Electrical Safety
The Ultimate Guide to Arc Flash Clothing: 7 Essential Considerations for Safety
December 18th, 2024
Why Choosing the Right Arc Flash protection Matters for Workplace Safety?
When working in both high– and low-voltage electricity environments, ProGARM makes sure workers are kept safe.
Where PPE is well understood to be important, Arc Flash incidents are often underestimated in the workplace. Reaching temperatures over 35,000°F—four times hotter than the surface of the sun—Arc Flash can cause serious burns in one-quarter of a second. Selecting the right Arc Flash Clothing is essential in order to safeguard workers and meet safety compliance standards.
Arc flash clothing and protection equipment including coveralls, gloves, helmets, face shields and general head-to-toe PPE (arc flash coveralls) are used to protect against flashover but will not prevent arc flash hazards.
Arc flash clothing and PPE such as arc flash suits should be worn when working on energised conductors, cables or circuits.
Layering is Crucial for Protection
Arc Flash PPE isn’t just about outer garments. The materials worn beneath the protective outer layers are equally critical in preventing burns and injuries. Everyday undergarments made of materials like nylon, cotton, or polypropylene can melt during an Arc Flash event, causing severe skin damage.
Pro Tip: Always wear Arc-rated base layers, including tops, leggings, and even underwear, to ensure maximum protection.
Flame Retardant vs Arc Flash Resistant
A common misconception is that flame-retardant (FR) clothing provides Arc Flash protection. However, FR clothing is tested against fire hazards, not the intense thermal energy of Arc Flashes.
Key Differences:
- Arc Flash-resistant clothing must meet higher tear resistance and tensile strength standards.
- Look for Arc-rated garments with long sleeves, no exposed metal, and designs for easy removal in emergencies.
Understanding the Fabric: Treated vs. Inherent
When selecting Arc Flash PPE, understanding the difference between treated and inherent fabrics is essential:
- Treated Fabrics: Treated chemically for fire resistance but may lose effectiveness after repeated washing or wear.
- Inherent Fabrics: Materials that are inherently flame-resistant; their properties remain consistent after repeated washing or wear.
Whereas treated fabrics may be more economical, inherent fabrics offer reliability and consistency over time.
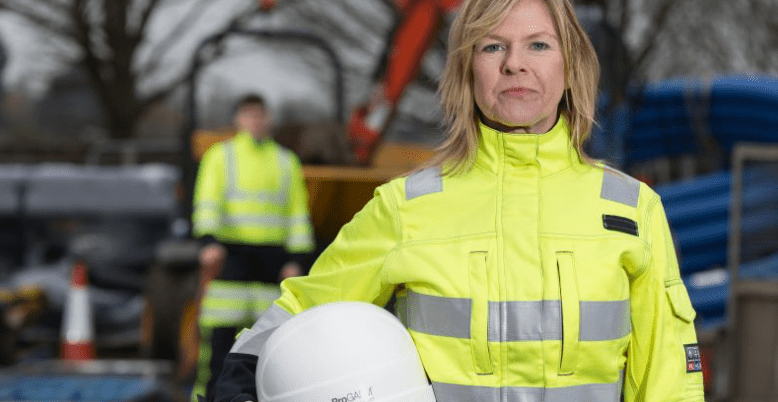

PPE Tailored arc flash Clothing
Poor-fitting PPE can compromise safety. Most women in the workforce are still being forced to wear unisex or men‘s garments, which can be too big and uncomfortable, leading to poor use–such as rolling up sleeves or unfastening jackets.
Solution: Specify PPE designed for women for a proper fit and optimal protection.
The New Standard for CAL Ratings
Recent developments in Arc Flash testing, including the ELIM method, better indicate the protection a garment can provide. Unlike the former system of ATPV that estimated the likelihood of burn, conservative measurements are taken with ELIM to ensure safety.
What to Check: Your PPE supplier should indicate whether the garments meet ATPV or ELIM requirements for your specific safety needs.
Don’t Overlook Fastenings
Not one single part of Arc Flash PPE is unimportant, including those fastenings such as zippers, buttons, and Velcro fasteners; all must be of flame-resistant material for complete protection.
Did You Know? ProGARM‘s ThermSAFE™ fastenings are manufactured using military-specification materials and offer unrivaled durability and safety.
Comfort is Non-Negotiable
Uncomfortable PPE often leads to improper use, reducing its effectiveness. Modern Arc Flash PPE made from breathable, lightweight, and moisture-wicking fabrics ensures workers remain safe and comfortable, even in challenging environments.
Features to Look For:
- Flexible fabrics for ease of movement.
- Moisture management to keep workers cool and dry.
- Durable designs for long-term wear.
IEC 61482 PROTECTIVE CLOTHING AGAINST THE THERMAL HAZARDS OF AN ELECTRIC ARC
Arc Flash-rated clothing and garments in layered ensemble provide workwear protection from hazards according to IEC 61482, as PPE protects a worker against electric arc flash dangers. According to IEC 61482-1-1:2009 (which includes NFPA 70E 2015), the 4 arc risk categories are numbered according to the severity threat and determine the clothing protection level required to protect against a minimum level of incident energy measured in calories / cm² – this is the ‘Open Arc‘ test method and measures clothing protection level according to the Arc Thermal Performance Value (ATPV).

