables MV HV
Further Reading
- Sealing Underground Cables & Pipes Under Constant Water Pressure
- Submersible Switch Applications By G&W Electric
- 21st Century Costs of Underground Distribution
LV, MV & HV Jointing, Earthing, Substation & Electrical Eqpt
Thorne & Derrick International are specialist distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Duct Sealing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, cable jointing, substation, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV.
THORNE & DERRICK Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV



