Blog
3M Scotch Super 33+ Vinyl Electrical Tape
May 11th, 2021
3M Scotch Super 33+ Vinyl Electrical Tape
3M Electrical Tapes
Scotch Super 33+ Tapes
When it comes to the your most demanding electrical maintenance and repair jobs where failure and equipment downtime are simply not an option look no further than the 3M Scotch Super 33+ Vinyl Electrical Tape.
The vinyl electrical tape has excellent resistance to abrasion, moisture, alkalies, acids, corrosion and varying weather conditions (including UV exposure) and forms part of the 3M Scotch Electrical Tapes. Scotch Super 33+ can be used in hot or cold temperatures, high humidity or in contact with contaminants and aggressive substances making the tape suitable for inside and outdoor environments.
Highly conformable and super-stretchy and designed to perform continuously in ambient temperatures up to 105 °C
Scotch® Super 33+™ Vinyl Electrical Tape is designed for:
- Primary electrical insulation of electrical connections up to 600V
- Protective cable jacketing and repairs
- Weatherproofing
- Harnessing of wires and cables

Thorne & Derrick – 3M Electrical Stockists & Suppliers | Scotch Tapes | Scotchcast Resins | Cold Shrink Products | UK & Export Sales
3M Scotch Super 33+ can be used in combination with other 3M professional tapes.
| 3M Tapes | Tape Description | 3M Tape Image |
| Scotch Vinyl Colour Coding Electrical Tape 35 | Scotch Vinyl Colour Coding Electrical Tape 35 is the professional grade vinyl electrical tape available in nine fade resistant colours: blue, brown, grey, green, orange, red, violet, white, yellow, and pink. Outstanding electrical and mechanical properties make this tape excellent for use in phase identification, colour coding of motor leads and piping systems, and for marking safety areas. Scotch® Tape 35 applies smoothly and conforms well down to 0 °C. Maximum operation temperature is 105 °C. |
 |
| Scotch Rubber Splicing Tape 23 | Scotch® Rubber Splicing Tape 23 is made from Ethylene Propylene Rubber. This product fuses to itself in a short time after application to create a solid piece of rubber with high dielectric properties and is impenetrable by moisture. It’s a great option when working on jobs with voltage up to 69 kV. Split resistant, crack resistant and flag resistant within harsh environments. Rated for 90 °C continuous operating temperature and over- load temperatures of up to 130 °C. Scotch® Rubber Splicing Tape 23 features a liner, making it easy to cut and apply the tape in strips and in messy environments. |
 |
| Scotch Rubber Mastic Tape 2228 | This product combines the advantages of rubber and mastic tapes for fast application. Scotch® Rubber Mastic 2228 is a conformable self-fusing rubber electrical tape designed for electrical insulating and moisture sealing applications at 90 °C with an emergency overload rating of 130 °C. It is flexible and conformable over irregular shapes. The thick construction allows quick application build-up and padding, good for cable jacket repair. It is UV resist- ant and has excellent adhesion and sealing characteristics with copper, aluminium and power cable jacket material. |
 |
| 3M Scotchfil Electrical Insulation Putty | 3MTM Scotchfil Electrical Insulation Putty is a noncorrosive electrical grade compound in a tape form, easy to mould by hand down to 0 °C. It’s a great solution for smoothing uneven surfaces and eliminating voids until good overall padding is provided. 3MTM Scotchfil Putty is recognized as a splice insulation for electrical conductors at temperatures up to 80 °C when overwrapped with Scotch® Super 33+TM. |  |
➡ Specialist Application 3M Scotch Tapes: Fire Retardant, Fire Resistant, Arc Proofing, Cable Sheath & Jacket Repairing, Bundling & Harnessing Cables.
3M Scotch Electrical tapes are used to cable joint, splice, repair, seal and protect cables against abrasion, fire and corrosion – this includes LV-HV (11kV-33kV cables) – please contact T&D should you require assistance with selecting the correct tape.