NFPA 70E outlines the requirements for safe work practices to protect personnel by reducing exposure to workplace electrical hazards.
The ‘Box Arc’ tests clothing materials and fabric according to a pass/fail test by exposure to electric arc produced by 4kA (Class 1) and 7kA (Class 2) short circuits – this is IEC 61482-1-2:2009.

Electrical PPE Products | Gloves | Arc Flash Clothing | Arc Suits | Coveralls | Helmets & Visors

Safety Wear & Arc Flash Protection | Thorne & Derrick understand how critical it is to have reliable, highest quality personal protection equipment (PPE), clothing and workwear available from stock at competitive prices – protecting utility workers against arc flash dangers posed during maintenance on underground electric cables, overhead line conductors or electrical equipment.
Dropped Objects Prevention Work Mat: Enhancing Safety on Elevated Gratings
June 4th, 2024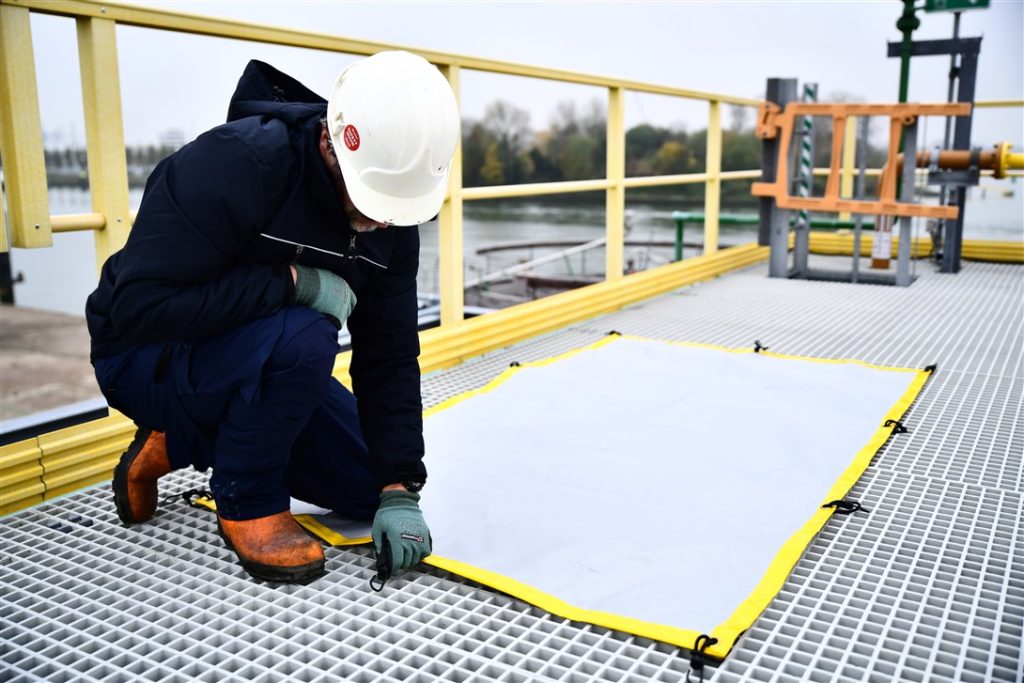
Dropped Objects Prevention Work Mat: Enhancing Safety on Elevated Gratings
Dropped Object Prevention Work Mat Enhancing Safety on Elevated Gratings
The CableSafe® Dropped Object Prevention Work Mat serves as a reliable resource for protecting tools and equipment from falling through the grating and is designed for use in wet and slippery conditions. It is also designed to protect your flooring or walkways from damage – matting is used for dropped object prevention across all industries and workplace applications.
One area where safety is important is when working at a height, especially on elevated gratings, catwalks, and platforms. The risk of dropped tools or equipment poses a significant hazard, potentially damaging equipment or causing fatalities.
Safety at work is of utmost importance when working on elevated platforms, especially if there are personnel or contractors working underneath. Dropped objects are still, unfortunately, a common contributor to severe accidents in industrial facilities across different sectors globally.
