Cable Joints & Terminations HV
33kV Cable Termination | Stripping Sheath with Bonded Aluminium Screen
March 28th, 2024Uploaded by Chris Dodds | Sales & Marketing Manager at Thorne & Derrick
Here the Jointer, Steffan Evans, from HVSM is shown expertly removing the cable sheath and bonded aluminium screen using the Ripley US15 Cable Sheath Stripping Tool (10-50mm) – the Jointing tool when used by Trained & Competent Jointers effortlessly and safely removes both the outer sheath jacket with aluminium foil screen without incurring damage to the copper wire screens on a 33kV single core 800sqmm XLPE insulated cable.
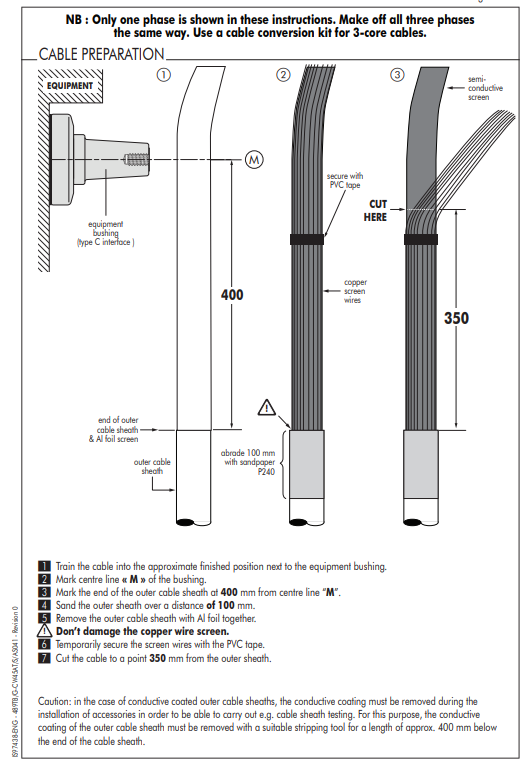
Cable Preparation | Excerpt from Nexans Euromold Type C Interface Connectors (K), (M), (P) 800PB/G Up to 20.8/36 (42)kV | Note the instruction references the requirement to remove the outer cable sheath with Aluminium foil together.
Caution: in the case of conductive coated outer cable sheaths, the conductive coating must be removed during the installation of accessories in order to be able to carry out e.g. cable sheath testing. For this purpose, the conductive coating of the outer cable sheath must be removed with a suitable stripping tool for a length of approx. 400 mm below the end of the cable sheath.
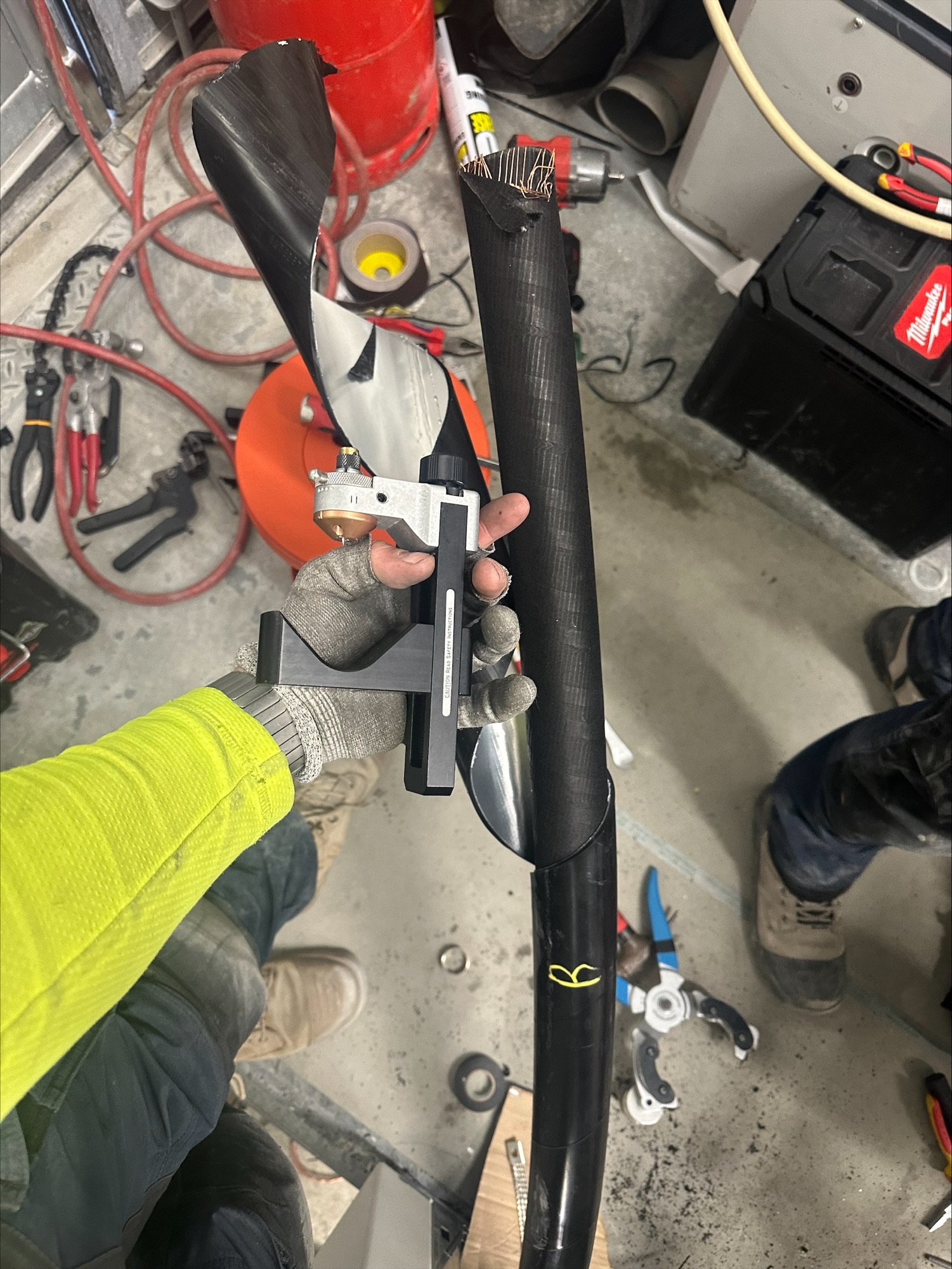