Brugg Cable Tools For Jointing & Straightening HV EHV Cables
May 11th, 2021
Image: Dean Wilson – Owner Director at D.C. Jointing Ltd
D.C. Jointing Ltd are Specialist Electrical Cable Jointers with a team of 15 skilled staff in all aspects of offshore and onshore cable jointing up to 132kV, including cable jointing LV, HV and EHV, major projects with Regional Electricity Companies, onshore wind farms, offshore windfarms, power stations and National Grid.
Pictured: Brugg Cable Tools For Jointing & Straightening HV EHV Cables

BRUGG CABLES
The development of high voltage XLPE Cable Systems goes back to the 1960’s. Since then production and material technology have significantly improved, to provide reliable and maintenance-free products to the utility industry.
At present, numerous high voltage XLPE cable systems with nominal voltages up to 500 kV and with circuit lengths up to 40 km are in operation worldwide.

Cable systems are equipped with accessories, which have passed the relevant type tests pursuant to national and international standards, such as long-duration tests. As one of the first XLPE cable manufacturers worldwide Brugg Cables passed a Prequalification Test on a 400 kV XLPE Cable System according to the relevant international standard IEC 62067 (2001).
This test required one year of operation, along with the thermal monitoring of all cables, joints and terminations installed. It was successfully completed at CESI Laboratory in Milan, Italy in 2004.
As one of just a few providers worldwide, Brugg Cables can offer a broad range of both XLPE cables (up to 500 kV) and oil-filled cables (up to 400 kV) as well as their accessories.

Jointers blog
Subscribe now to our POWER NEWSLETTER– a monthly email circulation packed with news, projects, videos, technical tips, training information, promotions, webinars, career opportunities and white papers.
Includes access to our popular JOINTERS BLOG with contributions from utility professionals, linesmen and cable jointers working on MV HV EHV cables and overhead lines typically at 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and up to 132kV.
Top Benefits of High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission
May 11th, 2021A Benchmark Brief
from Burns & McDonnell
Burns & McDonnell are a family of companies with an unmatched team of 7,600 engineers, construction professionals, architects, technologists and scientists. Their singular mission since 1898 has been to make clients successful – ‘When we plan, design, permit, construct and manage projects worldwide, we do it like we own it.’
Burns & McDonnell is a 100% employee-owned company who tackle every technical challenge, every complex detail, with the intent and attention of an owner. It’s what brings clients back, project after project.
Benefits of HVDC Transmission
As the demand for power is increasing, government policies are providing incentives to utilities for adopting renewable energy sources. Utilities are investing time and money to improve the transmission of renewables from offshore wind and solar.
Today, most power grids use high-voltage alternating current (HVAC) for transporting energy over long distances, but that technology is susceptible to losses during transmission, has limits on power transfer over long distances, and has limited power control capability. A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) system converts the power from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) at the sending end, transmits the power using DC, converts the power back from DC to AC at the receiving end, and delivers the power to the receiving end AC grid.
Application of HVDC technology is expanding not only for large bulk power transfer over long distances, but also in the interconnection of renewable energy sources.
Bulk Power Transmission Efficiencies
Transmission cost depends on numerous factors, such as the size and quantity of conductors, equipment needed at the terminal stations, and transmission tower size.
HVDC is particularly well suited for bulk power transmission over long distances for several reasons:
- A bipolar HVDC system consisting of two high-voltage conductors on one tower offers reliability comparable to a double-circuit HVAC line, significantly reducing the transmission line costs and right-of-way requirements.
- Losses in a transmission line depend on the resistance of the line. One factor that impacts the resistance is skin effect, which causes the effective resistance to increase with increasing AC frequency. Use of DC eliminates the skin effect, reducing overall transmission losses.
HVDC transmission systems require converter stations at each end of the line to convert the AC to DC and back. Cost of HVDC converter stations can be substantially more than a conventional AC substation with similar power throughput. That expense may be counterbalanced by reduced transmission line costs and reduced losses. This becomes more evident as the distance and/or power transfer level increases.
Cable Length Advantage
HVAC transmission cable length is limited because as the length of cable increases, the capacitive charging current increases. It can reach a point that the capacitive charging current approaches the total current carrying capacity of the cable. HVDC has no capacitive charging current, and higher levels of power can be delivered over longer distances. HVDC cable length is theoretically only limited by capital cost. Enabled applications include:
- Connection of offshore wind farms: As development of offshore wind generation assets increases, the location of wind turbines generators is moving farther from the shore. The increasing distances between the generators and the onshore point of interconnection means the necessary cable length is increasing. HVDC can be a viable transmission option, unlocking the true potential of renewable energy.
- Transmission into congested areas: Increasing demand, particularly in congested areas, coupled with challenges of accessing rights-of-way has driven the need to maximize power transfer and a push to go underground. HVDC is an excellent option for high-power cable transmission installations, maximizing the amount of power transfer per cable.
Power Controllability
Within an HVAC system, the ability to control power flows in any given parallel path is limited. Power flows are dictated by the relative impedance of various parallel paths from a given source of generation to a given load. HVDC, on the other hand, offers very fast and accurate control of the power flowing within its system. The operator can select the amount of power to be transmitted over the link. If that power is available at the sending end, it is then converted to DC, transmitted to the receiving end, converted back to AC and injected into the receiving AC system. Auxiliary control functions can further enhance AC system’s stability by providing frequency control and damping of power swings within the AC grid.
HVDC systems offer higher transmission capability and lower transmission losses over long distances than AC and provide better ability to control power flows. Additionally, they provide the ability to transmit more power over longer lengths of cables, making them an attractive alternative for the transition to renewable energy sources.

