Cable Pulling & Laying
Lace Up Cable Socks – A Guide For Users When Pulling Cables
June 26th, 2018
Cable Socks | Temporary Strain Relief LV MV HV Cable Pulling
-
uploaded by Chris Dodds - Thorne & Derrick Sales & Marketing Manager
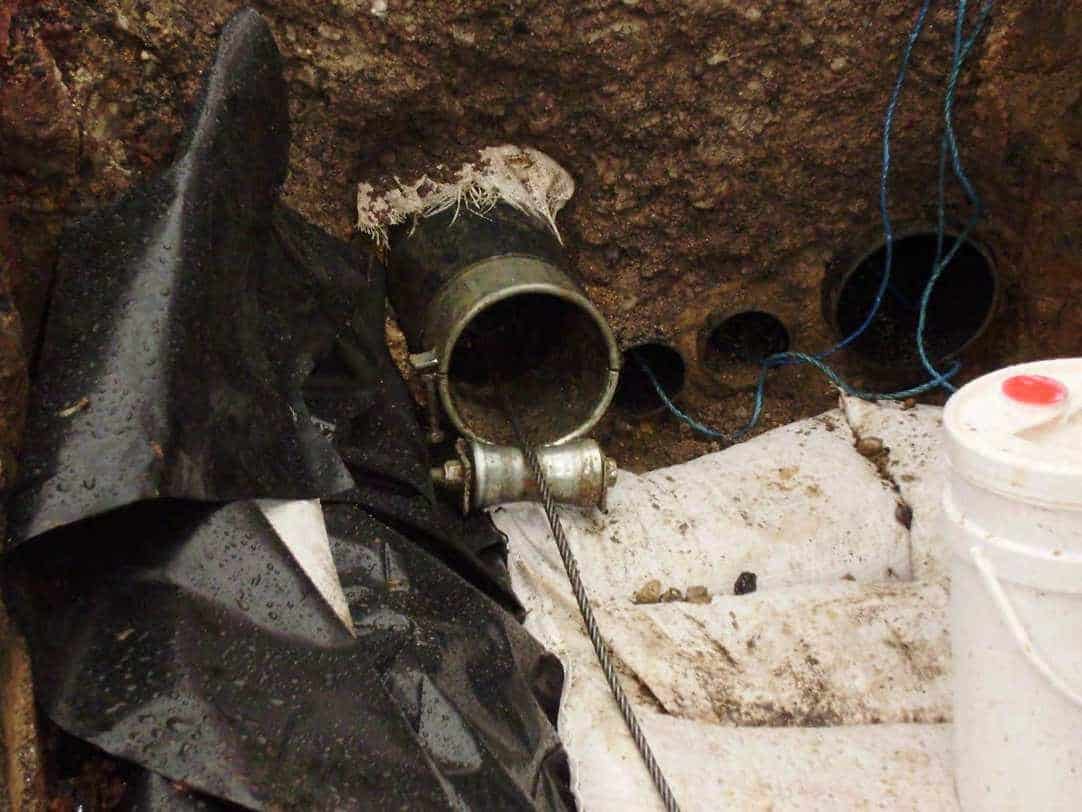
The following short article has been provided as guidance for the use of cable socks – specifically lace-up cable socks are used to pull and support cables mid-span and employed where a fitting or connector prevents a standard single or double-eye type cable sock from being slipped onto the open cable end.
Lace-up cable socks are typically used to “pull-in” and support electricity cables in a vertical or sloping position and is also ideally suited for use in manholes where the longitudinal movement of cables, caused by road vibration, needs to be monitored and checked.
Cable socks are a temporary use product not designed for fixed permanent location.
Using Cable Socks
- Start the lacing from the ‘eye’ end or anchoring end of the cable sock
- Thread the lace through the first two loops of the split and pull through until the laces are centered at this point
- Don’t pull the lace too tight at this stage. Leave a space between adjoining loops roughly equal to the width of one diamond of the mesh
- Continue down the length of the cable sock. Try to maintain equal tension and equal spacing throughout as this leads to a more stable and equal grip
- As you continue down the length, pull the open sides of the sock as wide apart as required
- Try to achieve an even and neat lace-up as this assists with the strength of the sock when pulling cables
- Finally, tie the ends of the lace once or twice round the end of the cable sock twisting the ends together securely. Excess lace can be cut off
- Add any additional support as required – banding is recommended

Where cables must be pulled through ducts cable lubricant is recommended to reduce friction damage to cable sheaths and ensure a smooth and low-tension installation without inflicting damage to the cables.
Cable socks are manufactured in galvanised steel, stainless steel or non-conductive (Aramid) material – the socks can be used with swivel links which are cable pulling fittings attached between the sock and the draw rope to reduce twisting.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Press Release | Thorne & Derrick Appointed Approved Stockist for UK Leading Cable Pulling Equipment Manufacturer
Cable Pulling Equipment
Thorne & Derrick International are the UK’s leading stockist and supplier of Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment for the installation of underground cables and overhead lines up to 400kV – the products support cable pulling teams to install LV MV HV cables into trench, cable duct, risers and all forms of cable containment.
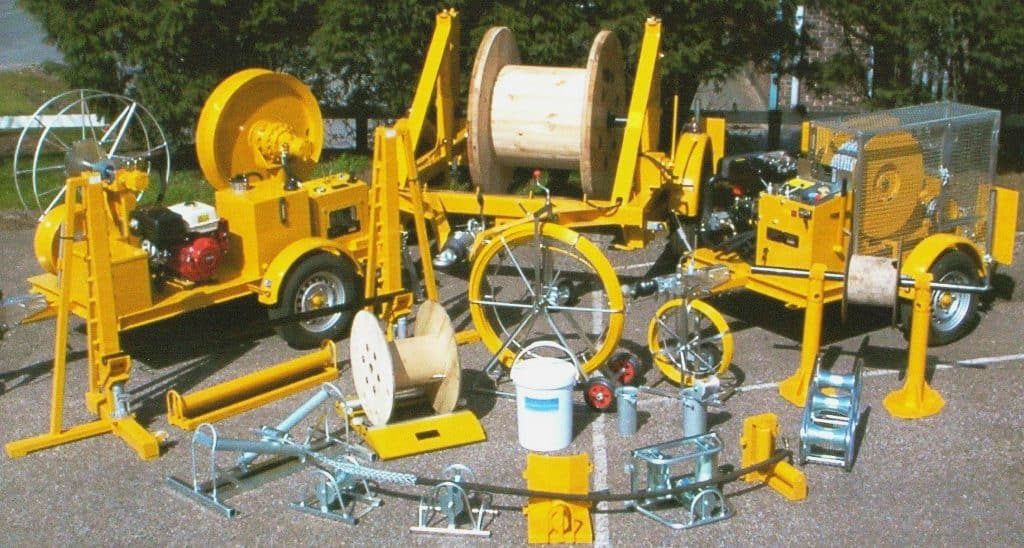

