Blog
BAND-FAST Reduces Cable Management Material & Labour Costs by 50%
March 30th, 2021Stainless Steel Cable Clamps
BAND-IT BAND-FAST
The Aker H-6e Drilling Rig is one of the largest and most sophisticated semisubmersibles ever commissioned. It is no surprise that every detail was carefully considered in its development – including how to best secure and clamps cables running through the rig.
Traditionally, cable cleats have been used for this application.
However, Aker Solutions was looking for a less expensive, easier to install and more lightweight option for cable management, one that also would minimize the risk of short circuits.
BAND-IT PPA-coated BAND-FAST clamps were recommended.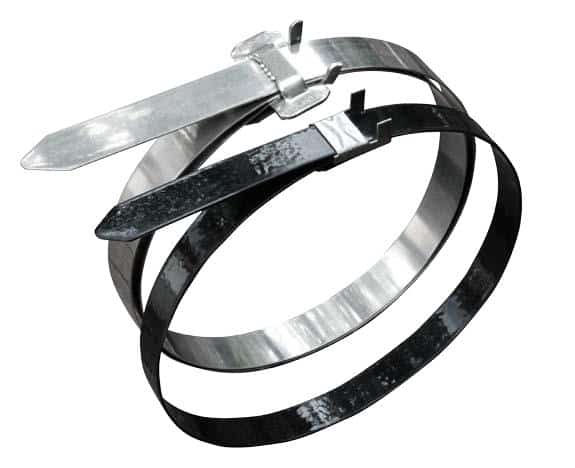
BAND-FAST ACES THE TEST
Adopting a new solution calls for rigorous evaluation. You need to assure not just cost savings but performance. To put the recommended clamp to the test, SINTEF (Norway’s largest independent research organization in Scandinavia) and Aker Solutions jointly evaluated the suitability of 5/8″ wide PPA Coated BAND-FAST clamps as an alternative to cable cleats under short circuit conditions.

BAND-FAST scored beyond expectations, and as a result more than 40,000 were used on the project.
Specifications for BAND-FAST Used on the Aker H-6e Rig
- 316 Stainless Steel, 5/8″ wide
- PPA 571 Coating: halogen-free, low smoke & fume
- DNV and GL Type approved materials
WHAT MAKES BAND-FAST BETTER?
BAND-FAST clamps are a superior choice for many reasons. The lower profile of finished cable runs save space, and the PPA coating reduces the risk of damaging cables as they are pulled. Using the BAND-IT C075 installation tool, the captive sealing clip is quickly and precisely locked into place when fastening,
Overall, labour is reduced by 50%, compared to installing cleats.
When it comes to the costs, it’s simple: clamps are less expensive than cable cleats. That difference really adds up when you consider that there are more than 40,000 fixing points on the Aker H-6e.

BAND-IT C075 Bantam Tool
Sometimes, One Size Fits All!
One dilemma with cleats is that you need to invest in a comprehensive stock to accommodate different sizes of wires. BAND-FAST clamps easily adjust to accommodate a wide range of cables and will hold single, trefoil and quadrafoil configurations.
By going with clamps instead of cleats, Aker was able to drastically reduce their inventory. A bonus is that the reduced weight of materials on rig leads to increased production capability.
More Than Just Cost Savings
Any reduction in risk is welcome in the Oil & Gas industry.
BAND-FAST clamps are light and easy to carry, which is precisely opposite of cleats. Their low weight translates into reduced fatigue and less stress-related injuries.
There is no danger of being hit by an accidentally dropped cleat, and in this case Aker further reduced drop-risk by adding a wrist strap to the installation tool – a simple yet important solution.
➡ In addition to 316 Stainless Steel, BAND-FAST is also available in 201 Stainless Steel, Titanium, Alloy 400, Alloy 625, and other materials upon request.
BAND-IT Can Help You Make Changes With Confidence
Balancing the potential positive impact of making a design change against the established specification can be risky. You need to make that decision with confidence. When it’s time for you to re-evaluate your cable management, turn to BAND-IT.
Thorne & Derrick can help you find the correct, cost-effective, tested solution that exceeds your performance requirements and helps cut costs.

➡ Thorne & Derrick stock and distribute the complete range of Band & Buckle products and tools manufactured by BAND-IT from stainless steel used to fasten, strap and clamp LV MV HV cables, pipes and hoses.