Thorne & Derrick supply the complete range of Safety Tools & Equipment to enable safe working in sectors such as the construction, renewables, data centres, rail, manufacturing and oil, gas, petrochemical industries.
dROPPED oBJECTS PREVENTION MATS
wHAT ARE THEY?
The CableSafe Dropped Objects Prevention Work Mats are designed to allow personnel to work confidently on grating surfaces, as they serve as a dual purpose for the following:
- Protection : This mat prevents tools and equipment from falling through grate openings and holes
- Safety: Personnel can easily work efficiently without worrying about dropped objects, especially during maintenance, turnarounds, inspections, and daily operations
Flame RetardAnt / Fire retardant
CableSafe Dropped Object Prevention Work Mats are available with flame retardant and fire resistant coated polyester fabric. This fabric is crafted with coated polyester mesh fabric, and it has a tear strength of 330N (DIN 53363). This range of flame retardant mats is available with spanners and is available with a flame-resistant material that is made of fibreglass double coated polyurethane and can withstand temperatures of up to 550°C.
The CableSafe Dropped Objects Prevention Work Mat is available with a flame-resistant material that is made of fibreglass double coated polyurethane. It can withstand temperatures of up to 550 °C.
The fire resistant mats are available with spanners or with magnets.
Work mAts
hOW TO CONNECT THEM:
- Prevention Work Mats can be secured with 14 strong magnets, which attach to the grating. The magnets in the hem are rated at 84N each, making them one of the strongest in the market to ensure that the mats are secured properly.
The CableSafe Dropped Objects Prevention Work Mat is a high-quality, reusable, and cost-effective safety tool that significantly reduces the risk of dropped objects and is fast and easy to install.
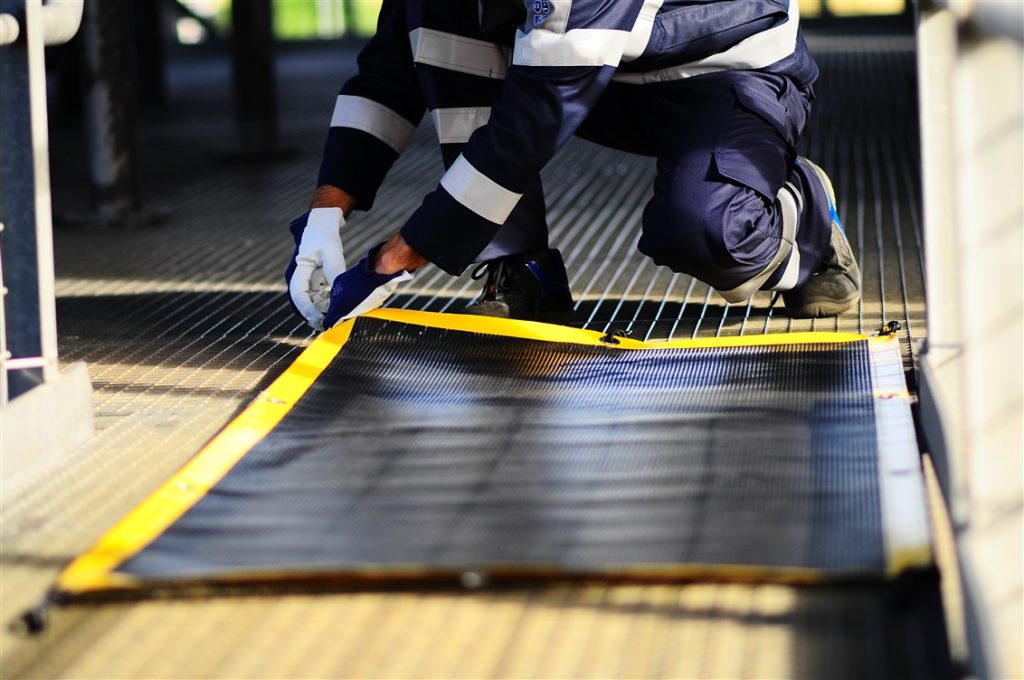