Duct Rods | Cable Jacks | Cable Rollers | LV MV HV Cable Pulling & Laying Equipment
Tape Tile & Stokbord Cable Protection Covers For MV HV Power Cables
March 22nd, 2018-
Uploaded By Chris Dodds – Thorne & Derrick Sales & Marketing Manager
Why Use Cable Protection Covers?
Tape Tile & Stokbord
Centriforce Stokbord underground cable protection covers are manufactured from high impact, recycled polyethylene designed to withstand damage and protect medium/high voltage cables from plant and hand tools – the cable covers protect high voltage cables from damage caused by diggers and excavators inadvertently causing cable strikes when working around underground cables and utility services.
Both Tape Tile and Stokbord cable covers are used to protect LV-HV cables and cable ducts installed by the ‘open cut’ trench method – the cable protection products are intended, during any future excavation work, to give a clear visual warning of the presence of underground cable, cable joints or cable ducts. The cable identification is compliant with ENATS Standard 12-23 and meets the impact requirements of BS2484.
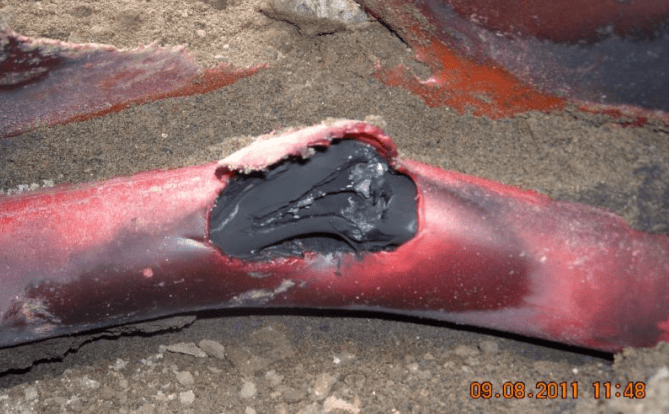
Pictured: High Voltage 11kV Cable Strike – an excavator has impacted onto a 11kV high voltage power cable penetrating the cable sheath and XLPE insulation to cause a power outage. Lack of planning on development projects increases the possibility of serious injuries to operatives and greatly increase cost to projects. On site cable records and use of cable fault locators should ensure worker safety and prevent accidental damage and strikes to high voltage cables.

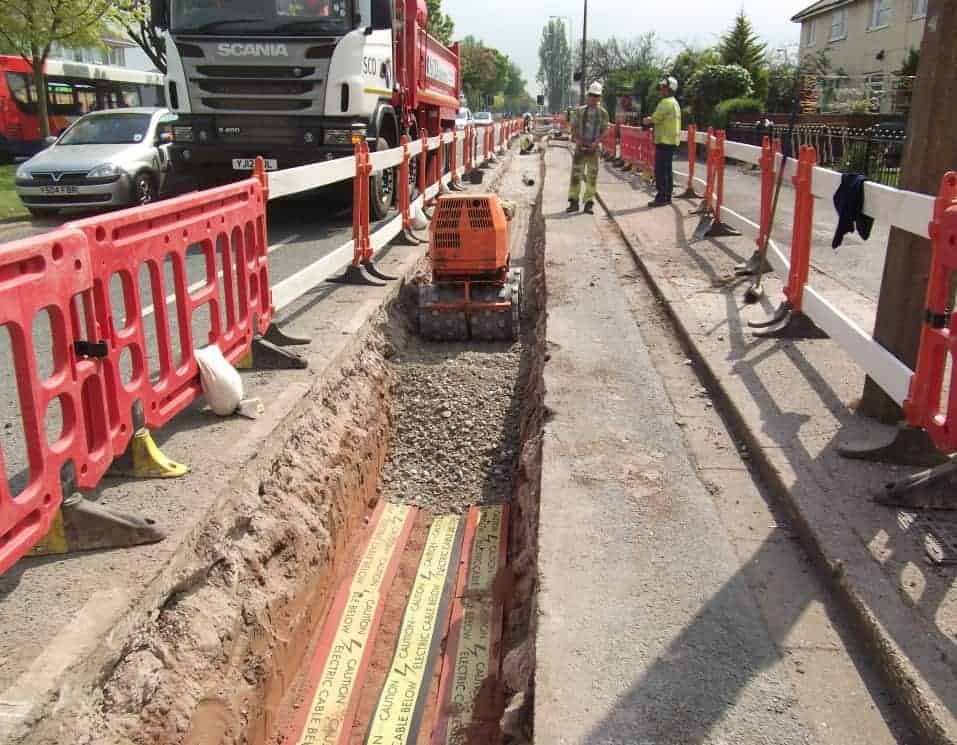
Damage to underground cables can have serious repercussions such as damage to anyone working on or near the cables or a power blackout such as that experienced in Londonderry, December 2013.