See also Cable Cleats | Cable Banding | Cable Ties | Cable Tags | Cable Markers

Innovation : Heat-Shrinkable Joint with Triple Layer Tube By Nexans
March 30th, 2021
Nexans JTS Heat Shrink Joints
JTS Triple Wall Heat Shrink Joints
By Nexans
Simple & Shorter Installation Time with Reduced Risk of Failure
-
Republished Article From Transmission & Distribution - Australasian Power Technologies By Nexans Australmold
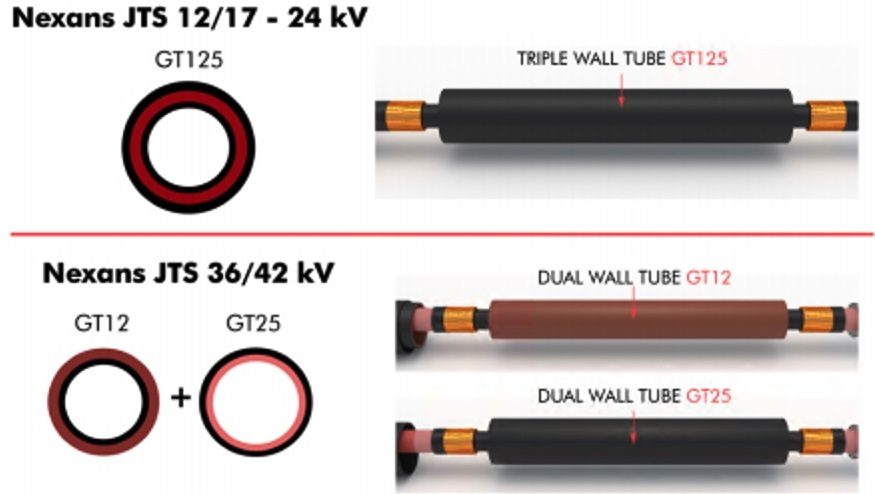
The Nexans Italy site of Offida launches the JTS, its new heat-shrinkable joint with triple layer tube. The triple layer heat shrink tube represents a technical innovation that allows MV cable jointers to heat only 1 tube instead of 3 for 12kV to 24kV applications, and 2 tubes instead of 3 for 36kV to 42kV cable jointing applications.
Nexans have reduced complexity and the time to install the cable joint, while improving the quality of the global connection by reducing its operations. The new range of Nexans JTS heat-shrinkable medium-voltage straight joints is compatible with MV single- or three-core polymeric cables with copper wire screen, copper tape screen or with aluminium tape screen.
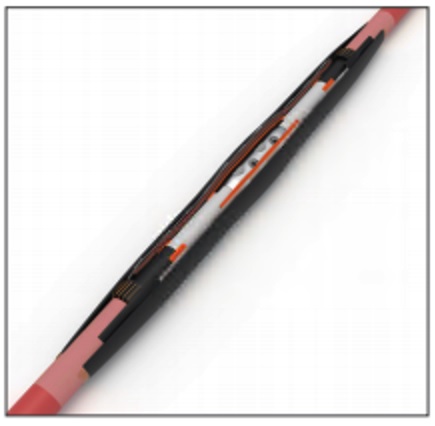

For 12kV to 24kV applications, the Nexans JTS 17/24 heat-shrinkable joint is the new high performance, compact and easy-to install joint: a single body with all electrical functions integrated!
The JTS 17/24 is using the Nexans “TRIPLE GT125”, an integrated stress control field, insulating and conductive tube, which can support voltage classes up to 24kV.
A double layer pad with conductive rubber inside and HK orange mastic outside ensure a Faraday cage and smooth the effect of the electrical field and of the voltage gradient in the connector area.
For ANZ customers, the electrical continuity of the screen is ensured by copper screened mesh and two mechanical shear-off screen links. Finally, the outer sheath is restored with heavy wall adhesive lined tubing. MC types are supplied with GPH® mechanical connectors.
For 36kV to 42kV applications, the Nexans JTS 36/42 heat-shrinkable joint is also a high performance, compact and easy-to-install cable joint: double bodies with all the electrical functions integrated!