T&D | LV MV HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment
Thorne & Derrick
T&D are Specialist Distributors to UK Distribution Network Operators (DNO’s), NERS Registered Service Providers, ICP’s and HV Jointing Contractors of an extensive range of LV, MV & HV Jointing, Earthing, Substation & Electrical Eqpt – this includes 11kV/33kV/66kV cable joints, terminations and connectors for both DNO and private network applications.
Contact our UK Power Team for competitive quotations, fast delivery from stock and technical support or training on all LV-HV products.
All international sales enquiries can be serviced and supplied by our Export Power Team.
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV

Cable Pulling & Laying | Technical Library
May 6th, 2021
Technical Library & Resources | Education & Learning with SEB International
Thorne & Derrick provide competitive prices and fast delivery as the main UK distributor of SEB Cable Pulling & Laying Products including handling and installation equipment for power (land and subsea), umbilicals, fibre and telecoms cables. SEB products are typically used to install transmission, distribution and medium/high voltage substation power cables into ducts or trenches, LV up to 400kV.
Thorne & Derrick International distribute the most extensive range of Cable Pulling & Laying Equipment to enable the installation of LV, MV HV Cables into underground trench or duct – products are also stocked for fibre optic blowing, OHL stringing, subsea trenching, offshore umbilical installations and pulling armoured cables onto cable tray.
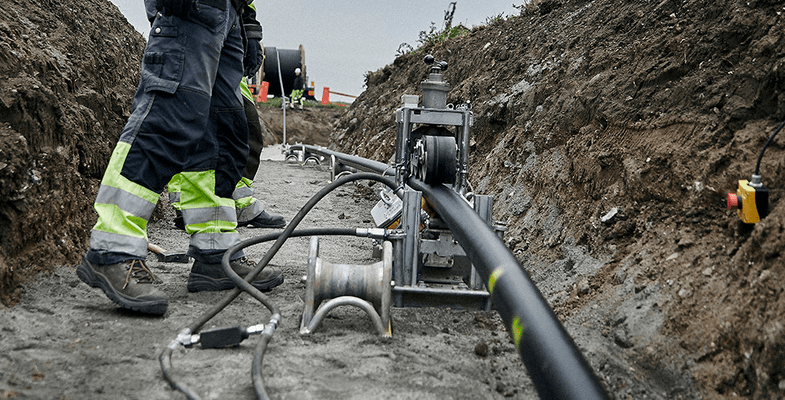