LV Low Voltage | MV Medium Voltage | HV High Voltage Cable Protection
Why Use Stokbord?
Centriforce Stokbord cable covers are suitable for underground high voltage cable protection (22kV, 33kV, 66kV, 132kV and up to 400kV). The 4 thickness variations of Stokbord covers are 6, 9, 12 and 18mm. This coupled with the fact that Stokbord is easy to fabricate ensures Centriforce Stokbords are the ideal product for protecting underground cables.
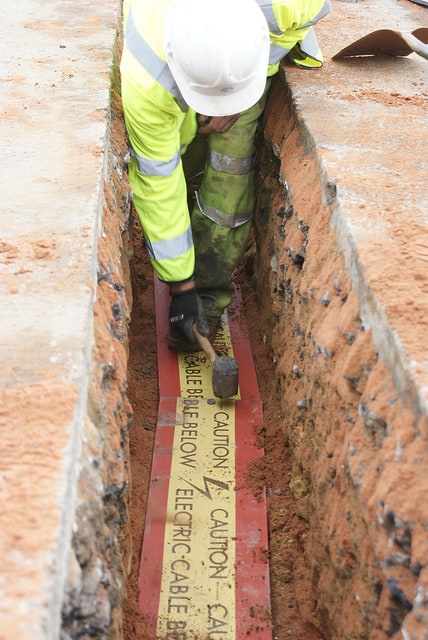

Stokbord Cable Cover Application
Centriforce Stokbord Cable Covers are fully jointed, laid overlapped and connected with plastic jointing pegs to provide safe high voltage underground cable protection.
Centriforce Stokbord cable covers feature a red background with yellow top tape containing visible warning “Caution Electric Cable Below” – Stokbord cable covers meet BS2482 impact requirements for underground cable cover protection.
Not only does this protect from any impact to the cables that would be made by excavation, it also shows exactly where cables are laid. The locating of cables is therefore simplified.
The features and benefits of Centriforce Stokbord makes the performance of the products far superior to steel and concrete cable covers / tiles /plates.
Stokbord Cable Covers – Benefits At A Glance
- Stokbord covers provide the clear warning to 3rd parties of underground buried cables
- Cable covers can be custom made with sizes to suit medium/high voltage cable trenches
- Contains bold warning text and company logo for clear MV-HV cable identification
- Damages to cables reduced – cost of repairs, HV jointing and supply disruption reduced
- Lightweight and easy to install Stokbord cable covers irrespective of weather conditions
- Durable with good impact resistance for MV HV EHV cable protection
- Rotproof and resistant to soil conditions for burial in underground cable trench
Plastic Cable Covers v Concrete Cable Covers
Cable Protection
Installation Of Cable Trench Covers & Cable Protection Tiles
All cables and ducts laid into cable trench should be over-protected by a cable protection cover or tape depending upon the highest voltage cable to be protected within the cable duct – typically in the UK the following cable protection tapes and covers are used for LV, MV and HV cables.
Marker tile tapes or Stokbord covers are installed over the cable in the appropriate trench drawings – usually there is no requirement to install either above approved cable ducts installed using trenchless techniques (i.e. directional drill) but either may be installed if it is deemed that additional MV-HV cable protection is required.
When Tape Tile is used it should be cut cleanly and installed so that the medium/high voltage cable is fully covered along the whole length of the installed cable duct.
- LV Service Cable 40m x 200mm x 2.5mm Tape Tile
- LV Mains Cable 40m x 200mm x 2.5mm Tape Tile
- 11kV MV Cables 40m x 200mm x 2.5mm Tape Tile
- 22kV MV Cables 40m x 200mm x 2.5mm Tape Tile
- 33kV MV Cables 1000mm x 244mm x 9mm Stokbord
- 66kV MV Cables 1000mm x 244mm x 9mm Stokbord
- 132kV MV Cables 1000mm x 244mm x 9mm Stokbord
More info ➡ Tile Tape | Stokbord
-
Further reading :
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cable In Duct (Part 1 of 2)
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cable In Trench (Part 2 of 2)
Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment
Suppliers & Distributors
Thorne & Derrick International distribute the most extensive range of Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment to enable the installation of low, medium and high voltage power cables into underground trench or duct – products also supplied for fibre optic blowing, subsea trenching, offshore umbilical installations and pulling armoured cables onto cable tray.
Contact us for 3M Electrical, ABB, Alroc, AN Wallis, CATU Electrical, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, CSD, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Euromold, Filoform, Furse, Lucy Electric & Zodion, Nexans, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec, Sicame, WT Henley.
Cable Blowers | Cable Lubricant | Duct Rods | Cable Socks | Cable Jacks | Cable Rollers | Cable Protection Covers MV HV | Cable Joints MV HV | Duct Sealing