Sheath Stripping with the Ripley US15
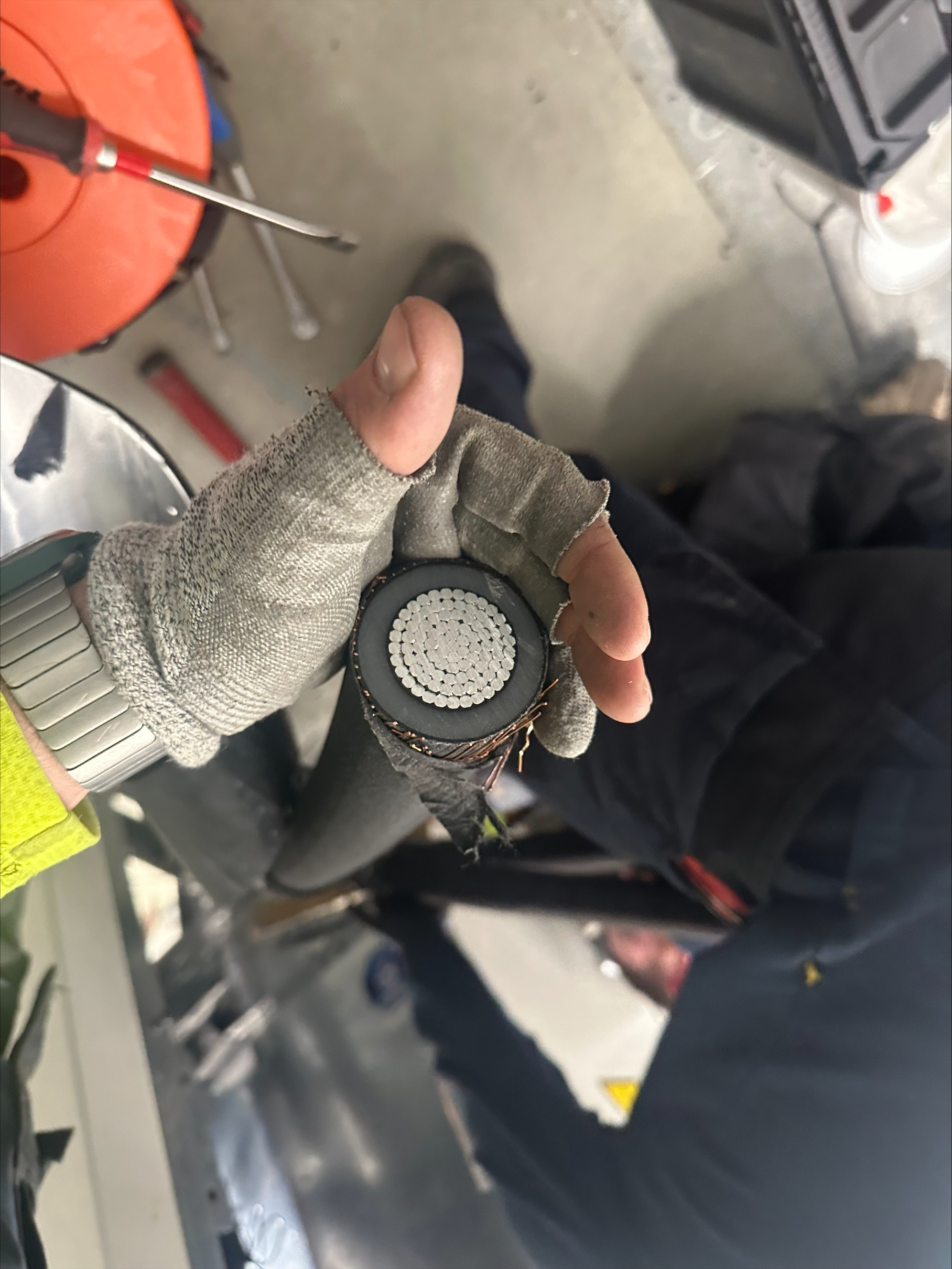
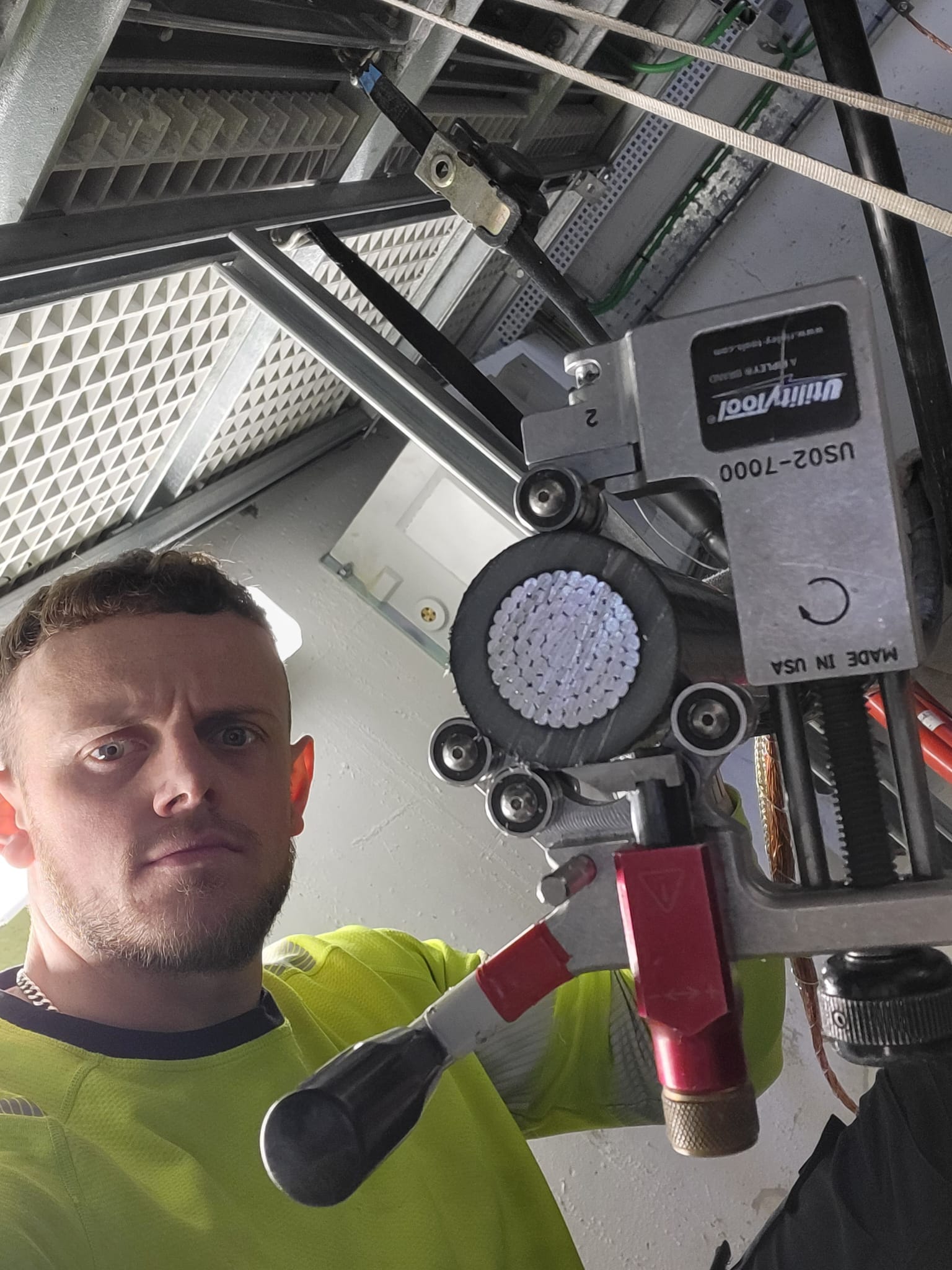


Stripping Bonded Screens 33kV
Here Steffan is shownly stripping bonded semi-conductor screen from medium voltage power cables (20/22kV) prior to terminating the cable into Siemens NXAIR type Vacuum Circuit Breaker – the Ripley US02-7000 comfortably caters for the precision stripping of the bonded screen from the 400sqmm cable for preparation of the Raychem (Tyco) heat shrink termination to be installed.
The US02 Tool manufactured by Ripley Tools features a revolving ergonomic handle and accessible adjustment knobs for comfort and ease-of-use, reducing effort and potential strain for cable jointers performing repetitive shaving functions in the field.
“Investing in innovation and introducing cable jointing tools to HVSM improves safety and reliability for our clients. The Ripley US02 is very Jointer-friendly with a spectacular finish to the XLPE insulation – the automatic cut-off and incremental blade adjustments ensure a professional perfection of cable preparation at medium voltages,” comments Steffan.
Stripping in the Switch | the US02 Tool is compact but robust allowing confined space working in Medium Voltage Electrical Equipment.
HVSM are one of Ireland’s most long-standing High Voltage Engineering companies, which has been operating since 1991. Headquartered in Ireland but present and operating globally, they provide best in class specialist service for High Voltage Power Industries such as Commercial, Utilities, Manufacturing, Life Science, Data Centres as well as the Renewable Energy Sector.
provide best in class specialist service for High Voltage Power Industries such as Commercial, Utilities, Manufacturing, Life Science, Data Centres as well as the Renewable Energy Sector.


Thorne & Derrick are now Official Distributors for the Vicera range of Cable Jointing Stands – the introduction of this new product range is an excellent extension to our core ranges of Cable Jointing, Pulling Equipment & Preparation Tooling and we look forward to further supporting efficient, easier and more reliable power cable installations.