Cable Pulling & Laying
TOP 20 BLOGS
See our collection of the Top 20 Cable Laying Blogs featuring SEB International, and their range of LV, MV & HV Cable Pulling and Cable Laying products:
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cables Into Trench
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cables Into Duct
- How Do Cable Socks React To Salt Water?
- Cable Pull Calculations – Installing & Pulling Heavy Cables
- Duct Rod Pushers | Installing Cables Into Conduits
- Cable Laying, Installation & Support Products | Offshore Oil & Gas Cables
- MV HV Cable Laying, Installation & Support Products | Offshore Windfarms
- Cable Pulling | Safe Pulling of Cables Using Manual Laying
- Lace Up Cable Socks – A Guide For Users When Pulling Cables
- Cable Socks – Technical Guide for Safe Cable Pulling Using Cable Socks
- What Is The Maximum Distance For Ease of HV Cable Pulling Between Manholes
- Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Duct Laying Guide From BT Openreach
- Stokbord®Drum | 33kV Cable Protection for Underground Medium Voltage Cables
- Stokbord Drum | Protection of High Voltage Electricity Cables
- Which Access Chamber Can Be Built Faster?
- Cable Winch | Customised & Refurbished 5 Tonne Cable Pulling Winch
- Cable Pulling | Safe Pulling of Cables Using Motorised Pullers
- Cable Laying | The Importance of Cable Installation Instructions
- Cable Drums | Recommended Transport & Storage
- How to Prepare Cables To Avoid Cable Damages & Faults
Further Reading | Cable Drum Handling & Laying Cables | A Guide from Nexans
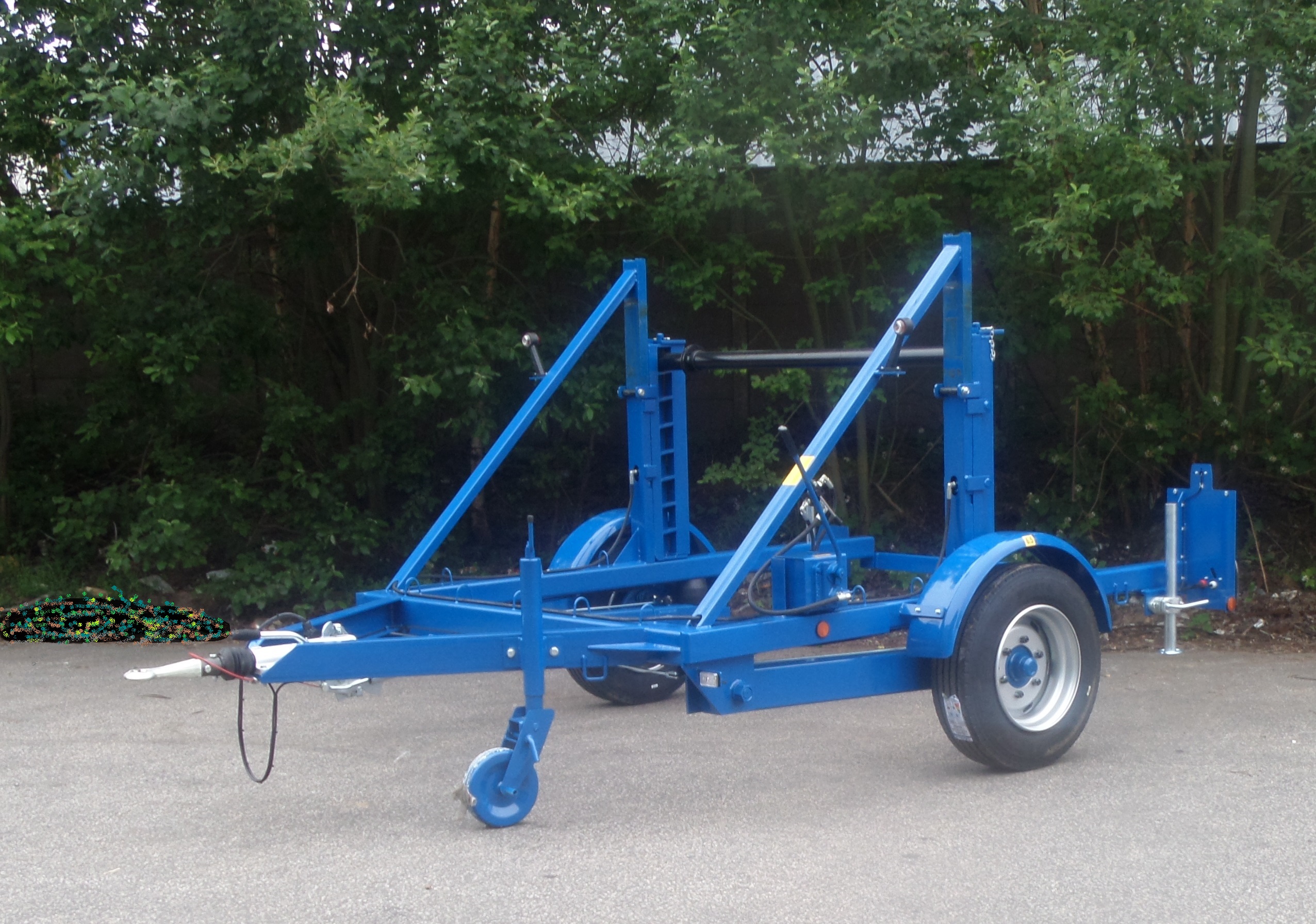