The JTS 36/42 is using an integrated coextruded “stress control field + insulating” (DUAL GT12) nested in a coextruded “insulating + conductive” tube (DUAL GT25), which can support voltage classes up to 42kV.
All the rest is the same as the 17-24JTS.

Nexans Italy in Offida has an extensive know-how in the fields of heat-shrinkable materials, as well as mastics. The heat-shrinkable (HS) technology dates from the 1960s. In Nexans, thanks to a strong R&D activity, the heat shrink technology has been improved and tailored for 50 years, according to the evolution of the market needs.
Today, Nexans produce a complete range of heat shrink tubes to cover Low (LV) and Medium (MV) voltage cable jointing applications up-to 52kV in our Extruders/Expanders lines, with diameters starting from 20mm till 300mm and up to 4 different layers.
Mastics for electrical use: the complete range of Nexans mastics have been developed and are manufactured totally in the company. They are produced by means of a 630 litre mixer in a dedicated part of the plant. Resins for electrical use, casting and insulating have been designed by Nexans Italy for more than 35 years.

Nexans R&D team of engineers and technicians use the most advanced tools and equipment to create, verify and test all our products among the different laboratories and material research centres of the Nexans Group.
Nexans Power Accessories Italy is well equipped to perform physical and chemical analysis of insulating, anti-tracking, and stress control materials, both for tubing and mastics. We supply jointer training and failure analysis for all our customers. In the electrical laboratory we can perform type test and routine test (PD measurement at hot and ambient temperature, heating cycles in air and water, humidity and salt fog). For steel wired armour cable and termite protection please contact your local sales office.
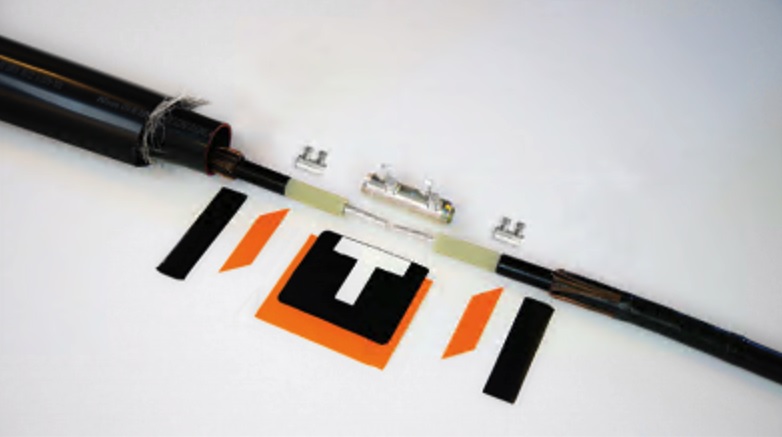
NEXANS JTS 17/24KV
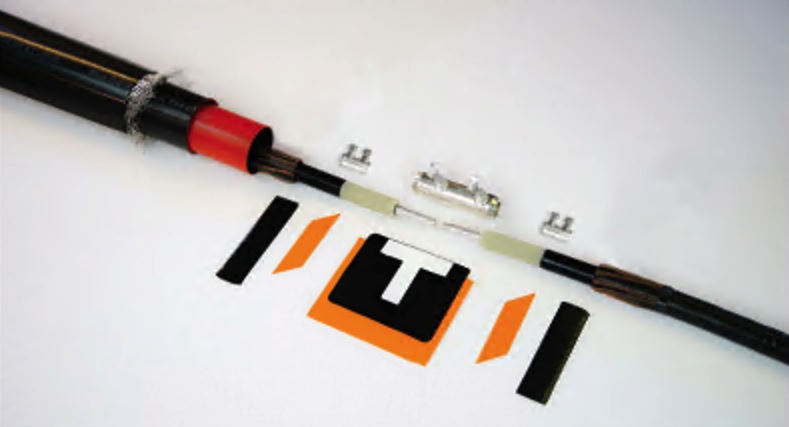

NEXANS JTS 36/42KV
Nexans JTS Heat-Shrinkable joint
Features & Benefits
- Tube nesting / positioning and parking issues eliminated => typical cable jointing errors eliminated
- Only one tube to shrink for the 3 functions (stress control – insulation – conductive) for voltage classes 12/17kV & 24kV
- Only two tubes to shrink for the 3 functions (stress control – insulation – conductive) for voltage classes 36kV & 42kV
- Reduced installation time / training time, with standard cable preparation tool work
- Simplified stress control with 2-layer plate as used with Nexans cold shrink joints => no need to conform the mastic before shrinking the tube
- Design adapted for all type and brands of mechanical / crimping connectors
Nexans JTS Heat-Shrinkable joint
highlights
- Short and slim design cable joint
- Quick and easy to install for medium voltage power cable systems
- Excellent electrical insulating properties
- Advanced screen connection and armour continuity of MV joint
- Heavy wall tubing for high mechanical strength and impact resistance
- Proof against water penetration and chemicals aggression
- Stabilised UV protection of the cable
- Halogen-free material content
- Compliant to reach regulations
- Premium technical support up to medium/high voltage classes
- Made in EU

Nexans manufactured Cable Accessories are in extensive service throughout the UK DNO power grid – the Euromold brand of separable connectors are approved and are approved by several DNO/IDNO operators dependent on the product, voltage and network.