Thorne & Derrick distribute the most extensive range of MV HV Medium & High Voltage Cable Joints, Terminations & Connectors from manufacturers including 3M, Prysmian, Nexans Euromold, Elastimold, Pfisterer CONNEX & SEANEX. Heat shrink, cold shrink, push-on and slip-over cable accessories enable the jointing, terminating and connection of 11kV-33kV and 66kV-132kV cables to oil, air or gas insulated switchgear, transformers, motors and overhead lines distributing electricity at medium/high voltages.
T&D hold large stocks of 11kV 33kV 66kV Joints & Terminations suitable for XLPE, PILC and EPR cables, in both heat shrink and Cold Shrink technologies, to service the medium/high voltage power cable accessory requirements of UK and international customers.
HV Cable Sheath Bonding Methods | High Voltage Power Systems
March 10th, 2024
Joint | Terminate | Connect Medium & High Voltage Cables MV HV
MV HV High Voltage Cable Joints | Cable Terminations | Cable Connectors
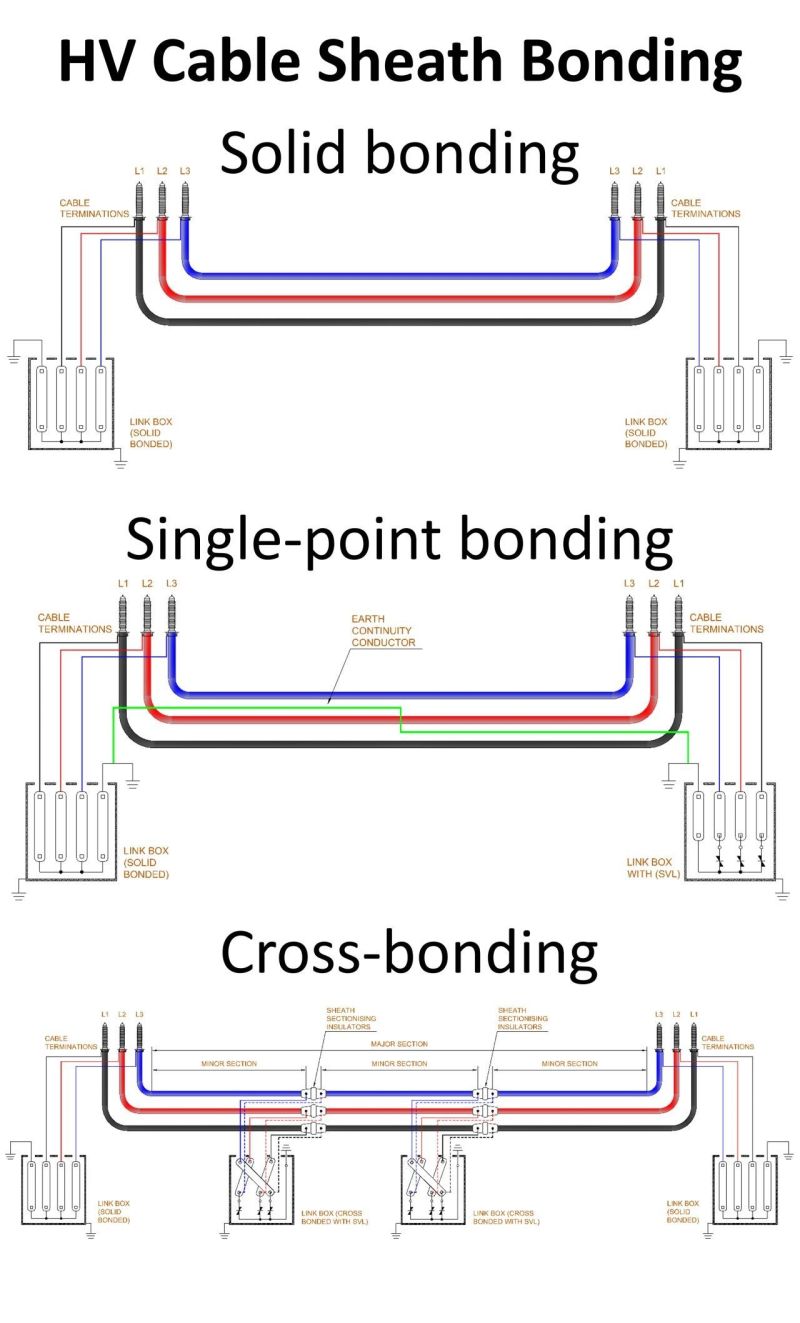
Cable Sheath Bonding
Each HV cable sheath bonding method has its advantages and applications.
Solid bonding of high voltage cables is simple but leads to sheath losses, single-point bonding eliminates circulating currents but requires voltage control, and cross-bonding is the most efficient for long HV cables, minimizing losses.
The choice depends on High Voltage Power System requirements, cable length and operational efficiency.
Solid Bonding
In this method, the metallic sheath of the cable is bonded at both ends and connected to the earth. This results in continuous current flow in the sheath due to the induced voltage.
Solid Bonding Advantages: Simple to install.
Disadvantages: High circulating currents in the sheath lead to power losses and increased heating. Best suited for: Short high voltage cable routes where sheath current losses are minimal.
Single Point Bonding
The sheath is bonded to the earth at only one end, with the other end left open and insulated. An earth continuity conductor is used to maintain equipotential grounding.
This method eliminates circulating currents but results in induced sheath voltages, which can be high. To control this, sheath voltage limiters (SVL) are used.
Single Point Bonding Advantages: Reduces power losses as no sheath currents circulate.
Disadvantages: Requires careful management of sheath voltages. Best suited for: Medium-length high voltage cable systems.
Cross Bonding
The high voltage cable length is divided into three equal sections (minor sections) within a major section. At each section junction, the cable sheaths are cross-bonded using link boxes to balance out induced voltages. This technique cancels out circulating currents, reducing sheath losses significantly.
Cross Bonding Advantages: The most efficient method, significantly reducing losses.
Disadvantages: Complex installation and maintenance. Best suited for: Long-distance high voltage cable routes.

Thorne & Derrick Specialist Electrical Distributor
LV ♦ MV ♦ HV
T&D distribute the most extensive range of LV, MV & HV Cable Jointing, Terminating, Installation & Cable Pulling Equipment – we service UK and international clients working on underground cables, overhead lines, substations and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV and EHV transmission and distribution voltages.
- Key Products: MV-HV Cable Joints & Terminations, Cable Cleats, Sealing Cable Ducts, Cable Transits, Underground Cable Protection, Cable Jointing Tools, Feeder Pillars, Cable Ducting, Earthing & Lightning Protection, Electrical Safety, Cable Glands, Arc Flash Protection & Fusegear.
- Distributors for: 3M, ABB, Alroc, Band-It, Catu, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Furse, Lucy Zodion, Nexans Euromold, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec.