Applications
- Marine & shipbuilding / Shipyards
- Metal gratings
- Elevated work platforms
- Walkways & catwalks
- Maintenance projects & industrial turnaround
- Oil and gas, refineries and power plants
- Offshore platforms, terminals and rigs
- Manufacturing facilities
Objects known to frequently cause accidents are hand tools or equipment left behind after a task, as well as equipment mounted in an elevated location that has the potential to fall due to movement or environmental conditions.
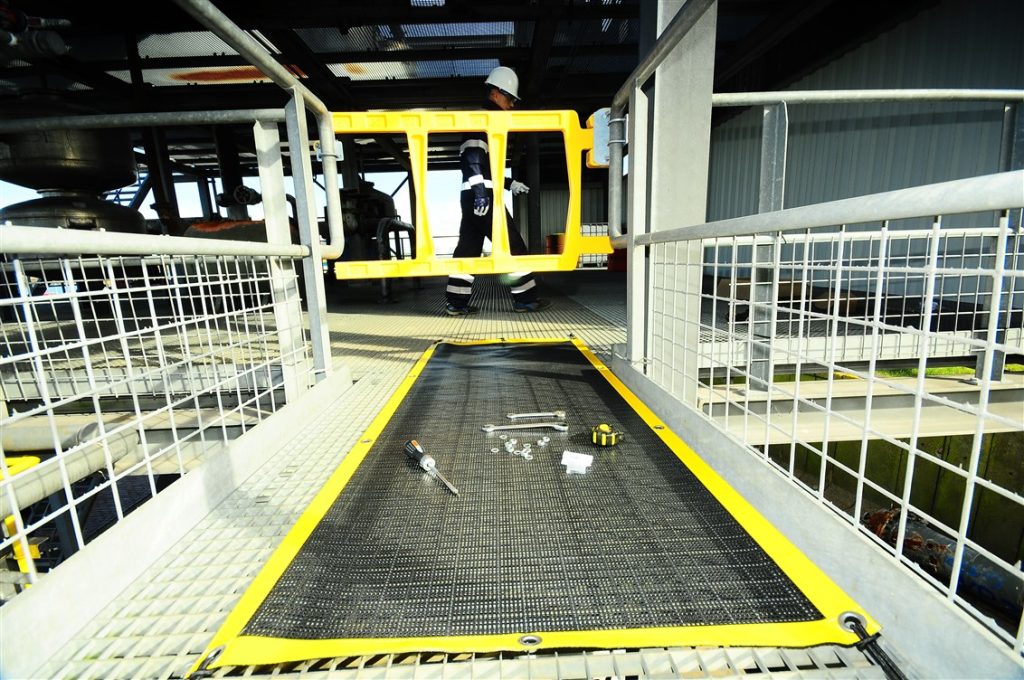

Benefits of the Prevention Work Mats
- Risk Reduction: Minimises the risk of dropped objects, protecting personnel and equipment
- Reusable: This range of high-quality mats can be used repeatedly to protect people in the workplace
- Fast Installation: No complicated setup– simply lay it down and secure it which helps reduce downtime and risk of workplace injuries and easy to deploy, fold and reuse
- Used as temporary Work Mat for dropped objects prevention
- Prevents small tools, fasteners & foreign objects falling from elevated work platforms creating a safer work environment
- Fire Resistant / Flame Retardant fabric available for heat sensitive areas

CABLE SAFETY EQUIPMENT
CableSafe® Safety solutions are critical cable essentials and are well proven construction safety products. The CableSafe® range of cable hooks can be used during maintenance, turnaround, outages, shutdowns, construction work to suspend cables and hoses and other work gear and equipment from the working space.

Cable Safety Equipment | Cable Stand | Cable Bridge | Cable Rail | Cable Guard | Dropped Object Prevention Mats
Electrical Safety in Wind Turbines
February 20th, 2024
Authored by Pieter Pijnenburg | Arc Flash Engineer from Leaf Electrical Safety