Nexans joints and terminations are increasingly preferred and adopted by NERS Accredited Independent Connection Providers (ICPs) working on 11kV private networks.
Thorne & Derrick have an International Distribution Agreement with Nexans Power Accessories UK and are their main stockists and suppliers for their range of Heat Shrink Joints & Terminations up to 33kV.


Specifying For Data Centre Safety : A Guide To Fire Protection For Vital Cabling
March 30th, 2021Author: Alex Smith, Technical Director at Flexible Conduit Manufacturer Flexicon
![]()
Commercial building contractors and data installers alike have a legal obligation to ensure that cables are suitably fire performance rated for the application and location.
According to its tenth annual data centre survey, the Uptime Institute claims that many operators admit that most downtime incidents could be avoided if they were to invest more in the resiliency of their facilities.
This not only apply to critical infrastructure affected by a mains power outage, but also extends to the appropriate protection of vital data and power cabling, especially in the event of a fire.
Let’s look at some of the common myths around fire protection performance and the array of differing standards in place, and details why operators should ensure that their cable protection meets all low fire hazard criteria requirements.
The background
In a data centre environment, all power cables seen as a possible cause of fire need to be jacketed in materials that provide the necessary fire protection for the given installation.
Commercial building contractors and data installers alike have a legal obligation to ensure that cables are suitably fire performance rated for the application and location and therefore, comply to the European cable fire standard, BS EN 50575. This includes classifications of ‘reaction to fire performance’ and considers heat release, flame spread and propagation, smoke production, flaming droplets and acidity.
BS 7671, commonly referred to as the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations, calls up EN 61386 for flexible conduit performance requirements, including fire. However, this standard for conduit systems, which was first published in 2008, only addresses non-flame propagation (self-extinguishing) – and no other fire performance properties such as enhanced flame retardancy, smoke and toxic fume emission are included.
This can give rise to a potentially dangerous situation where cables can be laid in flexible conduit that, by its standard, only needs to clarify if it is self-extinguishing and does not offer a comprehensive level of fire performance.