LV – Low Voltage Cable Joints, Glands, Cleats, Lugs & Accessories (1000 Volts)

MV HV – Medium & High Voltage Cable Joints, Terminations & Connectors (11kV 33kV EHV)

Cable Laying – Underground Cable Covers, Ducting, Seals & Cable Pulling Equipment
Basics of Cable Design and Engineering for Power Systems
January 29th, 2024
Guest Article : Authored by Ryan Smith MSc MIET | Owner of EasyCableSizing.com
As an Electrical Engineer, I’ve always been fascinated by the “hows and whys” in the design and engineering of power cables. In this Article, I delve into the essential aspects from the core components of a power cable to the considerations in choosing the right materials.
components of a power cable to the considerations in choosing the right materials.
Key highlights include:
- the critical roles of conductors, insulation, and sheathing
- a comparative look at copper and aluminium in cable applications
- insights into the evolving world of eco-friendly materials in cable design
- importance of understanding electrical properties like conductance, resistance, capacitance, and inductance
I also discuss the significance of standards like IEC 60287 and IEC 60502 in cable sizing, essential for anyone working with MV and HV power cables. Whether you’re a fellow engineer, a student, or just curious about the field, I believe there’s something valuable for everyone in this piece.
→ See original article here!
Table Of Contents
1.Introduction to Cable Engineering
1.1 Definition and Scope
2. Cable Construction Basics
2.1 Core Components of a Power Cable
2.1.1 Conductors
2.1.2 Insulation
2.1.3 Sheathing and Jacketing
2.2 Types of Power Cables
2.2.1 Low Voltage Cables
2.2.2 Medium and High Voltage Cables
3 Material Selection in Cable Design
3.1 Conductive Materials: Copper vs. Aluminium
3.2 Insulation Materials: XLPE, PVC, and Others
3.3 Advances in Eco-friendly Materials
4 Electrical Properties of Cables
4.1 Conductance and Resistance
4.2 Capacitance and Inductance
4.3 Impedance Considerations
5 Cable Sizing and Capacity Considerations
5.1 Calculating Current Carrying Capacity
5.2 Factors Influencing Cable Sizing
5.3 Utilizing Standards for Sizing
5.3.1 IEC 60287 Standard
5.3.2 IEC 60502 Standard
6 Key Takeaways
Introduction to Cable Engineering
Definition and Scope
Cable engineering is a specialised domain focusing on the design, implementation, and optimisation of electrical power cables. This field encompasses a range of activities from material selection to performance testing, ensuring that cables meet the demands of modern electrical networks.
Cable construction Basics
Core components of A POWER CABLE
Underground power cables consist of a minimum of two components, a conductor and insulation, however these are usually accompanied by other elements, each playing a critical role in overall functionality:
cONDUCTORS
Conductors are the principal element of a power cables, responsible for transmitting electricity. They are typically made of materials like copper or aluminium, chosen for their excellent conductivity and durability. In other applications where conductors are required, other materials are often used, like gold, but these aren’t feasible for power applications due to their high cost.
iNSULATION
Insulation in power cables primarily provides segregation from a conductor and other conductive materials, whether they’re intended to be conductors or not, but also protects it from environmental factors.
Sheathing and Jacketing
Sheathing and jacketing provide an additional layer of protection to cables, safeguarding against physical damage and environmental factors. This layer is crucial for cable longevity and reliability.
Types of Power Cables
Power cables are categorised based on their voltage capacity:
Low voltage Cables
Low voltage cables are designed for applications with voltage requirements commonly up to 1000V. They are commonly used in residential and commercial settings for everyday electrical needs, and in industrial settings for smaller loads. Learn more about low voltage, heavy-duty industrial cables like the H07RN‑F rubber cable in our detailed selection guide.
Medium and High Voltage Cables
Medium and high voltage cables cater to more demanding applications, such as industrial plants, generation, and power transmission lines. They are able to handle higher voltages and are key in large-scale power distribution.
Material Selection in cable design
Conductive materials: Copper vs. aluminium
The two main materials used for conductors are copper and aluminium, due to their wide availability and relatively low cost.
- Copper, known for its superior conductivity and durability, is often preferred for certain applications, despite its higher cost.
- Aluminium, being lighter and more cost-effective, is a viable alternative, especially for large-scale power transmission.
Insulation Materials: XLPE, PVC, and Others
Different insulation materials like XLPE, PVC, and EPR play a crucial role in cable performance:
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Known for high temperature resistance and excellent electrical properties, ideal for high voltage applications.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Offers flexibility and durability, used in a wide range of cable types.
- EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber): Notable for dielectric strength, flexibility, thermal stability, suitable for high stress environments.
- Others: Includes materials like Teflon and Rubber, chosen for specific applications based on properties like fire resistance, low toxicity, or extreme environmental conditions.
Advances in Eco-friendly Materials
The cable industry is evolving towards eco-friendly materials like polypropylene (PP) to minimize environmental impact. PP stands out for its excellent insulating properties and recyclability, making it a promising material for next-generation power cables. However, its application in cable insulation still faces challenges, such as optimising its mechanical and electrical properties. This drive towards sustainable materials is redefining cable technology, balancing environmental considerations with performance requirements. For an in-depth understanding, read more about the potential of PP in power cable insulation in this research article.
Electrical properties of cables
Conductance and resistance
Understanding the conductance (G) and resistance ® of power cables is essential for evaluating their performance. These properties are inversely related, where G=1⁄R. Conductance represents a cable’s ability to allow electric current flow, while resistance quantifies the opposition to current flow. This affects cable efficiency, with lower resistance implying less energy loss as heat. Factors such as material type, cross-sectional area, and temperature influence these properties.
To learn more about the impact of resistance in power systems, consider reading this comprehensive guide on resistance and its effects.
Capacitance and Inductance
Capacitance © and inductance (L) are key factors in cable design, affecting how cables react to different electrical loads and frequencies. Capacitance in cables arises from the electric field between conductors, typically calculated using where is the permittivity of the insulating material, the area of the conductor, and the distance between conductors. Inductance, on the other hand, is influenced by the magnetic field around the conductor and is given by , where is the permeability of the material, the number of turns in the coil, the area, and the length of the coil.
Impedance Considerations
Impedance (Z) in cables, a combination of resistance, inductance, and capacitance, is crucial in AC power systems. It can be represented as , where is the inductive reactance and the capacitive reactance. Impedance affects signal quality and power loss in cables, and its proper management is vital for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of electrical systems.
For an in-depth understanding of impedance and its impact on power systems, you might find this resource on impedance in AC circuits useful.
Cable sizing and capacity considerations
Calculating current carrying capacity
There are various methods used to calculate the current carrying capacity of cables (or ampacity), although the two methods predominantly referenced and used are IEC 60287 and Neher-McGrath. Both IEC 60287 and Neher-McGrath methods consider the heating of a conductor, and the cable’s and surrounding mediums’ ability to dissipate the heat until thermal equilibrium is met. An increase in current results in an increase in temperature, and the less thermal resistivity the cable and surrounding medium have, the more current can be carried.
Factors Influencing Cable Sizing
A principal consideration in cable sizing is the insulation selected for the conductor, as this determines the maximum temperature that can be reached before causing overheating and unnecessary stress or damage to the cable. Beyond that, it is primarily the surrounding medium and installation conditions that influence the thermal resistivity.
For cables installed underground, the soil itself has a thermal resistivity value to be considered. If sand, bentonite, or concrete are used, their own thermal resistivity values and geometry are incorporated into the formulas to determine the cable’s ampacity. If a cable is installed in a duct, the geometry, thermal resistivity of the duct itself, and the filling medium (such as air or bentonite) must also be considered.
Another major factor affecting the ampacity of cables is their proximity to other heat sources, such as other circuits (which are assumed to reach 90°C if insulated with XLPE), hot water pipes, steam pipes, etc. This mutual heating significantly impacts the ampacity calculations, especially in shared trenches or when cables are installed in ladders or trays.
Utilizing Standards for Sizing
When determining the appropriate size for power cables, adhering to established standards is crucial. These standards provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating various factors, ensuring that the chosen cable meets both current and future demands of electrical networks while adhering to safety and efficiency guidelines.
IEC 60287 Standard
The IEC 60287 standard is renowned for its systematic approach to cable sizing. It accounts for numerous factors, including conductor temperature, load pattern, cable laying conditions, and the thermal resistivity of the surrounding environment. This standard is particularly valued for its detailed thermal model, essential in accurately predicting cable behaviour under varying operational conditions.
EasyCableSizing.com plans to integrate this model into its platform, enhancing its cable sizing capabilities.
IEC 60502 Standard
IEC 60502 covers the requirements for the manufacture and testing of cables ranging from 1kV to 30kV. It includes tables of multipliers used against standard cable ampacity tables to determine adjusted ampacities based on specific conditions. These tables are derived from methodologies in IEC 60287, offering a practical guide for cable system development.
EasyCableSizing.com utilizes the IEC 60502 methodology in a user-friendly manner, helping users quickly and efficiently determine cable ampacities. This approach simplifies the complex process of cable sizing, making it accessible to a wider range of professionals and ensuring compliance with international standards. In Understanding the IEC 60502 Sizing System: A Double-Edged Sword this standard in particular is discussed in more detail.
Key Takeaways
- Cable Engineering’s Core Focus: Emphasizes the design, implementation, and optimization of electrical power cables, highlighting its crucial role in modern electrical networks.
- Components of Power Cables: Details the significance of conductors, insulation, and sheathing in cable construction, and their impact on cable functionality and durability.
- Conductive Material Choices: Discusses the use of copper and aluminium in power cables, outlining their advantages based on conductivity, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Insulation Material Varieties: Explores different insulation materials like XLPE, PVC, EPR, and their roles in high voltage applications, flexibility, and thermal stability.
- Eco-friendly Material Trends: Addresses the shift towards sustainable materials like polypropylene in the cable industry, balancing environmental considerations with performance requirements.
- Electrical Properties in Cables: Analyses essential properties such as conductance, resistance, capacitance, and inductance, crucial for cable efficiency and performance.
- Impedance in AC Power Systems: Highlights the importance of impedance, combining resistance, inductance, and capacitance, and its effect on signal quality and power loss.
- Current Carrying Capacity Methods: Compares IEC 60287 and Neher-McGrath methods for calculating ampacity, focusing on thermal equilibrium and thermal resistivity.
- Influences on Cable Sizing: Discusses how insulation, installation conditions, and surrounding medium impact cable sizing and thermal resistivity.
- Standards for Cable Sizing: Underlines the importance of adhering to standards like IEC 60287 and IEC 60502 for accurate and safe cable sizing, integrating these standards into EasyCableSizing.com for user-friendly access.
ib vogt – company