Electrical Safety
Any industrial or commercial workplace requires arc flash and electrical safety training, and it is essential in order to make sure your staff members know what they need to do to remain safe.
Leaf Electrical Safety is an electrical safety company that can provide expert advice on electrical safety to help teams build processes and improve safety culture. Working primarily across Canada and the USA, they help solve your industrial electrical safety problems.
Electrical safety compliance training should keep you on the edge of your seat, wanting more, because it will highlight the dangers that your team faces on a daily basis. Special thanks to Jon Travis for the kind permission to republish.
→ See original article here!
- What are the electrical safety hazards in wind turbines?
- How do I ensure my team works safely around them?
- What PPE should my electrical workers be wearing?
- How do you perform grounding with wind turbines?
Let’s jump right in!
The Definitive Guide to Arc Flash By Thorne & Derrick
WIND POWER FACILITY ELECTRICAL SAFETY
In our ever-changing renewable world, the safety of personnel is still and should remain a paramount concern. Wind Energy Conversion Systems (WECS) are some of the more prominent types of renewable generation whose safety concerns are exacerbated by two main factors:
- Remoteness: due to the nature of wind turbines being remote and/or offshore, any hospitalisation can turn into a race against time.
- Confined spaces: the electrical components and work areas within a wind turbine are typically in confined spaces, which becomes more problematic when you add multiple workers into the mix.
WHAT ARE THE ELECTRICAL SAFETY HAZARDS
IN WIND TURBINES?
In order to mitigate hazards and allow for adequate protection, WECS equipment and operators should be adequately equipped to deal with the following main hazards issues that commonly occur in WECS:
- Arc Flash
- Shock
- Overloaded Circuits
- Defective Insulation
- Wet Environment
- Damaged or Worn Equipment
ARC FLASH RISK IN WIND TURBINE
Potential arc flashes in WECS are potentially life-threatening issues which require detailed analysis and physical protection to be accounted for. Arc flash hazard analysis (incident energy calculations) is typically used and utilises standards such as IEEE 1584-2018 to perform the calculation. Once the calculation is made and the proper arc flash boundaries are determined, personal protective equipment (PPE) can be assigned based on the calculations (see CSA Z462 for more details).
SHOCK RISK IN A WIND TURBINE
Shock risk, like an arc flash, is a potentially life-threatening hazard if not properly accounted for. Usually, a shock risk assessment is performed to look at key system parameters such as voltage level, shock boundary, environment, equipment type, and condition.
OVERLOADED CIRCUITS
Overloaded circuits can cause various problems and increase the risks of shock and arc flash considerably if not protected and isolated properly. Preventative measures can be taken through routine inspection of protection devices and physical circuitry (with proper PPE) to check for any abnormalities in the equipment.
DEFECTIVE INSULATION
Defective insulation can cause system malfunction and exponentially increase the potential arc flash and shock risks. Regular insulation resistance (IR) tests, whose procedure for electric machinery is highlighted in IEEE 43-2013, should be performed to test the dielectric strength of the insulation.
WET ENVIRONMENT
Wet surfaces can prove hazardous to people as well as electrical equipment. In order to reduce these potential hazards, regular equipment checks should be carried out on the exterior and interior of the WECS for potential water seepage/damage.
DAMAGED OR WORN EQUIPMENT
Equipment can be compromised from its normal working state for a variety of reasons, but compromised equipment can cause major problems if it is not repaired or replaced quickly enough. To mitigate this, scheduled maintenance procedures should be made and followed (see CSA Z463).
ELECTRICAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR WIND TURBINE WORKERS
PROPER PERSONAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT
Each hazard risk category requires a different level of protection. Categories range from 1 to 5 as defined within CSA Z462 and laid out below as follows:
| PPE category | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Incident Energy | Up to 4 cal/cm² | Up to 8 cal/cm² | Up to 25 cal/cm² | Up to 40 cal/cm² | Up to 75 cal/cm² |
Figure 1:PPE category as defined by CSA Z462
ARC FLASH BOUNDARY
An arc flash boundary is the shortest distance at which a person working at the time of an arc-flash incident may receive an onset of a second-degree burn or worse (1.2 cal/cm2) if not adequately protected by flame-resistant (FR) clothing.
LABELING
Labelling is defined in CSA 22.1-18 for both small (64-300) and large (64-400) wind turbines as “a permanent marking” that must be created near an easily accessible location near the disconnecting for the wind turbine output circuit (64-300) or base of the tower (64-400) and display the following critical information:
- Overcurrent protection values provided by the wind turbine for the stator and rotor, if applicable;
- Short-circuit current rating (SCCR);
- A brief system description, including the type of generator (synchronous or induction);
- Rated output current; and
- Rated output voltage at the grid connection to the turbine.
- Warning notice (large turbines only)
Furthermore, arc flash and shock hazard labels should be provided for large wind systems. These labels are covered in CSA Z462 Annex Q, which highlights procedures for labelling arc flash hazards and shock protection. The minimum arc flash label requirement per CSA 22.1-18 (Canadian Electrical Code Part 1) is:

Figure 2:CSA Arc Flash label template for CSA 22.1 Requirements
Whereas the CSA Z462 recommends that the label look something more like:

Figure 3:CSA Z462 Annex Q Recommended ARC Flash label structures
WIND TURBINE GROUNDING
Like any generator, the WECS should be properly grounded and follow CSA standards and IEEE 142. Proper grounding of turbines follows the general ruleset of AC connections as defined by CSA 22.1 Section 64-312 as:
- 1) Exposed non-current-carrying metal parts of towers, turbine nacelles, other metallic equipment, and insulated conductor enclosures shall be bonded to ground in accordance regardless of voltage.
- 2) Metallic towers or supporting structures shall be bonded to the ground with a minimum No. 6 AWG.
- 3) Guy wires used to support turbine towers need not be grounded.
- 4) Towers or structures shall be grounded by means of grounding electrodes to limit voltages imposed by lightning.
- 5) Notwithstanding Subrule 4), metal towers located on steel-supported buildings shall be bonded to non-current-carrying metal parts of the building.
FAULT FINDING & TESTING
To effectively find faults in a WECS, proper fault monitoring relay devices should be installed particularly:
- 50 – Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
- 51 – AC Time Overcurrent Relay
- 59 – Overvoltage Relay
These devices will be able to monitor and indicate the levels of key parameters such as voltage and current.
ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDS AND TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE WIND ENERGY INDUSTRY
CSA 22.1-2018 lists several safety requirements for both small and large wind turbines (64-300 tot 64-414), including marking, maximum voltage, insulated conductors, wiring methods, overcurrent protection, disconnecting means, grounding and bonding, maintenance receptacles, lightning protection, surge protection and system demarcation (large turbine).
Training requirements are highlighted in Annex U of CSA Z462, which highlights procedures for human performance in electrical safety. It highlights risk control methodologies and procedures for human performance, such as
- Job planning and pre-job briefing tool
- Job site review tool
- Post job review tool
- Procedure use AND adherence tool
- Self check with verbalization
- Three-way communication tool
- Stop when unsure tool
- Flagging and blocking tools