Cable Socks – Technical Guide for Safe Cable Pulling Using Cable Socks
March 21st, 2018
Thorne & Derrick | Cable Laying & Pulling Equipment Distributors | LV MV HV
-
Uploaded By Chris Dodds – Thorne & Derrick Sales & Marketing Manager
Cable socks, sometimes called cable stockings or cable grips provide an efficient method of supporting cables for pulling and laying into open-trench or duct – this includes LV Low Voltage, MV Medium Voltage or HV High Voltage cables.
The correctly sized cable sock can be used to pull in short lengths of cable by hand (e.g. fault repairs prior to jointing).
Cable socks are re-usable tools (subject to inspection before re-use) and are not confined to cable applications but basically can be used to support or pull any cylindrical object within their grip and load carrying capacity.
Standard cable socks are manufactured from high tensile galvanised and stainless steel wire rope or Kevlar.
A skilled, hand woven construction process, coupled with individual product inspection throughout manufacture ensures a high quality product for reliable and long lasting application.
UK DNO’s generally specify according to their Engineering Standards that all pilot and telephone, LV, 11kV, 20kV, 33kV, 66kV and 132kV cables shall normally be pulled in using a correctly sized cable socks which are securely fixed to the cable. More difficult pulls may require the use of a pulling eye attached directly to the cable conductors, which has been installed by the manufacturer – cable rollers shall always be used when pulling cables.
LV MV HV
Further information on the main ranges according to voltage application for underground power cable pulling or overhead line stringing can be found here:
- LV Low Voltage & MV Medium Voltage Cable Socks & Conductor Grips 33kV
- MV Medium Voltage Cable Socks & Conductor Grips 132kV
- HV High Voltage Cable Socks & Conductor Grips 275kV – 400kV
Cable Socks
WL & FOS
The Working Load (WL) of a cable sock depends on the Factor of Safety (FOS) applied to the Minimum Breaking Load.
For example, where the operational risk is considered to be normal, it is recommended that a FOS of 5 be applied, for high risk operations a FOS of at least 10 should be considered.
The Approximate Breaking Load stated on any certification, the recommended Factors of Safety, and any implied or stated fitness for purpose, are all only applicable when the cable socks are new and unused.
There are many factors that the person using the cable sock must take into consideration when trying to calculate a safe working load as it is impossible to guarantee a suitable safety factor when there are many variables which change from cable pulling application to application.
In addition, before using any cable sock, the user must carry out a full assessment of its suitability for the proposed application, and the level of operational risk involved, including taking account of:
- size of the cable sock, in relation to the size and shape of the gripped cable
- stability of the cables when gripped
- grip surface of the cable
- anticipated path of movement, including possible obstructions
- resistive force of the cables being pulled
- minimum-breaking load (MBL) of the cable sock
- condition of the cable sock
- suitability and compatibility of any cable pulling attachments used
- environment / operating conditions
When selecting the cable sock users must allow for a 20% variance in break loads and, if there is ‘twist’ in the cable, a suitable swivel link must be used.
When the correct cable sock is selected, cable installation through cable ducts, conduits and trenches is made considerably easier. The cable sock adds little to the overall diameter of the cable and ‘free passage’ is normally available through sheave blocks and pipes.
Cable socks can often be used on a ‘new for old’ cable replacement by applying two grips on a ‘back-to-back’ basis with a solid link or swivel in between grips, allowing the old cable to be used to pull through the new replacement.
Swivel links can be used to allow for reduced torque build-up induced by the cable pulling equipment and inherent lay in the cables themselves, whether LV, MV, HV or EHV. Lace up cable socks can be applied anywhere along the cable length, preventing overloading of the cable.
To prevent winched cable pulls exceeding the maximum tension force of the cables, a cable sock fitted with a swivel can be used to connect the bond to the cable and a dynamometer used to check that the maximum pulling tension for the cable is not exceeded.
When pulling cables by mechanical cable winch, the load-limiting device must be used to ensure that the pulling tension applied to the cable does not exceed the manufacturers specified maximum permissible tensions. The pulling of cables by direct and unmonitored mechanical means (e.g. hitched to a vehicle, Land rover winch) is not permitted.
Several UK DNO’s including Northern Powergrid, specify in their Policy for the Installation of Distribution Power Cables that cable pulling by winch shall only be carried out where there is a serviceable and accurate dynamometer calibrated in kgs.

Press Release | Thorne & Derrick Appointed Approved Stockist for UK Leading Cable Pulling Equipment Manufacturer
Cable Socks – Typical Applications
- Power cable pulling – LV MV HV
- Overhead house service cables
- Portable tool supply cables
- Portable compressed air lines
- Conduit risers
- Moveable hydraulic hoses
- Cable strain relief
- Oil support cables
- Marine applications
- “Guy rope” adjusters
- Fibre optic cable applications
Pulling Overhead Power Line Conductors Using Cable Socks
According to the Ericsson Universal Cable Handbook the most critical moment in the pulling out operation is when the cable end and cable sock passes through the line roller or suspension clamp. To make the pulling out easier the cable end should be “sectioned down” at the end before the cable sock is applied.
Between 150 – 200 mm/core is enough, see figure below.

This will make the end smoother and more flexible when it passes the cable pulling devices.
If a cable sock of Kevlar is used this is more important as it is soft and does not form a natural cone the same as a galvanised steel cable sock. The cores can also be cut with a knife to avoid sharp edges which will simplify the pulling even more.
Type of Cable Socks
Single Eye Socks – available in single or double weave.
Double Eye Socks – standard support sock, with double eye. Available in single or double weave.
Lace Up Socks – cable sock for fitting at points along the length of a cable.
Open Ended Socks – socks designed to enable two cables, hoses or ropes to be connected for pulling or supporting purposes.
Single Eye Socks (Triple Weave) – high strength cable socks with heavy duty shoulders, for stringing or pulling-in non-insulated conductors on long, high voltage transmission lines, or other high load applications.