ib vogt is firmly committed to supporting the decarbonisation of the global electricity sector. The company focuses on the global development of turnkey PV plants and battery storage projects as well as the expansion of its IPP portfolio. In these areas, the company performs all integral services of the value chain from development, financing, and EPC, to O&M and asset management.
Headquartered in Berlin, Germany, ib vogt has established various offices across Europe, Asia Pacific, the Americas, and Africa as part of its presence in over 30 countries. The company works together with numerous partners globally, augmenting its in-house team of over 700 staff. ib vogt has built or has in construction more than 3.1 GW of PV power plants globally with a project pipeline of more than 45 GWp.

Thorne & Derrick distribute the most extensive range of MV HV Medium & High Voltage Cable Joints, Terminations & Connectors from manufacturers including 3M, Prysmian, Nexans Euromold, Elastimold, Pfisterer CONNEX & SEANEX.
Heat shrink, cold shrink, push-on and slip-over cable accessories enable the jointing, terminating and connection of 11kV-33kV and 66kV-132kV cables to oil, air or gas insulated switchgear, transformers, motors and overhead lines distributing electricity at MV HV.
T&D hold large stocks of 11kV 33kV 66kV Joints & Terminations suitable for XLPE, PILC and EPR cables, in both heat shrink and Cold Shrink technologies, to service the medium/high voltage power cable accessory requirements of UK and international customers.

Horizon Utility Supplies Introducing Cable Safety Improvements to UK DNO’s
January 25th, 2024
Press Release | 26.1.2024
Thorne & Derrick, the Specialist Distributor of LV HV Cable Accessories, Tooling & Substation Equipment, are delighted to announce a Partnership Agreement with Horizon Utility Supplies Ltd, one of the largest suppliers of Tools & Equipment to the UK DNO’s.
“Our Partnership Agreement is focussed on the introduction of the Vicera APU2.0 Cable Jointers Stand to the UK DNO’s and National Grid. Initial interest and sales uptake has been outstanding with immediate acceptance by several utility clients of Horizon and field trials ongoing with others. The APU2.0 is now available from stock at Horizon – please do hesitate contact them for further information, site demonstration or sales enquiries.”
“Thorne & Derrick introduced the Vicera range into the UK early last year and the product has been adopted by many High Voltage Power Contractors, ICP’s, Cable & Accessory Manufacturers including Nexans, 3M, Hellenic, NKT, Tyco and Pfisterer. Working alongside the team at Horizon we look forward to improving cable safety and working practices within the UK DNO’s,” comments Chris Dodds (Thorne & Derrick Sales & Marketing Manager).
“Horizon Utility Supplies are excited to announce our partnership with Thorne & Derrick, for promoting the Vicera APU2.0 Cable Jointer Stand into the major utilities in the Electricity Supply Industry. This collaboration allows us to use the strengths of both companies to deliver workplace solutions to our customers and reflects our shared dedication to meet the evolving needs of our industry.”
“The Vicera range of products offers a great opportunity to kick-start our Partnership, fitting perfectly into our portfolio of products for the supply of equipment for the care and maintenance of the utility network within UK DNO’s. We are very much looking forward to working with our partners at Thorne & Derrick,” comments Richard Casey (Horizon Utility Supplies, Managing Director).
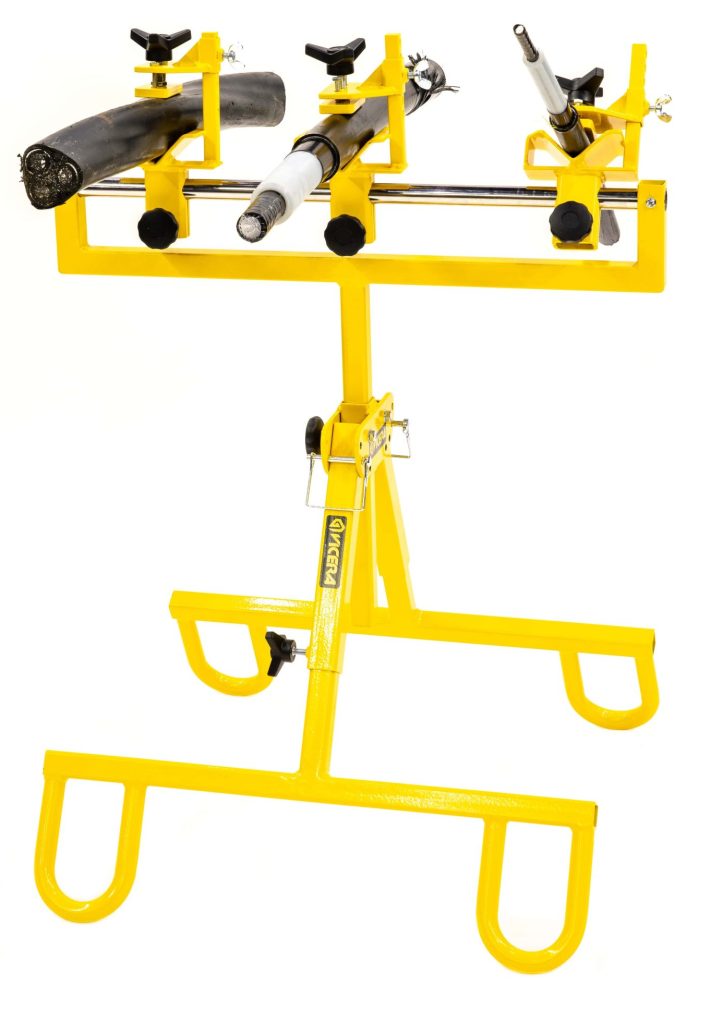