ELECTRICAL SAFETY PROVIDERS
Thorne & Derrick protect substation engineers, asset managers, SAPS, cable jointers, overhead linesmen and utility workers with PPE and safety equipment: this includes insulating gloves, arc flash clothing, voltage detectors, insulating matting and portable earthing to ensure worker safety when carrying out repair and maintenance on LV-HV switchgear, transformers, substations and turbines.
All of our Cable Connection & Energisation Accessories including Medium & High Voltage joints, terminations, connectors and cleats are tested to the latest international standards and supporting ranges of professional installation tools are stocked to reduce incident, accident and downtime to plant and people.

Use of Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL Live Line Testers & Indicators
February 16th, 2024
Use of Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL Live Line Testers & Indicators
Voltage Detectors Distributed from Stock | Approved Supplier | UK & Export Sales
Pfisterer Voltage Detectors
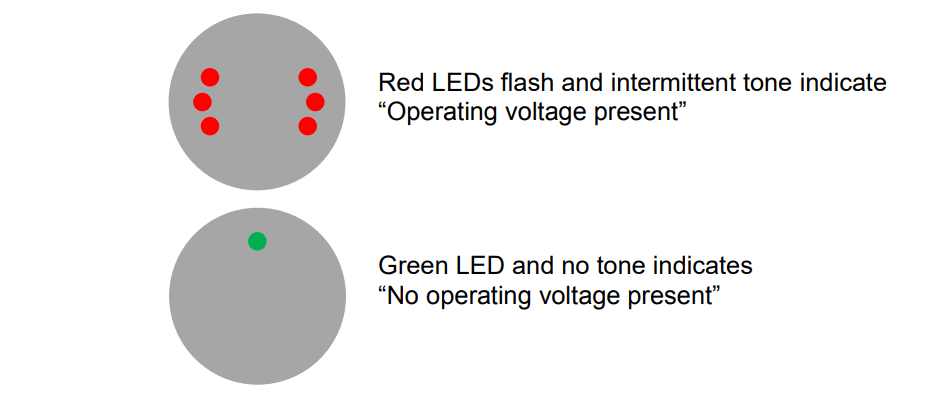
Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL is a capacitive voltage detector—the universal Medium & High Voltage Detection & Live Line Tester (LLT) product range for nominal voltages from 110kV to 220kV. The voltage detector presents the operating voltage when brought into contact with the MV HV overhead lines and conductors.
The Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL voltage detector provides a high level of user-friendliness and user safety – KP-Test 5HL is designed and type-tested to Standard IEC 61243-1.
Other versions of the HV high voltage detector with deviating voltages, ranges of nominal voltages, frequencies, and languages are available on request.
KP-Test 5 range of instruments from Pfisterer can detect voltage level 1 to 420 kV AC.
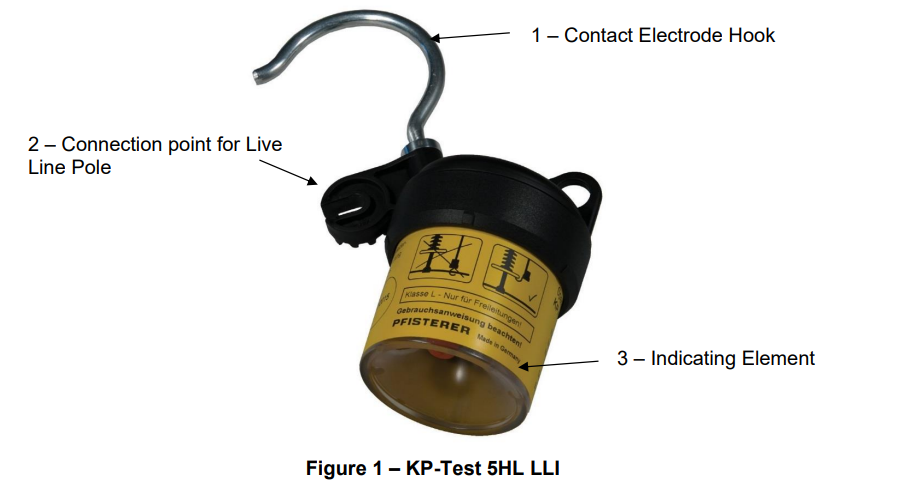