Single Eye | Double Eye | Lace Up | 11kV 33kV Triplex Cable Socks
Note : Cable socks must not to be used as primary lifting devices.
More Cable Pulling Blogs
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cables Into Trench
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cables Into Duct
- Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Laying, Duct & Installation Guide From SSE
- Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Duct Laying Guide From BT Openreach

Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment Suppliers & Distributors
Thorne & Derrick International distribute the most extensive range of Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment to enable the installation of low, medium and high voltage power cables into underground trench or duct – products also supplied for fibre optic blowing, subsea trenching, offshore umbilical installations and pulling armoured cables onto cable tray.
Contact us for 3M Electrical, ABB, Alroc, AN Wallis, CATU Electrical, Cembre, Centriforce, CMP, CSD, Elastimold, Ellis Patents, Emtelle, Euromold, Filoform, Furse, Lucy Electric & Zodion, Nexans, Pfisterer, Polypipe, Prysmian, Roxtec, Sicame, WT Henley.
Cable Blowers | Cable Lubricant | Duct Rods | Cable Socks | Cable Jacks | Cable Rollers | Cable Protection Covers MV HV | Cable Joints MV HV | Duct Sealing

11kV Cable Pulling – What Is The Maximum Distance For Ease of HV Cable Pulling Between Manholes?
March 14th, 2018
Thorne & Derrick | Cable Laying & Pulling Equipment Distributors | LV MV HV
-
Uploaded By Chris Dodds – Thorne & Derrick Sales & Marketing Manager
Cable Pulling
In response to a question posed on Voltimum, the leading electrical industry portal, Nexans provided the following answer in reply about the maximum 11kV cable pulling distances between manholes when laying medium/high voltage power cables using cable socks.
T&D, the UK’s leading Cable Pulling & Laying Equipment Supplier, can provide expert technical recommendations and support for all cable pulling and laying projects into both open trench (directly buried) and cable duct.
Important procedural requirements apply to the installation of all MV-HV underground cable pulls irrespective of the method used.
Installation shall be carried out by experienced cable pulling teams with a thorough understanding of the risks specific to the installation methods being used. The installation design, cable pulling equipment and techniques shall be designed to:-
- Minimise cable pulling forces on MV-HV cables
- Cause no damage to MV-HV cable sheaths during handling/installation into duct or trench
Often cables are snagged or damaged by bedding or backfill materials during the the cable pull process on the cable trench bed – contact us to discuss cable sheath repair products.
Pictured : Manhole Cable Rollers – care must be taken during high voltage cable pulling not to exceed the maximum pulling force and tension to avoid 11kV cable damage. The cable rollers are designed for placing at the edge of the manhole or pit entrance to ease the cable into position.
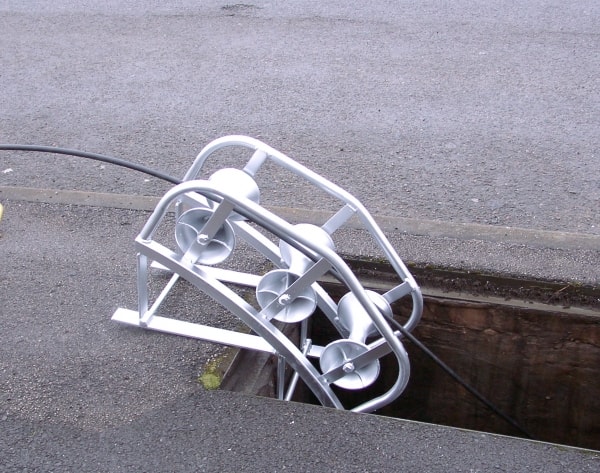

Cable Rollers – Order Code ML5
11kV
Question: I’m installing a high voltage 11kV cable in PVC sleeves and I want to introduce manholes on the straight length of the HV power cable route. What will be the maximum distance you would recommend for ease of high voltage cable pulling of the 11kV cable from one manhole to the other?
Answer: This can only be answered properly on a case-to-case basis as it depends a lot on the topography and direction of the proposed 11kV cable pulling route.
This is especially so in urban areas where many bends may be necessary to avoid underground utility cables and pipes such as like sewers, water and gas. If there are no bends, we have still must consider the friction coefficient of the particular cable duct with the 11kV cable.
Of course, cable lubricants can be used as long as they do not harm the sheath material or the duct material – lubrication of the 11kV will reduce the co-efficient of friction of the cable pull between the 11kV cable sheath and inner cable duct wall.
If we speak about 11kV triplex cables, you will get them only in smaller lengths because of the diameter – I suppose 350m on a perfectly straight line shouldn’t be a problem.
But please take into consideration the maximum pulling force, which is: 30N/mm2 of conductor cross-section for aluminium conductors and 50N/mm2 of conductor cross-section for copper conductors.
Going above these forces can damage the 11kV cables and maximum cable pulling vary according to the specification of the medium/high voltage cable.

Press Release | Thorne & Derrick Appointed Approved Stockist for UK Leading Cable Pulling Equipment Manufacturer
Maximum Cable Pulling Tensions
High Voltage Cables Up To 33kV
Maximum permissible pulling tensions for each 11kV/33kV cable type are given below.
These cable pulling tensions must not be exceeded under any circumstances. Efforts should always be made by the cable pulling teams to achieve lower figures by careful setting out of the work and positioning of the MV-HV cable drum.
| Maximum Cable Pulling Tensions LV 11kV 33kV Cables (kN) | ||||||||
| Conductor Size (sqmm) | 95sqmm | 150sqmm | 185sqmm | 240sqmm | 300sqmm Al | 300sqmm Cu | 500sqmm | 630sqmm |
| 3-Phase Waveform | 2.89 | – | 7.78 | 8.67 | 9.79 | – | – | – |
| 11kV PICAS | 3.91 | – | 6.36 | – | 9.79 | – | – | – |
| 11kV 1 Core XLPE | 2.85 | – | 5.55 | – | 9.0 | 15.0 | – | 31.5 |
| 11kV 3 Core XLPE | 3.91 | – | 6.36 | – | 9.79 | – | – | – |
| 33kV 1 Core XLPE | – | 5.5 | – | – | – | – | 14.6 | 18.0 |
♦ Info: Scottish Power Energy Networks, CAB-15-003: Handling & Installing Cables Up To 33kV
Risk Of Arc Flash & Safe Digging
Civil engineering contractors, jointers and pulling teams must be aware of the arc flash dangers associated with utility excavations when working around buried services including electricity cables. Attention is drawn to the requirements and recommendations contained in Health and Safety Executive guidance notes HSG47 “Avoiding Danger from Underground Services” and HSG185 “Health and Safety in Excavations”. UK DNO’s publish guideline documents about “Safe Digging” and these can be consulted online.
➡ Blog: Can Arc Flash Clothing Save Utility Workers Lives?