T&D distribute the complete range of LV-HV Cable Pulling and Laying Equipment including cable rollers, cable socks, drum jacks, drum trailers, cable lubricant, underground cable protection and conduit duct rod.

THORNE & DERRICK are Specialist Distributors of LV HV Cable Jointing, Earthing, Substation & Electrical Eqpt up to 66kV – this includes the most extensive range of Ex Stock Innovation Tooling to facilitate safe and reliable preparation, termination and installation of cables.
MV HV High Voltage Cable Joints | Cable Terminations | Cable Connectors | Distributed from Stock | UK & Export Sales
Jointing 44kV High Voltage Submarine Cables Using 3M Cold Shrink Splices
May 6th, 2021Images Courtesy of: Douglas Page (Instructor & Cable Splicer at Hydro One Training and Development Services).
HV Cable Splicers: Douglas Page & Jeff Silliphant.
Application: 3M 44kV Cold Shrink Submarine Cable Joint (Single Core 250 MCM).
Location: Lake Couchiching, Ontario. Canada.
Please note aspects of the installation were unable to be photographed as 4 hands were required simultaneously to be cable jointing and no stand-in photographer was available.
Let’s start Cable Jointing….
1. The cable splicing barge comes alongside the buoy marker for a previously installed cable and pulls it up onto the barge, secures it, and anchors all four corners of the barge.
2. The “reel” barge backs up and connects to the cable splicing barge and anchors all four corners, the cable is pulled to the cable splice point and secured.
3. Both 44kV cables are prepared to manufacturers specifications, in this case they were prepared using Speedy Systems high voltage cable preparation tools not hand tools.
4. All of the 3M Cold Shrink Cable Termination kit parts are slid on the appropriate sides and the cable is crimped together.
5. 3M supplied silicon grease is applied by the HV cable splicers – we believe it was changed to colour red to determine if it was actually used in the event of a future cable splice failure.
6. Inner 3M Cold Shrink cable splice body is cold shrink installed without the requirement for a heat source associated with the jointing of cables using heat shrink cable terminations. Aligned with marker tapes previously installed, then the concentric neutrals are brought back across the cable splice.
7. In this situation the high voltage splicing design was to have the neutrals individually crimped to each other, a soft mastic bed is made for the crimp sleeves to lie in to prevent damage to the insulation shield.
8. After the neutrals are all crimped and the shaped into their final position for the cable splice.
9. Once shaped they are evenly spread out and held in place to prevent hang up points for installation of the outer jacket 3M Cold Shrink tube.
10. Very important, the cable jacket is abraded, then two rows of multiple layers of aqua-seal mastic is installed, then the outer jacket is cold shrunk on.
11. To enhance the water-blocking ability of the cable joint the HV cable splicer applies extra wraps of 3M mastic tape.

12. After the outer jacket is installed and sealed using mastic and tape then the submarine armour is wrapped back around the high voltage cable .
13. The submarine cable armour wires are then individually crimped together using Burndy crimping tools and then wrapped in mastic and tape.
14. The entire 3M Cold Shrink cable splice is covered in three layers of 3M Armorcast, (installed wet and sets solid). Then all anchors are pulled, the barges stay attached and the cable barge travels the route, paying off the cable to the end of the reel.

Jointers blog
Subscribe now to our POWER NEWSLETTER– a monthly email circulation packed with news, projects, videos, technical tips, training information, promotions, webinars, career opportunities and white papers.
Includes access to our popular JOINTERS BLOG with contributions from utility professionals, linesmen and cable jointers working on MV HV EHV cables and overhead lines typically at 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and up to 132kV.