APU2.0 | Cable Stability & Support for MV HV Cable Jointing & Termination
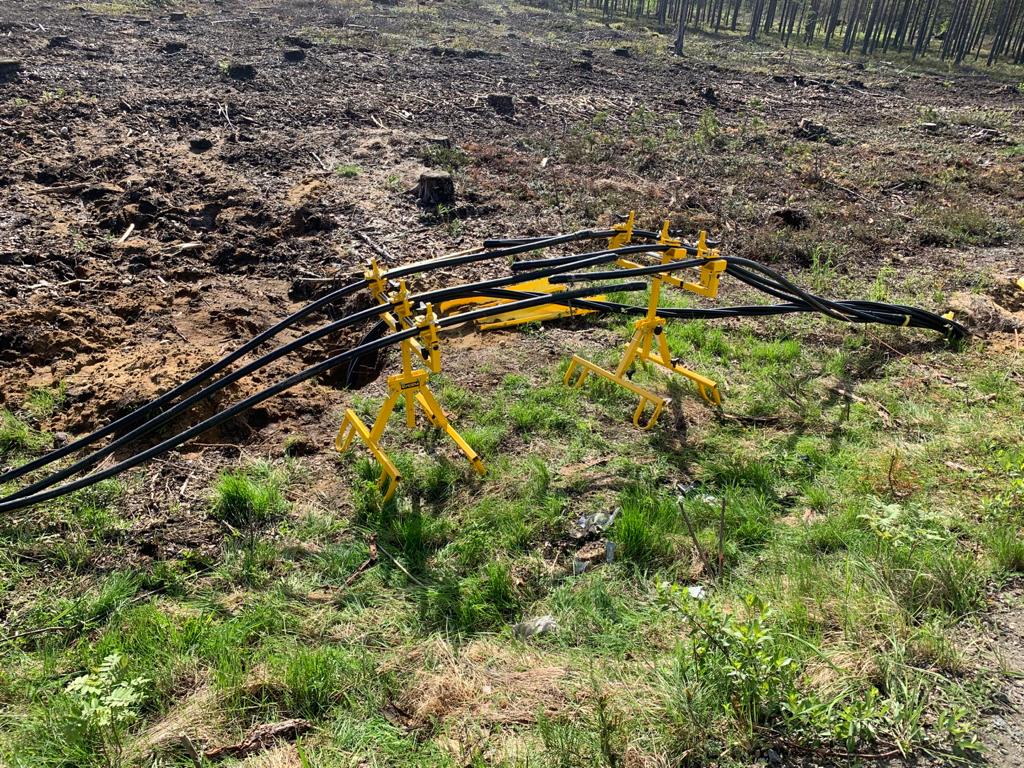
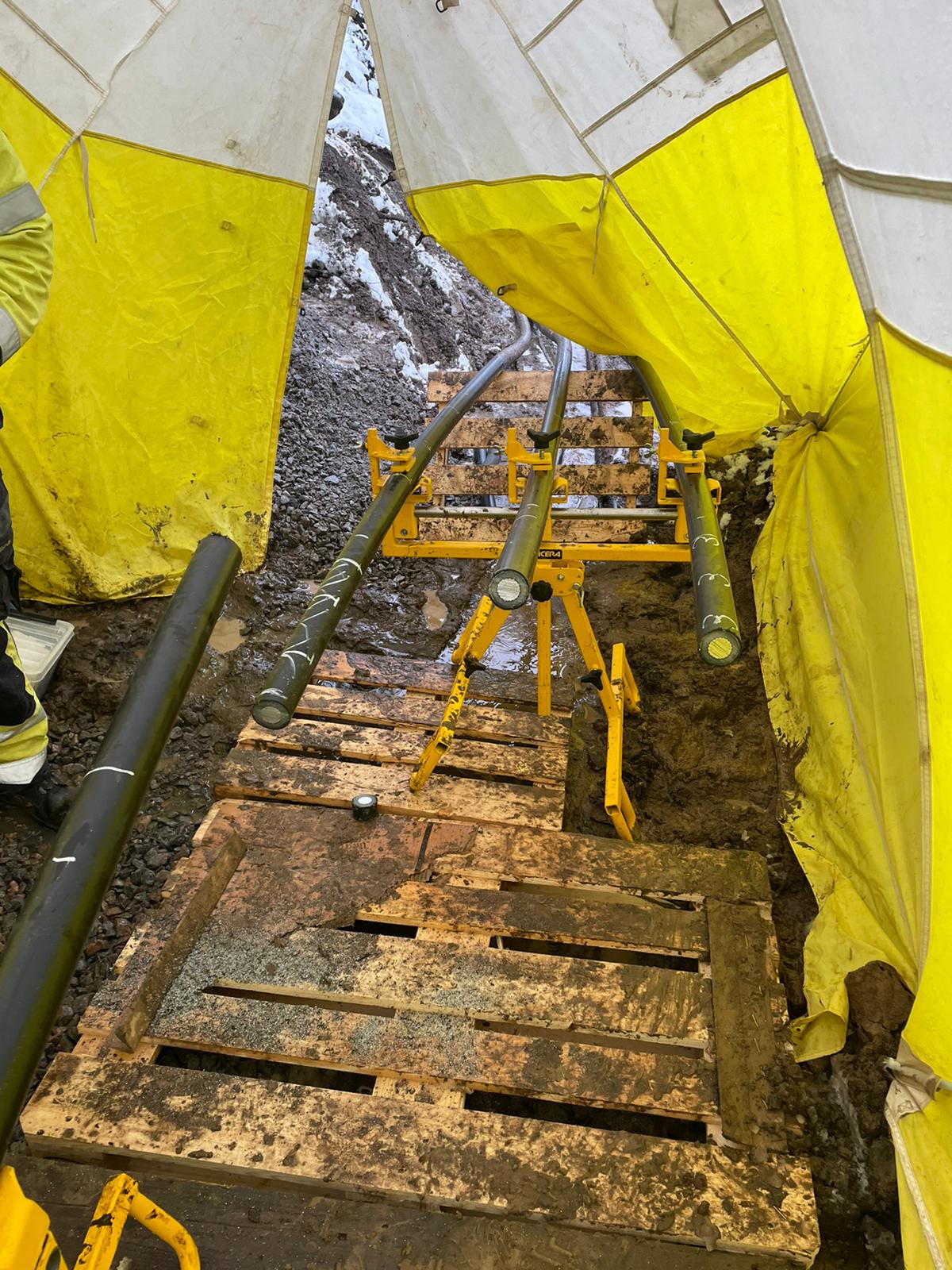
The Vicera APU2.0 Jointers Stand for both field or training centre use provides safe and stable support of Low, Medium & High Voltage Cables – the cable stands are suitable for cable diameters 18-90mm with adjustable height for substation, joint bays or trench use.
The Cable Joint Stands feature step-less lateral and tilt adjustment and high strength clamps to prevent cable slippage or movement while jointing – secure and balanced cables when Jointers are undertaking highly skill-sensitive cable preparation prevents inadvertent damage to cables and future potential O&M reliability.
The cable support stands are rugged and durable for outdoor use in joint bays and trenches in all ground terrain conditions – this includes the support of 11kV/33kV/66kV cables to enable precise cable preparation by the Jointer prior to installation of joints, terminations or connectors on medium/high voltage power cables.
Stability & Security of Power Cables
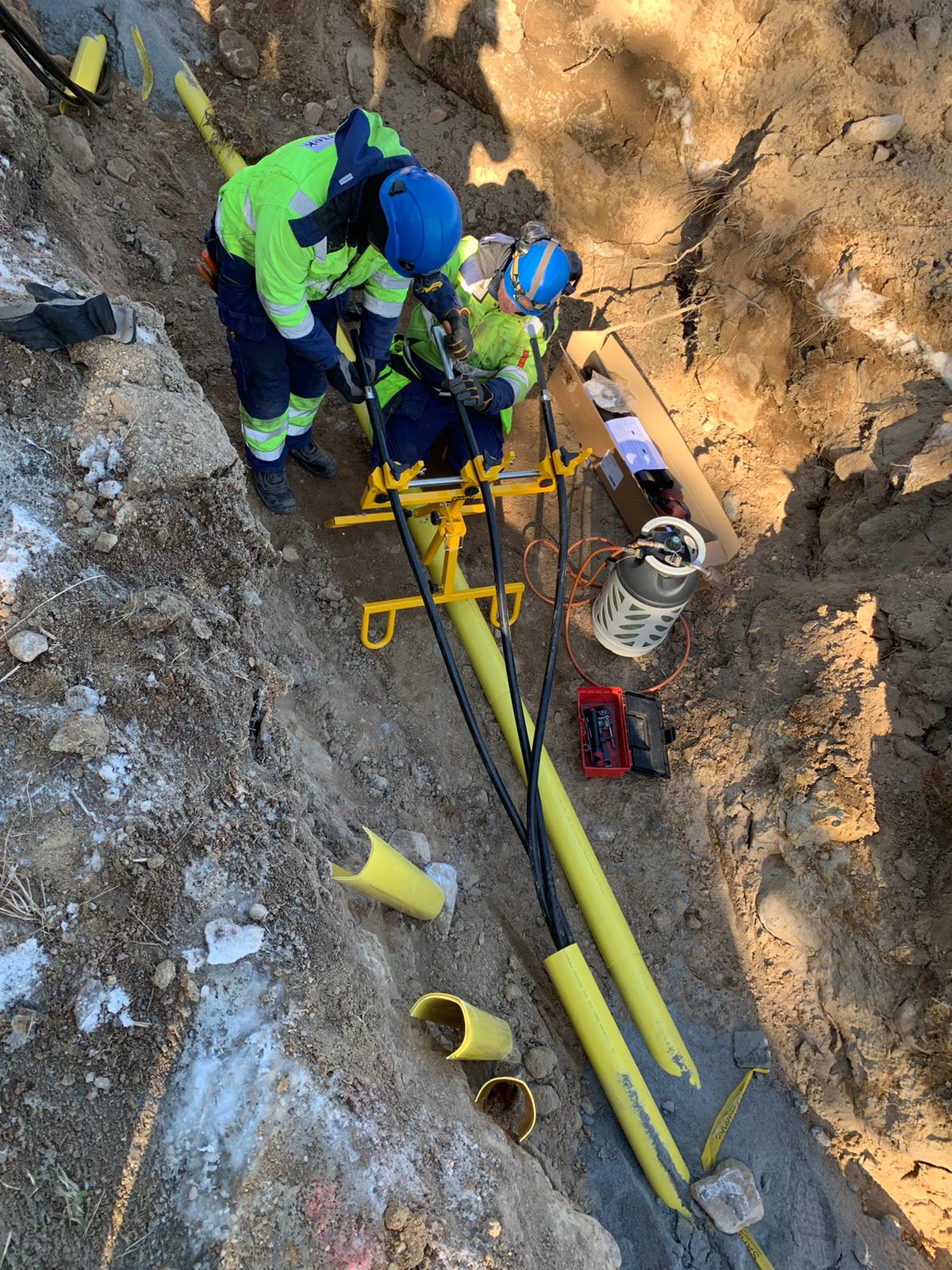
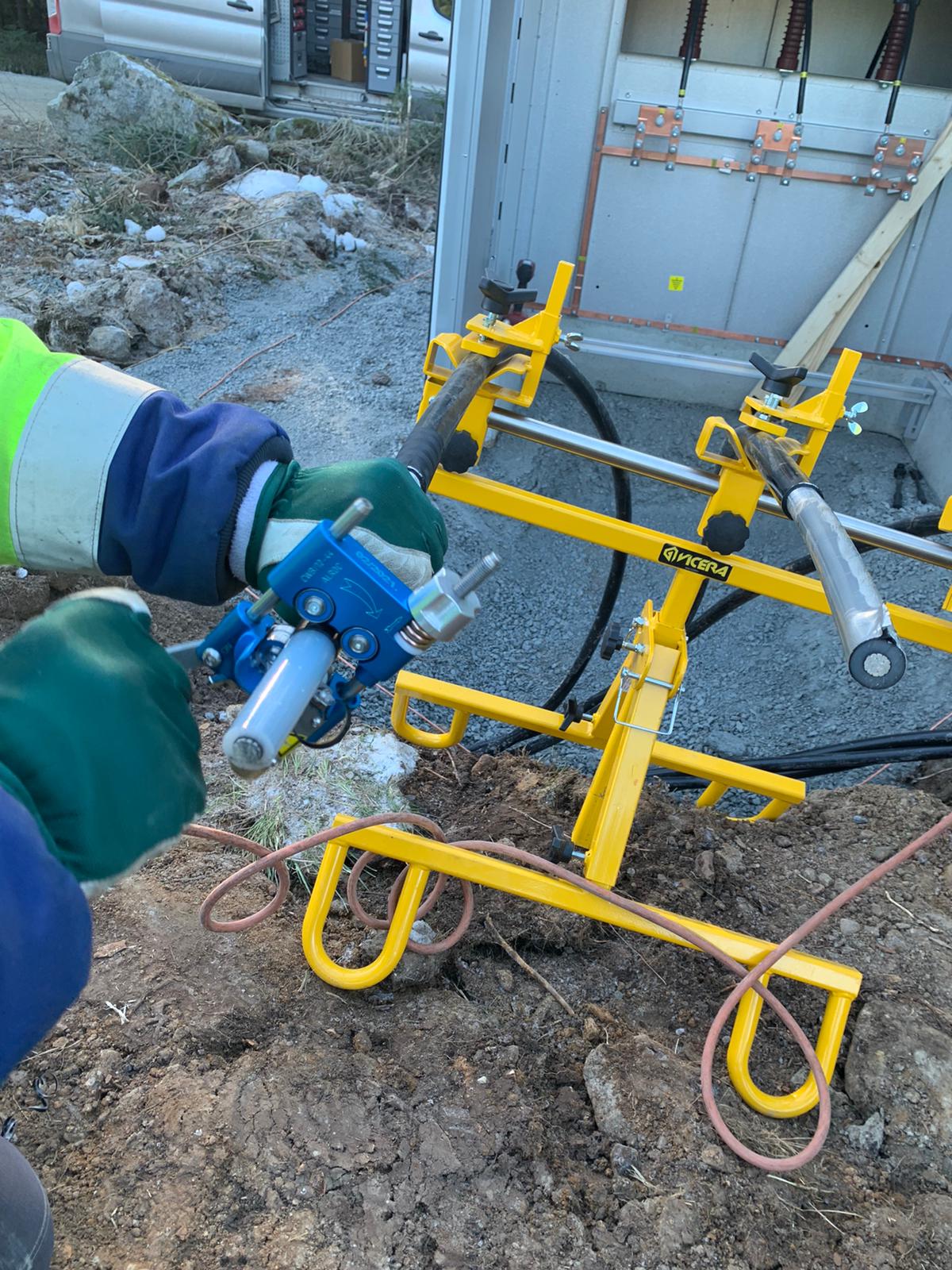
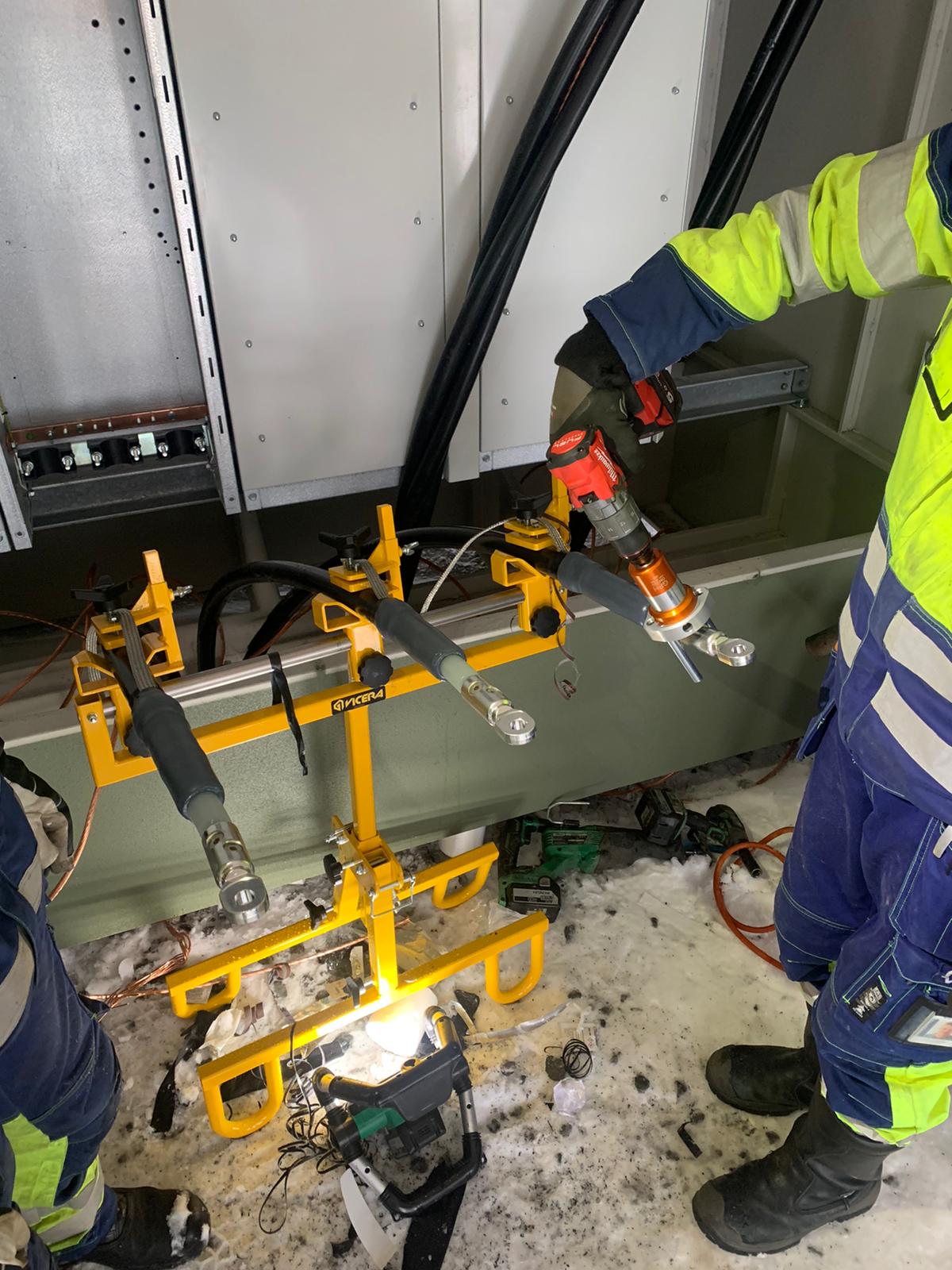