Pfisterer KP-Test 5HL
KP-Test 5HL Live Line Indicators
The KP-Test 5HL is one of several certified live line indicators (LLI’s) that have been used to test 25kV conductors to ensure that they have been disconnected from the power source prior to connecting to earth or testing before touching. LLIs are safety devices on which human lives may depend. These should be handled with extreme caution and protected against damage.
To discharge any induced voltages, field equipment earthing, also known as portable earthing, may be necessary when employing voltage detectors to determine whether operating voltages are present on MV-HV power cables or overhead lines. This is because the equipment may be operating close to live conductors.
KP-Test 5HL is limited to use on the lowest conductor of the objects being tested, such as the bottom autotransformer feeder (ATF) or contact wire. Only those with a valid competency (authorised person or nominated person) and who have attended a familiarisation briefing should use it.
| Voltage Detector Part Number | Nominal Voltage (kV) | Nominal Frequency (Hz) | Diameter of hook (mm) |
| KP-Test 5HL | 110-220 | 50 | 70 |
Benefits of using Voltage Detectors
Furthermore, voltage detectors are crucial instruments made to improve electrical safety in a range of settings. These tools are essential for averting mishaps, lowering the risk of casualties, and safeguarding infrastructure. An extended explanation of the features stated is provided below:
- Weather Resistance: They are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including rain. This allows operators to use them in diverse weather conditions without compromising their functionality. This feature ensures that the detectors remain operational even when exposed to rain, providing continuous safety in outdoor settings.
- Personnel Safety: Voltage detectors significantly reduce the risk of serious injury to personnel working with electrical systems. Their ability to detect live voltage without physical contact ensures that operators can assess the presence of electrical energy safely. This minimizes the chances of electrical accidents, protecting personnel from electric shocks and other potential hazards associated with working in proximity to live electrical components.
- Infrastructure Protection: Voltage detectors play a vital role in safeguarding electrical infrastructure. By providing a means to detect live electrical components, they help prevent accidental damage to critical equipment and wiring. This protection extends the lifespan of electrical systems, reduces the frequency of repairs, and contributes to the overall reliability of the infrastructure.
- Quick Drying: After being exposed to rain or wet conditions, voltage detectors are designed to dry quickly once not in use. This feature is essential for maintaining the reliability of the device. The rapid drying capability ensures that the detector can be stored or reused promptly after exposure to moisture, minimizing downtime and allowing for efficient use in dynamic work environments.

THORNE & DERRICK
Thorne & Derrick stock and distribute PFISTERER CONNEX Connectors for medium / high voltage cable connection and termination to electrical systems up to 33kV – we provide competitive prices for PFISTERER CONNEX connectors used to terminate and connect polymeric insulated MV-HV cables into gas insulated switchgear and electrical equipment from extensive UK stocks.
Thorne & Derrick are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing businesses involved in cabling, jointing, substation, earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV. Supplying a complete range of power cable accessories to support the installation and maintenance of low/medium and high voltage cable systems:
- Slip-on Cable Terminations
- Cold-shrink Cable Terminations
- Heat-shrink Cable Terminations
- Cable Joints – Heat & Cold-shrink
- Separable Connectors (Euromold)
- Surge Arresters & Switchgear/Transformer Bushings

Voltage Detectors | Phase Comparators | Insulating Poles | Portable Earthing | LV MV HV
EV Insulated Matting | Enhancing Safety in the Workplace | LV MV HV
January 2nd, 2024
Mitigating Risks | High Voltage Systems | CATU
EV Insulated Mats
Protecting against accidents in LV MV HV Systems
CATU’s electrical insulating matting provide electrical safety protection for individual and collective protection for workers involved on LV MV HV installations for voltages of 3.3kV, 6.6kV, 11kV, 15kV, 20kV and 33kV – generally used in conjunction with additional PPE such as insulating gloves for worker safety.
Insulated Mats, manufactured by CATU Electrical Safety and distributed by Thorne & Derrick, made from elastomer are used to cover ground for electrical protection of operators during work or interventions on electrical installations.
By incorporating insulated matting into safety protocols, the EV sector can enhance workplace safety, comply with industry standards and mitigating any risks associated with high voltage systems in electrical vehicles.
The mats are tested to IEC61111 and certification is provided upon request.