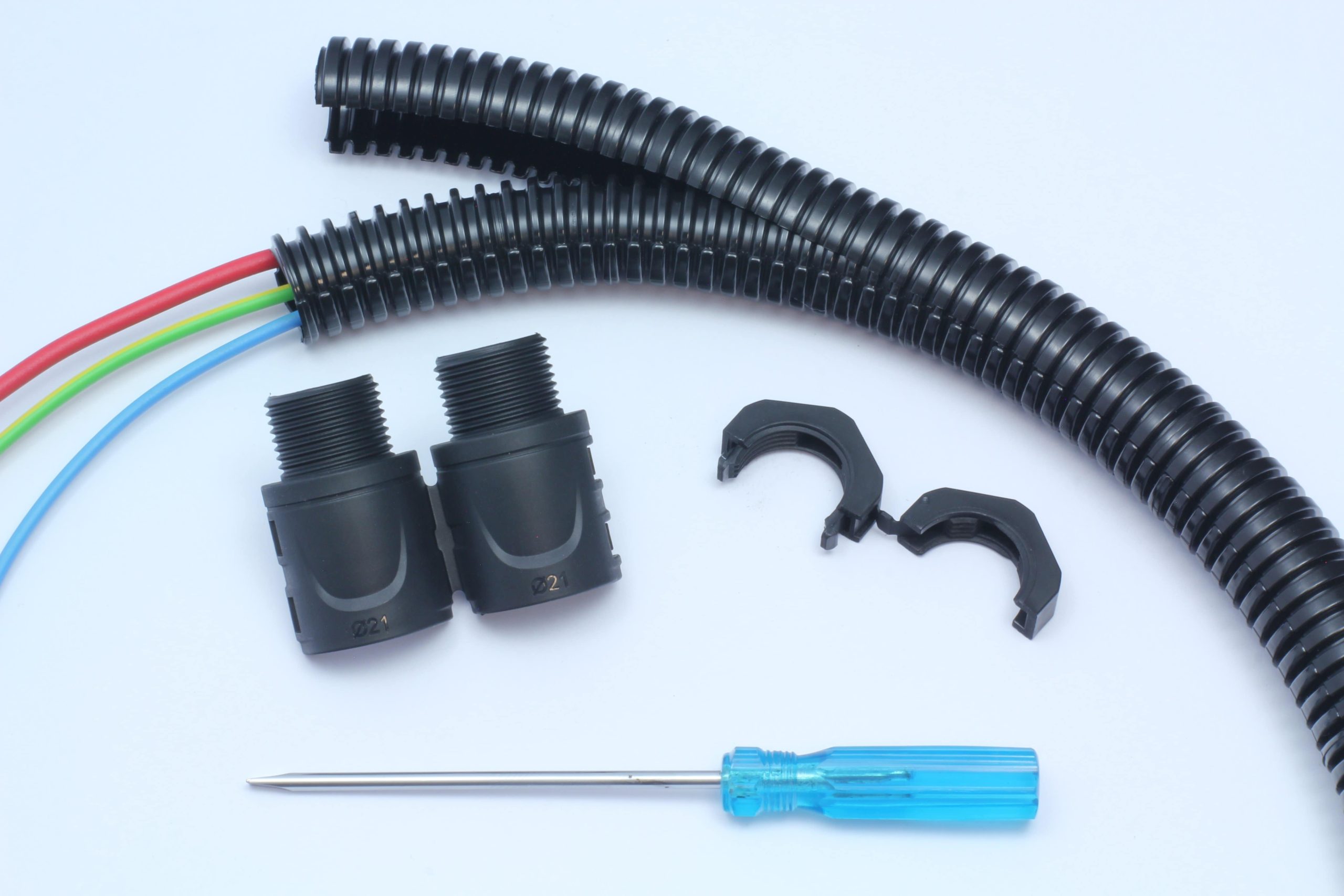

Flexicon Flexible Conduit
Fire hazard assessment
Fire hazard assessment is essential in buildings where there is a significant risk to people, processes or property, such as in a data centre or server room. This assessment should include possible sources and the likelihood of a fire starting and the consequences of such a fire including; evacuation and safety of people, loss of service and damage to equipment.
When assessing the fire hazard, suppliers should work with customers to assess the installation and environment that the conduit system will be used in. For example, in a data centre environment, factors such as high temperatures in confined server rooms should be considered. Also, conduit systems containing halogens, such as PVC, will give off chlorine acid gas in a fire that can destroy electronic equipment in another part of the building.
Almost all applications will require non-flame propagating (self-extinguishing) as called for within the UK wiring Regulations (BS 7671) and tested by means of the flame propagation test in EN 61386 as a bare minimum. Many customers will assume that this basic requirement will be met by any flexible conduit they specify, but this is not always the case.
Meeting low fire hazard specification
For a product to be classified as low fire hazard, it must display four clearly defined characteristics. It must be highly flame retardant, have low smoke emission, low toxic fumes and be halogen-free.
All metal conduit systems are an inherently low fire hazard as there is no plastic to burn, however, most conduit systems are now plastic coated or all plastic so their performance needs to be assessed.
Traditionally, Halogen Free conduits have been specified, often based on the common misconception that they offer comprehensive fire protection performance. Although such a conduit may prevent the generation of toxic gases in some settings, it does not mean necessarily that it is also flame retardant or have low smoke properties and may still be flammable if exposed to a heat source.
Add to this the fact that there is no single European classification standard for low fire hazard cable management products that defines terms, test methods and results expected, and it is easy to see why there is confusion in the industry.