Horizon Utility Suppliers were established in 1996 specialising in the distribution of equipment and PPE for working live on overhead power lines and underground cables – Horizon hold a reputation for engineering custom-solutions to provide problem solving and innovative products for Linesmen, Jointers, Substation Fitters & Utility Engineers.
Tel: +44 (0)1275 342700 | [email protected]
Utility Troughs | Anderton Concrete Cable Troughs
October 30th, 2023
Anderton | Utility Cable Troughs
Concrete Utility Cable Troughs
Anderton’s range of straight, tee, cornered and angled cable trough allow you to easily adapt to the environment you are working in. Whether that is requiring the ability to change direction or take off to another part of the construction site.
Anderton’s optimised Utility Troughs and Lids deliver outstanding protection for your large power and communications services. Not only that, but they are also manufactured here in the UK.
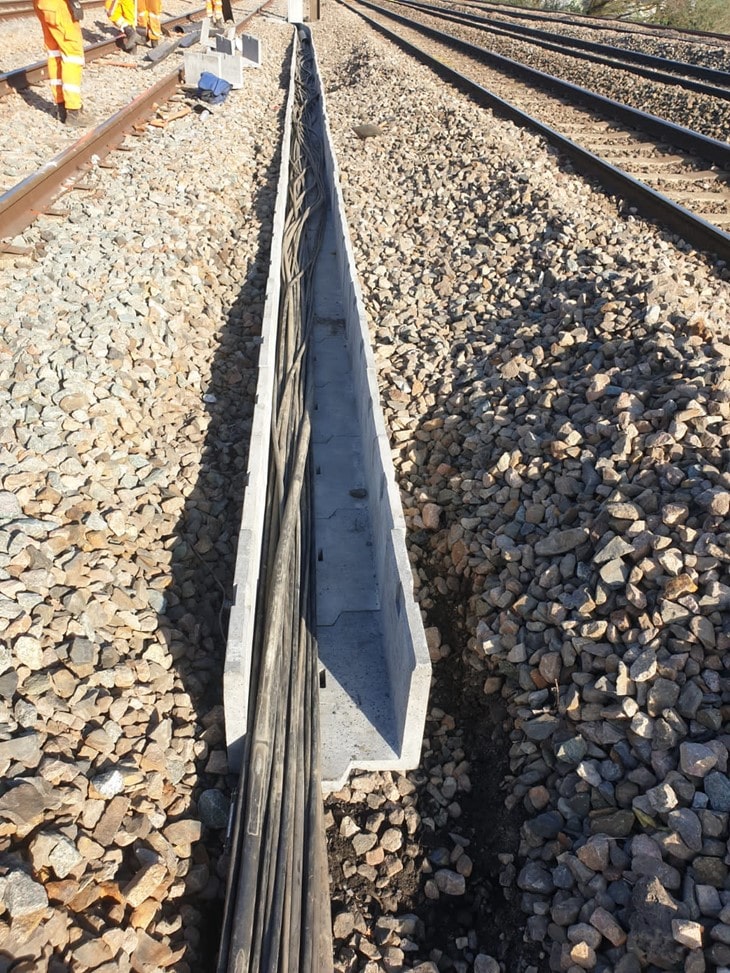