Insulating Matting | Thorne & Derrick hold the largest stocks in the UK of all types and Class of electrical matting for LV MV HV substations and switchgear applications to protect workers from protect people from hazardous electric shocks.
Purposes of using EV Insulated Matting
EV insulated matting is commonly used for a variety of reasons:
- Electrical Safety – Electric Vehicles (EV) operate with high voltage systems, preventing a risk of electrical shock during maintenance or repair.
- Preventing Grounding
- Compliance with Safety Standards
- Workplace Safety Practices
- Protecting against accidents
Meeting these specific standards is essential for creating a safe working environment and ensuring the well-being of technicians.
EV Insulated Mats | Compliance with IEC Standards
IEC61111 Standards
Insulated Mats, manufactured by CATU Electrical Safety and distributed by Thorne & Derrick from elastomer is used to cover ground for electrical protection of operators during work or interventions on electrical installations. By incorporating insulated matting into safety protocols, the EV sector can enhance workplace safety, comply with industry standards and mitigating any risks associated with high voltage systems in electrical vehicles.
The withstand test of insulating matting for electrical insulation is applied to each manufacturing batch of switchboard matting to ensure it does not have an electrical breakdown if exposed to high voltages – the working and withstand voltages must not be confused.
The proof test of insulating matting are dielectrical resistance tests provided by the mat manufacturer on the total running metre of the product and are used to safeguard a standard conformity of resistance throughout the entire section, roll or surface area of the electrical mat – the proof test must be applied to the insulating mats for a set time at a specified voltage level.
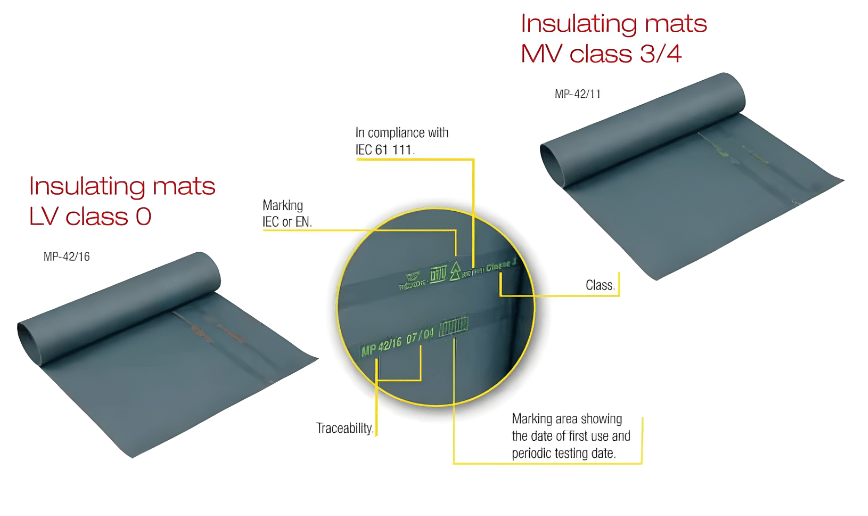
The information table below highlights and explains the IEC standard classification according to the maximum working voltages for rubber insulating matting.
| Class Of Insulating Matting According To IEC61111 | Proof Test | AC Maximum Working Voltage | Withstand Test Of Insulating Matting |
| Class 0 Matting | 5kV | 1000V – LV Low Voltage | 10kV |
| Class 1 Matting | 10kV | 7500V – MV Medium Voltage | 20kV |
| Class 2 Matting | 20kV | 17000V – MV Medium Voltage | 30kV |
| Class 3 Matting | 30kV | 26500V – MV Medium Voltage | 40kV |
| Class 4 Matting | 40kV | 36000V – HV High Voltage | 50kV |

High Voltage Electrical Safety
Further Reading
- Electrical Safety – Arc Flash Accidents & Electrocution In LV-HV Installations
- Arc Flash Calculation – Selecting Clothing & PPE To Protect Lives Against Arc Hazard
- IEC 61482-2:2018 – Get Up To Speed With The New Arc Flash Standard
- Arc Flash PPE | 7 Top Considerations
- Arc Flash The Basics

Insulating Matting | Voltage Detectors | Substation Kits | Phase Comparators

Arc Flash Clothing | Polo Shirts | Jackets | Coveralls | Trousers | Sweatshirts | Helmets
THORNE & DERRICK
Thorne & Derrick are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing businesses involved in cabling, jointing, substation, earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV. Supplying a complete range of power cable accessories to support the installation and maintenance of low/medium and high voltage power systems:
- Slip-on Cable Terminations
- Cold-shrink Cable Terminations
- Heat-shrink Cable Terminations
- Cable Joints – Heat & Cold-shrink
- Separable Connectors (Euromold)
- Surge Arresters & Switchgear/Transformer Bushings
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV

Thorne & Derrick stock and distribute a complete range of IEC61111 insulating matting for electrical safety, protection and working on low, medium and high voltage substations and switchgear up to 33kV – the IEC61111 standard provides a selection category for Low Voltage (1000V) to High Voltage (36kV).