Terms are commonly used which suggest that adequate fire protection is in place, when the product may only meet one of the four required facets. For example, ‘low smoke and fume (LSF)’ rated products may not address toxicity and ‘low smoke zero halogen (LSOH)’ specification may not address flame retardancy.
The good news, however, is that there are numerous flexible conduit solutions available that meet all four requirements for low fire hazard specification. Let’s examine what operators should be asking their supplier to demonstrate as proof of comprehensive fire performance.
Flame retardancy
First, a supplier must be able to demonstrate appropriate flame retardancy and there are a number of established test methods to prove performance.
Flammability – the measure of how difficult it is to ignite the conduit if it is exposed to a heat source – is often cited here. The minimum requirement is that the product is self-extinguishing, according to conduit system standard EN 61386. Here a vertical sample of conduit is exposed to a 1kW burner and must extinguish within 30 seconds of the removal of the flame with no flaming droplets.
To assess how flame retardant a material is, the normal test method is to measure the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) according to BS EN ISO 4589-2. This determines the percentage of oxygen that needs to be present to support combustion. The higher the LOI percentage, the greater the flame retardancy of the material.
Another method is to use a glow wire test, BS EN IEC 60695-2, which applies a glow wire to a plaque of material at 7500C, 8500C or 9600C.
Low smoke emission
If the conduit is involved in a fire, the smoke generated may obscure the vision of people trying to escape, or the firefighters trying to extinguish the flames. Any data center operator will therefore want to ensure that the flexible conduit specified provides superior protection if this scenario occurs, to ensure staff are afforded sufficient time to exit the building safely.
There are a number of fire tests, where a specified sample of material is burnt under controlled conditions in a given size smoke chamber and the smoke obscuration of a defined beam of light is measured.
Low toxicity
The generation of toxic gases may incapacitate people trying to escape from the fire, so appropriate protection must be provided at all times.
To test for toxicity, a specified sample of material is burnt under controlled conditions in a given size smoke chamber and the fumes are analysed for various gases. The concentration of each gas is then multiplied by its toxic potency to give a toxicity index.
If halogens, sulphur or phosphorus are present in a material, it is unlikely to pass the low toxicity tests.
Halogen-free
As mentioned, one of the main misconceptions is that a halogen-free material is automatically a low fire hazard product. The fact remains that a material cannot be considered as low fire hazard if it contains halogen, but as we have learned, without the accompanying low toxicity, low smoke and flame-retardant properties, it will not meet the full criteria.
Typical halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine. Chlorine is the most common in PVC, fluorine is present in fluoro-polymers and bromine appears in flame retardants. All of them produce highly toxic fumes and thick smoke if exposed to a naked flame; another reason why operators may have tended to rate this area of performance above other fire hazard properties.
Specification first
While fire performance is of prime concern, it is worth noting that specifying cable protection based on one property alone can be a costly mistake and the full range of environmental factors should be considered. These can include exposure to extremes of temperature, UV radiation, harsh chemicals, compression strength, abrasion resistance and the likelihood of water or dust ingress.
While many products may look the same, performance properties can vary greatly so customers should always check suitability and compatibility for their application and consider the installation as a complete end-to-end system.
Polypropylene, NFR (Non-flame retardant) is a commonly used material for data centre cable protection as it is halogen, sulphur and phosphorous free, so will not aid acid formation, but is highly flammable, and flame propagating.
In contrast, PA6 (nylon) is self-extinguishing, halogen, sulphur and phosphorous free.
The specifier should look for independent test results to back up the supplier’s claims rather than relying on un-substantiated jargon.
Retrofitting options
For existing installations, data centre operators may require new conduit systems to be retrofitted to ensure low fire performance properties are met.
Retrofitting cable protection has, traditionally, been a complex task, with the installer required to pull existing cabling through the open end of a conduit system.
Conduit system manufacturers are therefore developing enhanced retrofit options to make it easier and quicker to install cable protection.
Bespoke-designed cable protection
For more complex application requirements, customers should speak to their supplier to discuss bespoke options.
These could include conduit supplied in non-standard or pre-cut lengths, in larger or smaller diameters or with different thread termination or fitting options. 45- and 90-degree elbows can also be used to help maintain bend radius.