Arc Flash Protection Clothing & Garments | Polo Shirts | Jackets | Coveralls | Trousers | Sweatshirts | Helmets | Gloves | LV MV HV
High Voltage Cable Pulling
Calvi Electric Company uses Southwire A-Frame truck to facilitate a 1300′ high voltage cable pull through a manhole system. During the video you will observe the high voltage cable being taken up in sections. At the other end of the cable pull a Greenlee Ultra Tugger set up is located, the average for this cable pull was 6 ft per second.
The reason for the sporadic uptake was variable stretch and tension being placed on the cable pulling rope. The total length of the HV cable pull was 1270′. The utility learned that with the ease at which the Southwire A-Frame trucks payoff that it was not necessary to have this large of a crew to handle the consolidation of cable into the trunk of the cable pull. Once set up this cable pull could have been performed with 4 crew members. Additional crew members were necessary and productive in initial manhole set-up, reel set-up and attending to manholes where the wire was being pulled straight through.
Sealing Cable ducts
Where electricity, pilot and telephone cables are installed into electricity cable ducts the utility engineering standard would normally recommend all cable ducts entering substations and buildings to be duct sealed to prevent the ingress of water and gas – this also applies to 33kV, 66kV and 132kV high voltage substation cables where cable transits are required.

Thorne & Derrick distribute an extensive range of Duct Sealing & Cable Transit Systems to protect utility assets and provide flood protection to substations from water entry via unsealed cable ducts and building penetrations.
Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment Suppliers & Distributors
Thorne & Derrick International distribute the most extensive range of Cable Pulling & Cable Laying Equipment to enable the installation of low, medium and high voltage power cables into underground trench or duct – products also supplied for fibre optic blowing, subsea trenching, offshore umbilical installations and pulling armoured cables onto cable tray.
More Cable Pulling Blogs
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cables Into Trench
- Cable Laying & Pulling – Installing LV-HV Cables Into Duct
- Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Laying, Duct & Installation Guide From SSE
- Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Duct Laying Guide From BT Openreach
Cable Blowers | Cable Lubricant | Duct Rods | Cable Socks | Cable Jacks | Cable Rollers | Cable Protection Covers MV HV | Cable Joints MV HV | Duct Sealing

Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Laying, Duct & Installation Guide From SSE
February 1st, 2018
Thorne & Derrick | Cable Pulling & Laying Equipment Stockists and Suppliers
-
by Chris Dodds T&D - estimated reading time 2 minutes
Cable Pulling
The following information based upon a document produced by UK DNO, Scottish & Southern Electricity Networks, provides information and guidance on New Connections and best practise for cable pulling and laying and when installing LV (Wavecon | Concentric), 11kV (3 Core | Single Core) and 33kV (Single Core) cables into underground cable trenches.
The cable pulling equipment for ensuring safe and compliant installation of LV-HV cables up to 33kV is briefly outlined – should you require any further information or technical support please contact us.
All work carried out and cable pulling equipment used must be compliant with SSE technical guidance (TG-PS-881) available from the SSEN website.
It is also recommended that contractors and clients review the ‘Practical Guide to Streetworks’ before undertaking any excavations prior to installing LV-HV cables to form part of new connections.
The following cable trench section shows the position of cable and the cable duct in the ground – it is important that the top of any apparatus is at these depths as a minimum, this includes the top of the cable duct. In addition to the cable or duct there is a requirement for 75mm finefill material on all sides. Cable marker tape or cable tiles/covers must be installed 150mm above the top of the apparatus, this needs to have SSEN branding on.
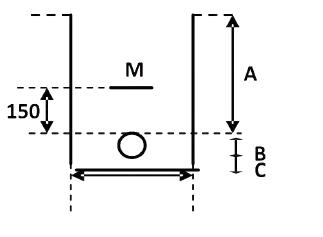
This table shows the minimum depths to top of apparatus (A within the diagram above)
| Minimum Apparatus Depth | Unmade Ground, Verges & Footway (mm) | Carriage (Road) (mm) | Agricultural (mm) |
| Cables LV | 450mm | 600mm | 1000mm |
| 11kV Cables HV | 600mm | 750mm | 1000mm |
| 33kV Cables HV | 800mm | 900mm | 1100mm |
Minimum Excavation depth required = (A) minimum depth of apparatus + (B) outside duct/cable size + (C) 75mm of sand bedding.
Please note that (M) represents the cable marker tile (for 33kV cables use Stokbord covers) or cable protection tape for all other installations including 11kV cables and cable joint protection.
Please note: Where there are sudden changes in surface type (e.g footway to carriageway), excavations should always be at the greater of the depths required.
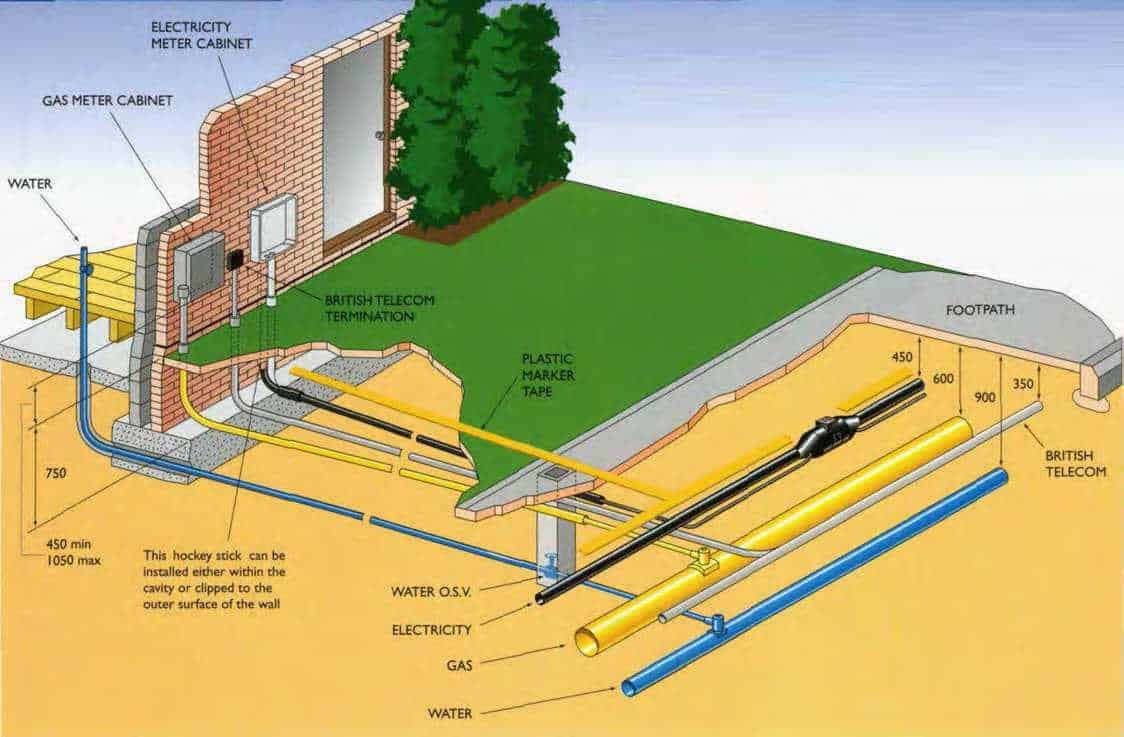
New Housing Service Cable Installation Guide
Experience has shown that by using a service tube the disturbance to the site is reduced when the electricity supply is connected.
The service tube can be laid in the same cable trench as the other services are shown, with an identifying plastic cable marker tape installed above to give advanced warning of service cable location on private property.
External meter cabinets
The external meter cabinets must be positioned in agreement with SSE to provide unrestricted access.
The preformed ‘hockey sticks’ can be installed either within the cavity or clipped to the outer surface of the wall below the meter cabinet.
White ‘hockey sticks’ must be used on the outer surface of walls. The service tubing must be securely coupled to the ‘hockey sticks’. The cabinets are only large enough to house SSE service and connection equipment.
Clients must fit own main switches on an inside wall so that the length of interconnecting cable does not exceed 3 metres.
This cable must only enter through the bottom of the cabinet, using the right hand hole, when viewed from the front.
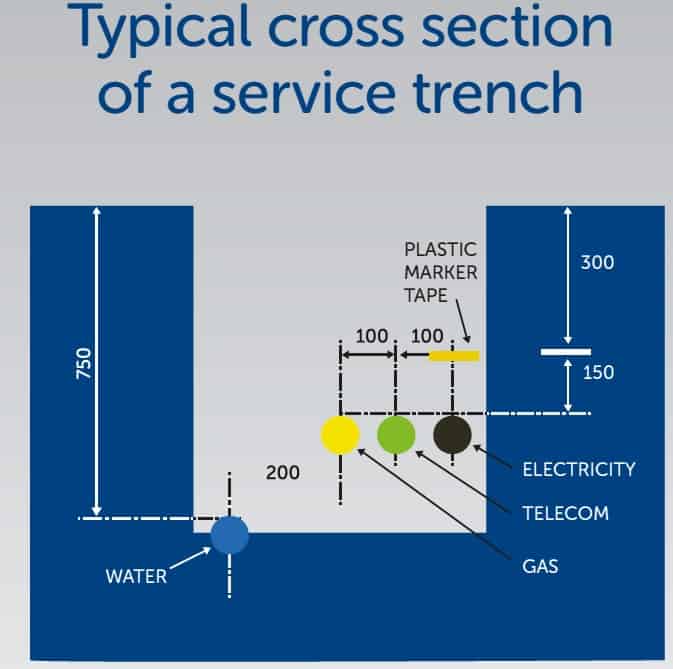
Typical Cross Section of A Service Trench
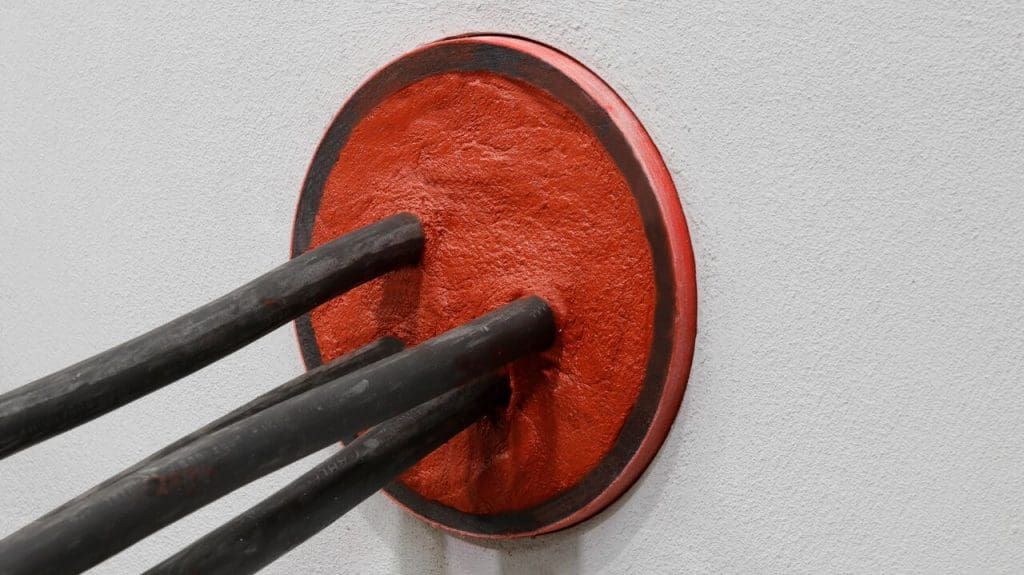