Utility Cable Troughs | Anderton
Utility Troughs and Lids
Anderton’s precast reinforced concrete Utility Troughs and Lids are used for a variety of purposes, from housing and protecting power and communications cables through to pipes carrying gas, water and chemicals. They safeguard against malicious or accidental damage and are easily accessible for maintenance and repair work. They can deliver up to 60% less embodied carbon than traditional concrete mixes.
cABLE tROUGHS
Anderton concrete cable troughs provide long term cable protection and easy access for cable repair, jointing and cable additions or diversions.
Cable troughing is an affordable sustainable solution to rail, highways and power industries for the protection and troughing of power, fibre optic, signal and rail cables including low and high voltages.
Concrete cable troughs are available in a variety of shapes and sizes ensuring cable protection solutions are possible for all routes of LV, MV & HV cables – rail cable trough provides trackside protection of power and S&T (Signal & Telecoms).
They are available for Pedestrian (LD) Occasional (LD) and Highways (HD) .
This is specified for cable containment in power, industrial, highways and nuclear projects.
Key Benefits of Concrete Cable Troughs
- Provides 60% less embodied carbon compared to traditional concrete mixes
- Safeguarding against accidental damage
- Easy to install
- Easy manual handling
- Anti-slip surface
Further Reading
- Anderton Concrete Cable Troughs
- LV Cable Joints & Terminations – Cold Shrink, Heat Shrink & Resin LV Cable Joints & Terminations
- GRC Cable Trough
Cable Sealing & Protection Case Studies
- Sealing Cables | Decarbonisation & Storage Depot Case Study
- Sealing HV Cables | A Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) Case Study
- Sealing Cables | 400kV Substation Cable Sealing using CSD Systems]

Specialist Distributors to the UK and international Offshore Wind & Renewable industry to provide safe and reliable LV HV Electrical Cable & Power Distribution Systems up to 66kV – we are highly customer responsive and absolutely committed to providing a world-class service. Contact our UK Power Team for competitive quotations, fast delivery from stock and technical support or training on all LV-HV products.
Since 1985, T&D have established an international reputation based on SERVICE | INTEGRITY | TRUST.
Contact us for 3M Electrical, ABB, Alroc, AN Wallis, CATU Electrical, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, CSD, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Euromold, Filoform , Furse, Lucy Electric & Zodion, Nexans, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec, Sicame, WT Henley.

Stockists & Suppliers | UK & International Projects