Additionally, more complex requirements, such as altering performance characteristics to meet a certain temperature requirement, compression strength or abrasion resistance or to achieve a greater fatigue life may also be considered.
Fire Resistant Cable Glands | Fire Resistant Cable Cleats
In conclusion
With so many areas to consider when assessing fire performance, it is important to work with a competent manufacturer or specifier. Specifying based on price alone, or by using standards that do not take all aspects of fire performance into account, could leave vital infrastructure vulnerable to failure.
Operators should expect their chosen supplier to be able to provide detailed evidence of the material properties, and the tests that they have conducted to ensure that all four criteria are met and that critical performance factors are maintained.
THORNE & DERRICK
Thorne & Derrick are national distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Installation, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing businesses involved in cabling, jointing, substation, earthing, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV. Supplying a complete range of power cable accessories to support the installation and maintenance of low/medium and high voltage voltage power systems:
- Slip-on Cable Terminations
- Cold-shrink Cable Terminations
- Heat-shrink Cable Terminations
- Cable Joints – Heat & Cold-shrink
- Separable Connectors (Euromold)
- Surge Arresters & Switchgear/Transformer Bushings
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV
Splicing, Wiping & Laying Submarine Cable In San Francisco Bay (1936)
March 30th, 2021-
uploaded by Chris Dodds | Sales Marketing Manager at Thorne & Derrick
Picture the scene, its 1936 and in San Francisco harbour a ship arrives from Baltimore having travelled through the Panama Canal bringing with it 6 reels of submarine telephone cable which is transferred to a waiting barge. After a long journey the final resting place is the floor of San Francisco Bay to provide telephone communications to America.
Unique skills and techniques are shown throughout the film.
The underwater cable circuit must be installed by cable splicers with protection against leakage. The protection can be seen when the camera zooms in as it pictures two cable lengths being spliced together – multiple layers of water-blocking jute and double armouring protect the cables against water ingress.
Splicing is no small task – 1,056 wires must be spliced per cable. This wire is separately insulated and the boiling out process with petrolatum removes any moisture. The lead sleeve is then pulled over the cable splice. The lead sleeve becomes very hot as it is to be made part of the protective metal cable jacket.
The cable engineers need to make sure the cable splice is airtight so they carry out testing investigations. A hole is made in the lead and nitrogen gas at twenty pounds pressure per sq inch is forced through the hole made to surround the wires just spliced. Soap suds are used to check whether any gas escapes as the soap will bubble at the exact point.
Corrosion is minimised as the cable gets two overcoats to reduce the risk of salt water on the metal. Finally the two miles of armoured cable is added to a drum before it is transported out to sea.
Thorne & Derrick
T&D are Specialist Distributors to UK Distribution Network Operators (DNO’s), NERS Registered Service Providers, ICP’s and HV Jointing Contractors of an extensive range of LV, MV & HV Jointing, Earthing, Substation & Electrical Eqpt – this includes 11kV/33kV/66kV cable joints, terminations and connectors for both DNO and private network applications.
Contact our UK Power Team for competitive quotations, fast delivery from stock and technical support or training on all LV-HV products.
All international sales enquiries can be serviced and supplied by our Export Power Team.
Key Product Categories: Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Cable Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling | Earthing | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV


ANSI Connectors | Screened Separable Connectors from Cooper Power Systems
March 30th, 2021
ANSI Connectors | Medium Voltage Power Cable Connectors for Transformers & Switchgear Bushings from Cooper Power Systems
Cooper Power Systems Separable Connectors (ANSI) & Bushings are rated for 15kV, 25kV and 35kV medium voltage power systems in accordance with the following ratings.
What is ANSI?
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States.
ANSI Separable Connectors are waterproof cable connectors that can be easily installed – these cable accessories use imported high quality EPDM rubber for reliable field performance and are widely used in pad-mounted switchgears and pad-mounted transformers on MV Power Systems.

Connectors & Bushings from Cooper Power Systems
For further information download the Cooper Power Systems catalogue.