Duct Seals – contact us for duct sealing solutions and products to provide sealing against water (flood prevention) to copper and ducted low, medium and high voltage power cables.
Installation of Cable ducts
For the installation of ducted schemes the use of Black electric cable ducts only (see table below for approved suppliers) are permitted for use.
Clients should consider the type of cable ducts intended to use before ordering as excavations will be different depending on which cable duct supplier you use – the minimum cable bending radius must also be considered by referring to the manufacturers specification and selecting the appropriate cable pulling equipment to include cable rollers, socks, drum jacks and cable winches.
Emtelle cable duct range includes a smooth bore type of ducts which have rigid preformed bends at differing angles. When pulling and laying cables it is important that angles or bends should not be placed too close together otherwise cable pulling tensions will become greater than the manufacturers guidelines during the installation process.
Winch Cable installation
All cable must be installed not exceeding the manufacturers recommended cable pulling tensions – this applies to low, medium and high voltage power cables. Contractors must familiarise themselves with these cable pulling loads before hiring the equipment to ensure that these loads are not exceeded.
For all Cable Pulling applications contractors should use the following cable laying equipment and products:
- Cable winch
- A display of the cable pulling tension on the winch (calibrated)
- A free moving cable pulling swivel link
- Cable rollers located typically every 4 metres and/or where LV-HV cable would come into contact with ground
- Cable socks to ensure excellent grip and support of LV-HV cables
In addition to cable trench installations, for ducted cable schemes you will also need;
- Bell mouth roller
- Cable lubricants
- Cable drum trailers for each cable drum
For 33kV single core cables it is recommended that the contractor put colour indicators on each cable for identification – the cable installer must securely anchor the cable drums and the cable winch at either end and ensure that the LV-HV cable does not come into contact that could inflict cable sheath damage.
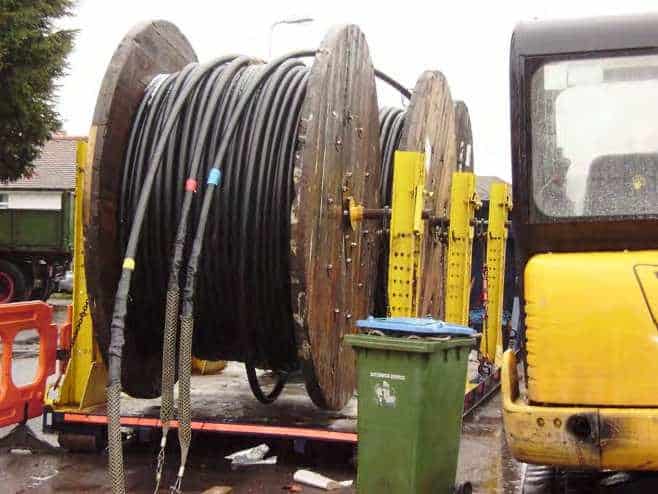


Cable Socks – high tensile strength galvanised steel cable socks provide support and grip for LV-HV cable pulling into duct or laying into trench.
Cable Pulling Equipment
Cables, Duct, Duct Seals & Cable Tiles Approved Equipment
| Item | Manufacturer | Manufacturing Location | Notes |
| LV Concentric Cables | Tratos | UK | |
| Cabelte | Portugal | ||
| LV Wavecon Cables | Prysmian | Wrexham UK | |
| Hellenic | Greece | ||
| 11kV Three Core Cables | Nexans | Hannover, Germany | Aluminium stranded & solid conductors 11kV |
| Prysmian | Wrexham UK | ||
| 11kV Single Core Cables | Tele-Fonica Kable | Poland | Copper or aluminium stranded for all conductor sizes Solid aluminium up to and including 300sqmm conductors 11kV |
| Prysmian | Wrexham UK | ||
| Nexans | Hanover, Germany | ||
| 33kV Single Core Cables | NKT | Cologne, Germany | Copper or aluminium stranded for all conductor sizes 11kV or
Aluminum stranded for all sizes or solid aluminium up to and including 300sqmm |
| Tele-Fonica Kable | Poland | ||
| Prysmian | Wrexham UK | ||
| Nexans | Hanover, Germany | ||
| Cable Duct | Polypipe Civil Ltd | UK | |
| Emtelle UK Ltd | UK | ||
| Cable Tile | Centriforce | UK | |
| Cable Warning Tape | Centriforce | UK | |
| Plastic Tape Tile | Centriforce | UK | |
| Duct Seals | TE Connectivity | UK | Rayflate Inflatable Cable Duct Seals |
| WT Henley | UK | Services Ducts (Green Plastic Compound) | |
| Winn & Coates (Denso) | UK | Denso Mastic Denso Tape |
|
| CSD Cable Sealing System | UK | CSD RISE Cable Duct Sealant System |

Joints | Terminations | Glands | Cleats | Cables | Tools | LV MV HV 11kV 33kV
Cable Laying & Pulling Equipment
Thorne & Derrick distribute an extensive range of Cable Laying & Pulling Equipment to enable the safe installation of utility power cables including LV Waveform and MV-HV Power Cables 11kV/33kV – full range of cable spiking tools available to ensure LV-HV power cables are dead prior to jointing or cable termination works.
➡ Further reading: Cable Pulling Equipment – A Cable Duct Laying Guide From BT Openreach