Standard Interfaces For Separable Connectors and Components
Certified Tests and Performance
Conductor Sizing
AEIC Insulation Diameter Chart
ICEA Insulation Diameter Chart
200 A Loadbreak Connectors
200 A Deadbreak Connectors
200 A Stacking Dimensions
Clēēr 600 A Loadbreak Connectors
600/900 A Deadbreak Connectors
600/900 A Components and Replacement Parts
600/900 A Connector Systems
600 A Stacking Dimensions
Junction Bars/Cable Transition and Oil Stop Modules
Splices
Underground Surge Arresters
Tools & Maintenance
Bushings
Fusing
MagneX Single-Phase Interrupter
MagneX Three-Phase Interrupter
Faulted Circuit Indicators
Sectionalizing Cabinets
Part Number Index
Support Available When You Need It
Product Application Overhead and Underground Distribution Systems
Connectors
Eaton’s Cooper Power Systems 200 A and 600 A connector products are designed for applications on XLPE, EPR or other solid dielectric insulated underground electrical cables. In order to maintain a reliable termination, the cable accessories must be sized correctly with the cable conductor size and cable insulation diameter.
The cable conductor size is used to determine the compression connector used. Proper sizing is important to ensure reliable current transfer from the underground cable conductor to the elbow connector.
Conductor diameters are dependent on the conductor size in AWG or kcmil, and conductor type (stranded, compressed, compact or solid). The cable insulation diameter (the diameter over the insulation) is critical because it is important to maintain a tightly sealed fit between the cable insulation and the elbow housing at the cable entrance. As the insulation thickness changes, so must the range of the cable accessory. Cable insulation diameter can be determined from the cable manufacturer’s specification, or by referring to pages 8 (for cable made to the AEIC Standard including the ± 0.030 inch tolerance) or 9 (for cable made to the ICEA Standard) for minimum and maximum diameters.
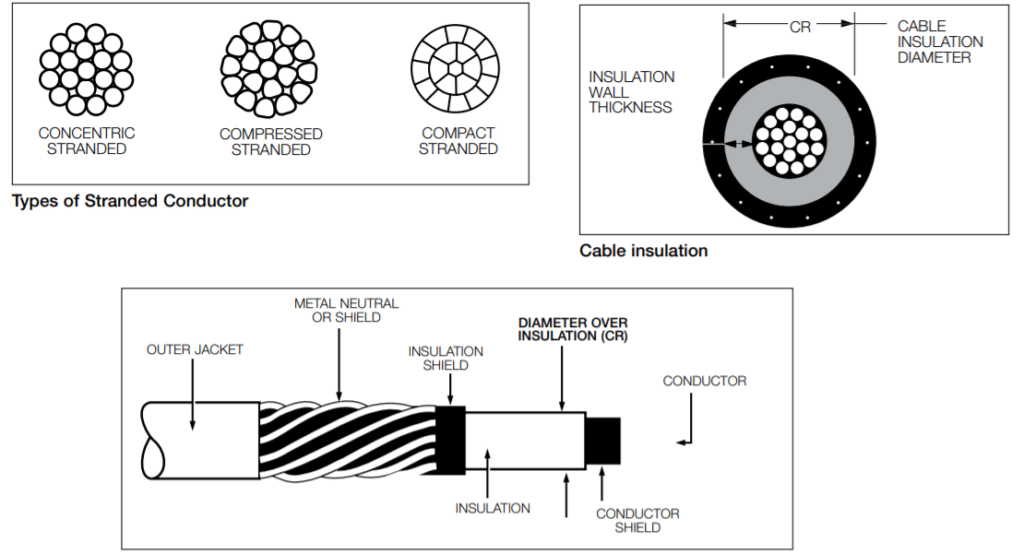
ANSI Connectors | MV Medium Voltage Power Cable Construction
Thorne & Derrick
Contact us for Competitive Prices & Fast Delivery from Stocks for Heat Shrink, Cold Shrink & EPDM Rubber Connectors, Joints & Terminations up to 66kV.
Thorne & Derrick International are specialist distributors of LV, MV & HV Cable Accessories, Jointing, Substation & Electrical Equipment – servicing UK and global businesses involved in cable installations, jointing, substation, overhead line and electrical construction at LV, 11kV, 33kV, 66kV and EHV.
Stocking & Supplying | Duct Seals | Cable Cleats | Cable Glands | Electrical Safety | Arc Flash Protection | Jointing Tools | Cable Pulling Eqpt | Earthing & Lightning Protection | Feeder Pillars | Cable Joints LV | Joints & Terminations MV HV




